|
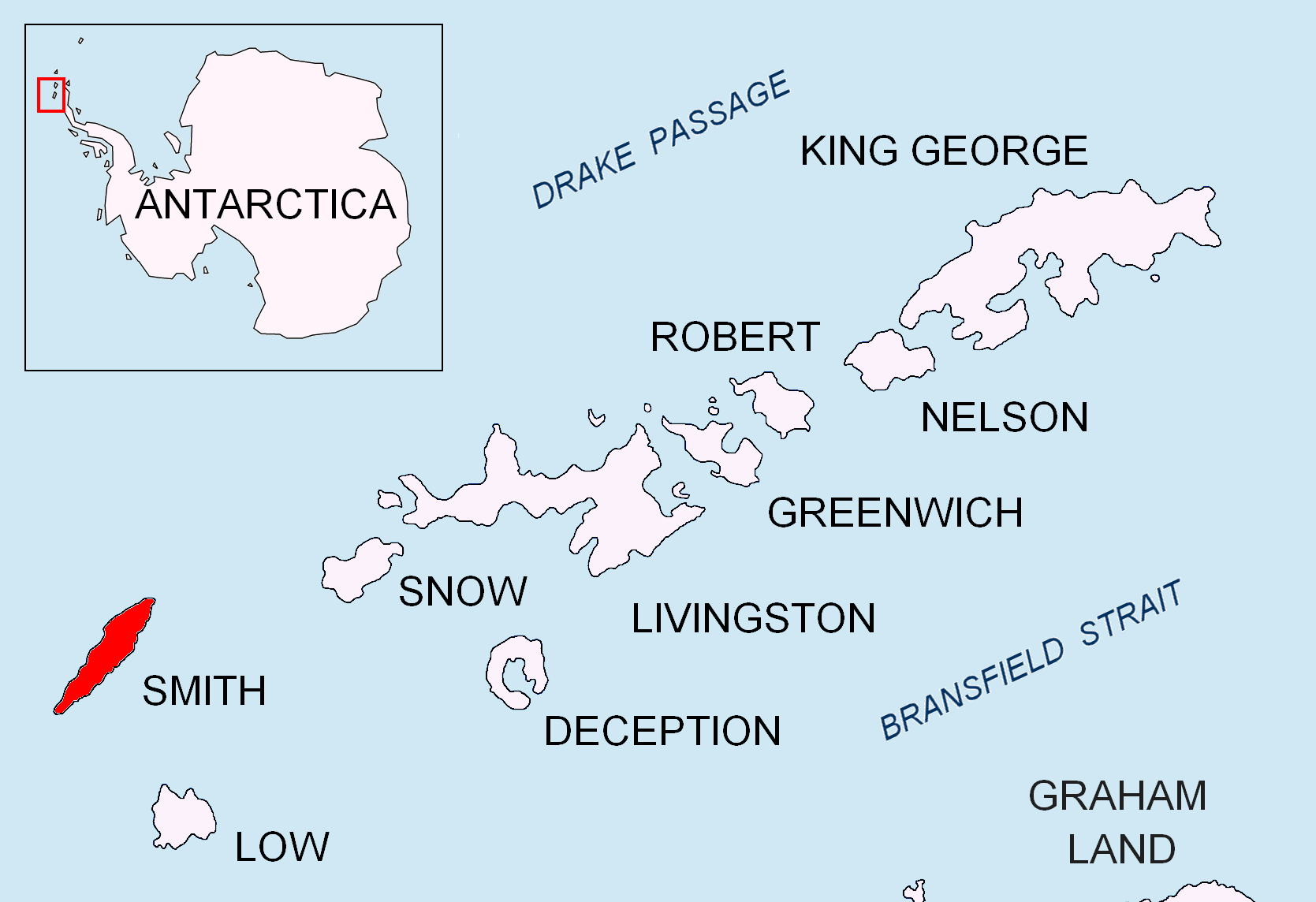
Kostenets Saddle
Kostenets Saddle ( bg, Костенечка седловина, ‘Kostenechka Sedlovina’ \'ko-ste-nech-ka se-dlo-vi-'na\) is the saddle of elevation 1520 m in Imeon Range on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica bounded by Mount Pisgah to the north and the east ridge of Drinov Peak to the south. It overlooks the head of Vetrino Glacier to the west. The saddle is named after the town of Kostenets in southwestern Bulgaria. Location Kostenets Saddle is located at . Bulgarian mapping in 2009 and 2010. MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. * L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. ) South Shetland Islands: Smith and Low Islands.Scale 1:150000 top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kostenets
Kostenets ( bg, Костенец ) is a town in Sofia Province in southwestern Bulgaria, and the administrative centre of the Kostenets Municipality (which also contains a separate village of Kostenets). The town is situated at the foot of Rila Mountain, about southeast of capital Sofia. The average monthly and annual air temperature at daylight varies from -4.2C (January) to +16.1C (July). The abundance of mineral springs is one of the special characteristics of the region. The spa resort of Momin Prohod is a specialised centre for rehabilitation and recreation and attracts many visitors. The spa resorts Villas Kostenets, Pchelinski bani, and the village of Kostenets are near the town. The favourable climatic factors, the unique combination of the thermal mineral water resources with the immediate proximity to the resort of Borovets and the country's capital, and the natural and historical sights provide a potential for all-the-year-round tourism, recreation and sport. Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gaze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Gazetteer Of Antarctica
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetrino Glacier
Vetrino Glacier ( bg, ледник Ветрино, lednik Vetrino, ) is a 3.2 km long glacier on the northwest side of Imeon Range on Smith Island (South Shetland Islands), Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is situated northeast of Yablanitsa Glacier, southwest of Dalgopol Glacier and northwest of Ovech Glacier, drains the northwest slopes of Imeon Range north of Drinov Peak, northwest of Kostenets Saddle and west of Mount Pisgah (Smith Island), Mount Pisgah, and flows northwestwards into Drake Passage both northeast and south of Gregory Point. The glacier is named after the town of Vetrino in northeastern Bulgaria. Location The glacier is centred at (Bulgarian early mapping in 2009). See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinov Peak
Drinov Peak ( bg, Дринов връх, Drinov Vrah, ) is a peak rising to 1630 m in Imeon Range on Smith Island (South Shetland Islands), Smith Island, South Shetland Islands. Situated 3.6 km north-northeast of Antim Peak, 1.9 km north of Slatina Peak, 2.91 km east-southeast of Jireček Point and 1.85 km southwest of Mount Pisgah (Smith Island), Mount Pisgah. Overlooking Ovech Glacier to the southeast, Vetrino Glacier to the north, Yablanitsa Glacier to northwest, and Chuprene Glacier to the southwest. Bulgarian early mapping in 2009. Named after the Bulgarian scientist Marin Drinov (1838–1906), founding chairman of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. * L.L. Ivanov. :commons:File:Livingston-Island-Map-2010.jpg, Antarctica: Livingston Island and Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Pisgah (Smith Island)
Mount Pisgah is a peak rising to 1860 m in the north-central part of Imeon Range on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is linked by Kostenets Saddle to Drinov Peak to the southwest, and surmounts Dalgopol Glacier to the north and Vetrino Glacier to the west. Because the peaks of Smith Island gave it a forked appearance when seen from a distance, American sealers in the 1820s called it ''Mount Pisgah Island'' after the double-topped Mount Pisgah in the town of Durham, CT. The name has since been restricted to the peak described. Location The peak is located at which is 7.64 km northeast of Mount Foster, 1.85 km northeast of Drinov Peak, 3.9 km southeast of Gregory Point, 4.74 km southwest of Mount Christi and 1.1 km west of Mezek Peak (Bulgarian mapping in 2009). MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |