|
Krokodeilos Kladas
Krokodeilos Kladas (; 1425–1490), also known as Korkodeilos, Krokondeilos, or Korkondelos, was a military leader from the Peloponnese who fought against the Ottomans on behalf of the Republic of Venice during the late 15th century. Biography Krokodeilos Kladas was born in Koroni in 1425. His father was the military chief Theodore Kladas. When the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II (r. 1444–1446 and 1451–1481) took the Morea in 1460, Kladas handed over his castle of Saint George (Agios Giorgios) and was given in exchange the castle of Vardounia in Upper Mani and the territory of Elos. By 1465, the Kladas brothers, Krokodeilos and Epifani, were leading bands of '' stratioti'' (warrior bands) on behalf of Venice against the Turks. They put Vardounia and their lands into Venetian possession, for which Epifani then acted as governor. The Kladas brothers were frequently complimented by Venetian officials, and received generous Venetian gifts. Krokodeilos Kladas and his followers stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
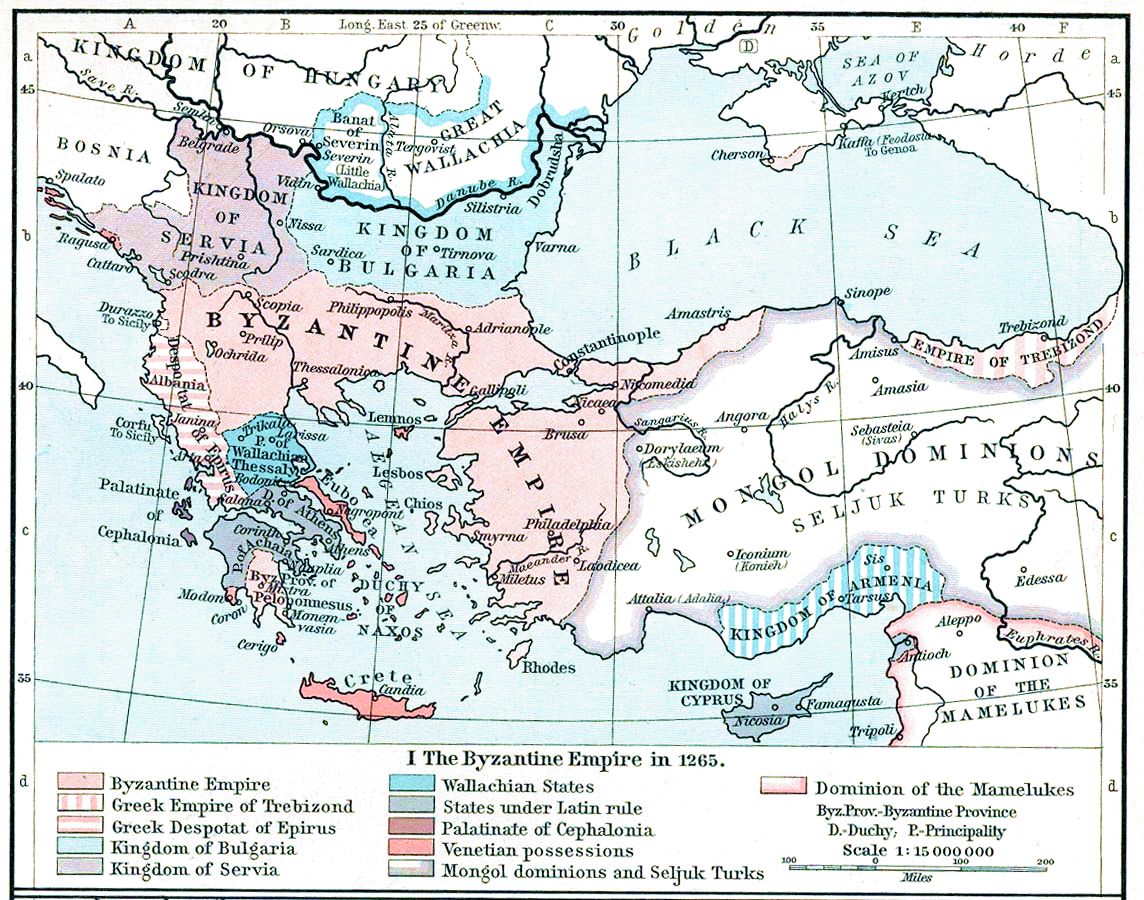
Morea
Morea ( or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used by the Principality of Achaea, the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the Ottoman Empire for the Morea Eyalet, and later by the Republic of Venice for the short-lived Kingdom of the Morea. Etymology There is some uncertainty over the origin of the medieval name "Morea", which is first recorded in the 10th century in the Byzantine chronicles. Traditionally, scholars thought the name to have originated from the word ''morea'' (μορέα), meaning morus or mulberry, a tree which, though known in the region from the ancient times, gained value after the 6th century, when mulberry-eating silkworms were smuggled from China to Byzantium. The British Byzantinist Steven Runciman suggested that the name comes "from the likeness of its shape to that of a mulberry leaf". History After the conquest of Constantinople by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomeo Minio
Bartolomeo Minio was, among other things, a Venetian captain and commander (''provveditor e capitanio'') of Napoli di Romagna (modern Nafplion, Greece), a Venetian outpost on the Morea (Peloponnese) from 1479 to 1483. His reports (''dispacci'') to Venice provide a unique historical source for southern Greece in the later 15th century, during the first decades of the Ottoman occupation. Family The Minio family records date back to 904 when a Paolo Minio moved to Rialto. In the 14th century, Bartolomeo's family held many office positions and were also counted in the ''estimo'' of 1379. Nine members of his family were listed in Karl Hopf's catalogues of governors for Greece and the Aegean islands. Bartolomeo was born in Venice around 1428 to Marco Minio and Cristina Storlado, the youngest of five sons. Cristina died when Bartolomeo was only two years old and Marco remarried in 1431. In 1455, Bartolomeo married Elena Trevisan. Three sons were known to have reached adulthood (Marco, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Achaea
The Principality of Achaea () or Principality of Morea was one of the vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom of Thessalonica, along with the Duchy of Athens, until Thessalonica was captured by Despotate of Epirus, Epirus in 1224. After this, Achaea became the dominant power in Greece, lasting continuously for 227 years and cumulatively for 229. Foundation Achaea was founded in 1205 by William of Champlitte and Geoffrey I of Villehardouin, who undertook to conquer the Peloponnese on behalf of Boniface I, Marquis of Montferrat, Boniface of Montferrat, Kingdom of Thessalonica, King of Thessalonica. With a force of no more than 100 knights and 500 foot soldiers, they took Achaea and Medieval Elis, Elis, and after defeating the local Greeks in the Battle of the Olive Grove of Koundouros, they became masters of the Morea. The victory was decisive, and after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Palaiologos (half-brother Of Michael VIII)
Constantine Palaiologos or Palaeologus () (died 1271) was a Byzantine nobleman and the younger half-brother of the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos. Life and career Constantine was born , to Andronikos Palaiologos (governor-general), Andronikos Palaiologos, Grand domestic of the Empire of Nicaea and his unknown second wife. The life of Constantine is unknown until 1259, when he was appointed ''Caesar (title), Caesar'' by his elder half-brother, Michael VIII. The following year, he was also created a ''sebastokrator''. He commanded the Byzantine forces on an unsuccessful campaign against the Latinokratia, Latin Principality of Achaea, where his army was routed at the Battle of Prinitza. However, Constantine had already left the region by the time of the major Byzantine defeat at the Battle of Makryplagi in 1263/1264. Sometime after returning from the campaign against the Principality of Achaea, Constantine became a monk under the name Kallinikos. He died in 1271. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' (, ; ; ), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers whose states bordered the Empire or were within its sphere of influence (Bulgarian Empire, Serbian Empire). The word is a compound of '' sebastós'' (, the Greek equivalent of the Latin ''Augustus'') and ''krátōr'' ('ruler', the same element as is found in '' autokrator'', 'emperor'). The wife of a ''Sebastokrator'' was named ''sebastokratorissa'' (, ''sevastokratórissa'') in Greek, ''sevastokratitsa'' () in Bulgarian and ''sevastokratorica'' in Serbian. Eastern Roman Empire The title was created by Emperor Alexios I Komnenos () to honour his elder brother Isaac Komnenos.. According to Anna Komnene, Alexios did this to raise Isaac above the rank of '' Caesar'', which he had already promised to his brother-in-law, Nikephoros Melissenos. Anna Komnene compares the rank of ''sebastokratōr'' to "a second emperor", and also records that along with the ''Caesar'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Palaiologos
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinization of names, Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored empire's final decline. The Turks conquered most of Byzantium's remaining Anatolian territories, and Andronikos spent the last years of his reign fighting his Andronikos III Palaiologos, own grandson in the First Palaiologan Civil War. The war ended in Andronikos' forced abdication in 1328, after which he retired to a monastery for the remainder of his life. Life Early life Andronikos was born on 25 March 1259, at Nicaea. He was the eldest surviving son of Michael VIII Palaiologos and Theodora Palaiologina (Byzantine empress), Theodora Palaiologina, grandniece of John III Doukas Vatatzes. Andronikos was acclaimed co-emperor in 1261, after his father Michael VIII recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire, but he was not crowned unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologos, Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He Reconquest of Constantinople, recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and Byzantine navy, navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Rum
The Sultanate of Rum was a culturally Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim state, established over conquered Byzantine territories and peoples (Rum) of Anatolia by the Seljuk Turks following their entry into Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. The name ''Rum'' was a synonym for the medieval Eastern Roman Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. The name is derived from the Aramaic () and Parthian () names for ancient Rome, via the Greek () meaning the Anatolia. The Sultanate of Rum seceded from the Seljuk Empire under Suleiman ibn Qutalmish in 1077. It had its capital first at Nicaea and then at Iconium. It reached the height of its power during the late 12th and early 13th century, when it succeeded in taking key Byzantine ports on the Mediterranean and Black Sea coasts. In the east, the sultanate reached Lake Van. Trade through Anatolia from Iran and Central Asia was developed by a system of caravanserai. Especially strong trade ties with the Genoese forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaykaus II
Kaykaus ibn Kaykhusraw or Kayka'us II (, , ''ʿIzz ad-Dīn Kaykāwus ibn Kaykhusraw'') was the sultan of the Seljuqs of Rûm from 1246 until 1262. Life Kaykaus was the eldest of three sons of Kaykhusraw II. His mother was Prodoulia, who was a Byzantine Greek, may have had Kaykaus baptized as a child. It was common for the Christian slave-concubines and wives of the Seljuk harem to baptise their son. He was a youth at the time of his father's death in 1246 and could do little to prevent the Mongol conquest of Anatolia. For most of his tenure as the Seljuq Sultan of Rûm, he shared the throne with one or both of his brothers, Kilij Arslan IV and Kayqubad II. Mongol commander Baiju threatened him and warned him of being late with paying tribute and requested new pastures in Anatolia for the Mongol cavalry. The Mongols defeated Kaykaus who then fled to the Roman empire in 1256/1257. At some point, Kaykaus returned to the Sultanate but had to again flee to Byzantium followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turcopole
During the period of the Crusades, turcopoles (also "turcoples" or "turcopoli"; from the , literally "sons of Turks") were locally recruited mounted archers and light cavalry employed by the Byzantine Empire and the Crusader states. A leader of these auxiliaries was designated as Turcopolier, a title subsequently given to a senior officer in the Knights Templars and the Order of the Hospital of St John of Jerusalem, in charge of the coastal defences of Rhodes and Malta. In addition to the two Military Orders, the army of the Kingdom of Jerusalem employed ''king's Turcoples'' under the direction of a ''Grand Turcopolier''. Byzantine origins The crusaders first encountered Turcopoles in the Byzantine army during the First Crusade. Reference is made to 30 Turcoples being lent by the Emperor Alexius I to act as guides for one division of the Franks. These auxiliaries were of mixed Byzantine and Turkic origins. Raymond of Aguilers writes that they were called Turcopoles becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Sathas
Constantine Sathas (; Athens, 1842 – Paris, 25 May 1914) was a Greek historian and researcher. Sathas spent his life unearthing hitherto unknown material pertaining to the history of late medieval and early modern Greece that he later published. He researched archives in Greece, Constantinople (now Istanbul), Venice and Florence. In 1900, he moved to Paris Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ..., where he lived until his death. Many of the numerous documents he brought to light still remain primary sources of information. It can be argued that his work was never fully appreciated and some of his views are regarded eccentric nowadays. Yet, he carried out groundbreaking work and has been considered as the best historian of Greece in the 19th century. He published the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Greeks
The Byzantine Greeks were the Medieval Greek, Greek-speaking Eastern Romans throughout Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. They were the main inhabitants of the lands of the Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire), of Constantinople and Asia Minor (modern Turkey), the Greek islands, Cyprus, and portions of the southern Balkans, and formed large minorities, or pluralities, in the coastal urban centres of the Levant and northern Egypt. Throughout their history, they self-identified as ''Ῥωμαῖοι, Romans'' (). Latin speakers identified them simply as Greeks or with the term Romaei. Use of Koine Greek, Greek was already widespread in the eastern Roman Empire when Constantine I () moved its capital to Constantinople, while Anatolia had also been Hellenization, hellenized by early Byzantine times. The empire lost its diversity following the loss of non-Greek speaking provinces with the 7th century Early Muslim conquests, Muslim conquests and its population was overwhelmingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |