|
Kratke Mountains
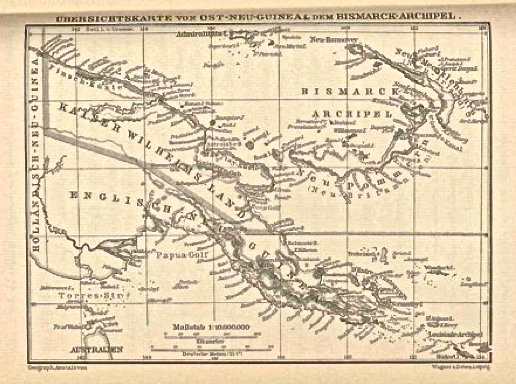
Kratke Range () is a mountain range in Eastern Highlands, Papua New Guinea. Several rivers, including Aziana, Yaiga, Lamari and Ramu originate from the mountain. History In November 1889, Hugo Zöller became the first European to enter the Kratke Range from the former German colony Kaiser-Wilhelmsland in German New Guinea during an expedition to the Finisterre Range. He then called it ''Krätkegebirge'', after the governor of German colony, (1845-1934). Kratke Range was only explored after the German colonial era at the beginning of the 1920s. Geography Kratke Range runs south of the Finisterre mountains on the other side of the river Markham and joins the Bismarck Range to the east. One of the peaks is called Zöllerberg after Hugo Zöller. The highest peak is Mount Tabletop with 3.686 m height. The mountain is volcanic in nature and is overgrown by tropical mountain rainforest. Above 3,000 m, alpine grasslands predominate. Various endemic bird species live in the moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. It has Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, a land border with Indonesia to the west and neighbours Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest list of island countries, island country, with an area of . The nation was split in the 1880s between German New Guinea in the North and the Territory of Papua, British Territory of Papua in the South, the latter of which was ceded to Australia in 1902. All of present-day Papua New Guinea came under Australian control following World War I, with the legally distinct Territory of New Guinea being established out of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Highlands (Papua New Guinea)
Eastern Highlands is a highlands province of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital is Goroka. The province covers an area of 11,157 km2, and has a population of 579,825 (2011 census). The province shares a common administrative boundary with Madang Province to the north, Morobe Province to the east, Gulf Province to the south, and Simbu Province to the west. The province is the home of the Asaro mud mask that is displayed at shows and festivals within the province and in the country. The province is reachable by air, including Goroka Airport, and road transport, including the main Highlands Highway. Districts and LLGs Each province in Papua New Guinea has one or more districts, and each district has one or more Local Level Government (LLG) areas. For census purposes, the LLG areas are subdivided into wards and those into census units. Demography Eastern Highland Province had a population of 432,972 (PNG citizens) and 1,173 (non-citizens) in the 2000 Census. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamari River
The Lamari River is a river that originates in the Kratke Range in the south central highlands of Eastern Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea. It flows into the Purari River basin. Population Awa speaking indigenous people populate the Lamari river basin. The Lamari River serves as the demarcation line between the Kukukuku people and their neighbours to the north-west, the Fore people The Fore () people live in the Okapa District of the Eastern Highlands Province, Papua New Guinea. There are approximately 20,000 Fore who are separated by the Wanevinti Mountains into the North Fore and South Fore regions. Their main form of ....Werner H. StöckliKukukuku : Medical Patrol into one of the last restricted areas in the New Guinea HighlandsActa Tropica 25 (1968) References Rivers of Papua New Guinea Gulf of Papua {{PapuaNewGuinea-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Zöller
Hugo Zöller (12 January 1852 – 1933) was a German explorer and journalist. His brother Egon Zöller was an author and friend of Karl Pearson. Hugo was born near Schleiden, Kingdom of Prussia. He studied law and in 1872 to 1874 travelled to countries in the Mediterranean Sea region. In 1874 he became a journalist for '. In 1879 Zöller started his travels around the world. The result was a two-volume book ''Rund um die Erde'' (Köln 1881). In 1881 and 1882 he travelled across South America and then published ''Die Deutschen im brasilianischen Urwald'' (Stuttgart 1883) and ''Pampas und Anden'' (Stuttgart 1884). By the end of 1882 he worked as a war correspondent in Egypt during the British campaign there. In 1883 he was ordered to explore territories in Western Africa previously explored by Gustav Nachtigal. First he travelled across the Togoland, then he went to Cameroon where he in 1884 made a successful ascent of Mount Cameroon together with Stefan Szolc-Rogoziński. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiser-Wilhelmsland
Kaiser-Wilhelmsland ("Emperor William's Land") formed part of German New Guinea (), the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor () from 1871 to 1888, it included the northern part of present-day Papua New Guinea. From 1884 until 1920 the territory was a protectorate () of the German Empire. Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, the Bismarck Archipelago (including New Mecklenburg and New Pomerania), the northern Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, Palau, Nauru, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands comprised German New Guinea. Most of the German settlers in Kaiser-Wilhelmsland worked as plantation owners, miners, or government functionaries; the number of European settlers, including non-Germans, was never very high. In 1885, Lutheran and Catholic congregations sent clergy to establish missions; they experienced moderate, but very slow, success with the indigenous peoples. Missionaries and plantation owne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German New Guinea
German New Guinea () consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups, and was part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , became a German protectorate in 1884. Other island groups were added subsequently. The Bismarck Archipelago (New Britain, New Ireland (island), New Ireland and several smaller islands), and the North Solomon Islands were declared a Protectorate, German protectorate in 1885. The Caroline Islands, Palau, and the Mariana Islands (except for Guam) German–Spanish Treaty (1899), were bought from Spain in 1899. German New Guinea annexed the formerly separate German Protectorate of Marshall Islands, which also included Nauru, in 1906. German Samoa, though part of the German colonial empire, was not part of German New Guinea. Following the outbreak of the First World War in 1914, Kaiser-Wilhelmsland and nearby islands Australian occupation of German New Guinea, fell to Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finisterre Range
The Finisterre Range is a mountain range in north-eastern Papua New Guinea. The highest point is ranked 41st in the world by prominence with an elevation of 4,150 m. Although the range's high point is not named on official maps, the name "Mount Boising" is used locally. This peak was possibly the most prominent unclimbed peak in the world until the first known ascent on 25 June 2014. The range runs into the Saruwaged Range to the east and together they form a natural barrier between the Ramu and Markham valleys to the south and Vitiaz Strait to the north. Many rivers originate in this range, including some tributaries of the Ramu. History The Finisterre Range campaign (1943–1944) of World War II, including a series of actions known as Battle of Shaggy Ridge, saw fierce fighting between Australian and Japan Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markham River
The Markham River is a river in eastern Papua New Guinea. It originates in the Finisterre Range and flows for to empty into the Huon Gulf at Lae. Course The Markham is a major river in eastern Papua New Guinea. Its headwaters (''Umi'' and ''Bitjia'') originate in the Finisterre Range. From their confluence, it flows swiftly southeast through steep mountains and empties into Huon Bay. Its wide (0.5–2 km) but shallow bed forms a series of braided channels through a large central depression, the Markham Valley. Its sparsely populated flat valley includes considerable agricultural land downstream ( cocoa and groundnut plantations, cattle ranching). Its lower 70 km are navigable. Its largest tributary is the ''Watut River'', which originates in the Bulolo Valley. The river was named in 1873 by Captain John Moresby, R.N., in honour of Sir Clements Markham, then Secretary of the Royal Geographical Society. A single-lane steel bridge, 1690 feet long – by far the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismarck Range
The Bismarck Range is a mountain range in the Western Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea. The range is named after the German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck. The highest point of the range and the country is Mount Wilhelm at . At over 3,400 metres (11,155 ft), the landscape is alpine with tundra, in spite of the tropical climate. The Ramu River has its source in the range. The Bismarck Forest Corridor, which bridges the provinces of Chimbu, Eastern Highlands, Jiwaka, and Madang, is located on the Bismarck Range. This corridor is an intact montane forest composed of Papua New Guinea oak and beech forest Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted species i .... The forest is a critical habitat for endangered species such as the Goodfellow's tree-kangaroo, giant rats, and man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modest Tiger Parrot
The modest tiger parrot (''Psittacella modesta'') is a species of parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It is found in the Arfak Mountains and New Guinea Highlands. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist montane forest Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures lapse rate, fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is ...s. References modest tiger parrot Least concern biota of Oceania modest tiger parrot Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{parrot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kratke Range Languages
The Angan or Kratke Range languages are a family of the Trans–New Guinea languages in the classification of Malcolm Ross. The Angan languages are clearly valid as a family. They were first identified as such by J. Lloyd and A. Healey in 1968; Wurm (1975) classified them as Trans–New Guinea. Glottolog treats Angan as a separate or unclassified family, ignoring further evidence. The languages are spoken in the Kratke Range of Eastern Highlands Province and adjoining areas of Gulf Province and Morobe Province. Languages Ross (2005) classifies the languages as follows: *Angan ** Angaatiha ** Angan proper (Nuclear Angan) *** Angan branch A: **** Hamtai (Kapau) **** Kamasa **** Kawatsa **** Menya **** Yagwoia *** Angan branch B: **** Akoye (Lohiki) **** Yipma (Baruya) **** Safeyoka **** Simbari **** Susuami **** Tainae (Ivori) Branch A is defined by the pronouns ''ni'' and ''ti''. Ankave is not listed in Ross's classification. It has the pronouns based on ''n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |