|
Kostanay
Kostanay or Qostanai (, , rus, Костанай, p=kəstɐˈnaj) is a city located on the Tobol River in northern Kazakhstan. It is the administrative center of the Kostanay Region. As of 24 March 2022, the city's governor is Marat Zhundubayev. History Kostanay was founded by Russian settlers in 1879 and named Nikolaevsk, in honor of Tsar Nicholas II. In 1888, the town had more than 3,000 inhabitants involved in the building of a mill and a brewery, which are still operational. In 1893, Kustanay was granted city status. The Red Army took control in 1918 and changed the city's name to Kustanay. The Kustanay Region was established in 1936 with its administrative center in Kustanay. Six years after fall of Soviet Union, Kazakhstan renamed it to Kostanay. In 2009, the city population was Geographic location The city is located in the steppe zone in the north of the Turgay plateau, in the south-eastern part of the West Siberian Plain, on the Tobol River, 571 km north-west of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kostanay Region
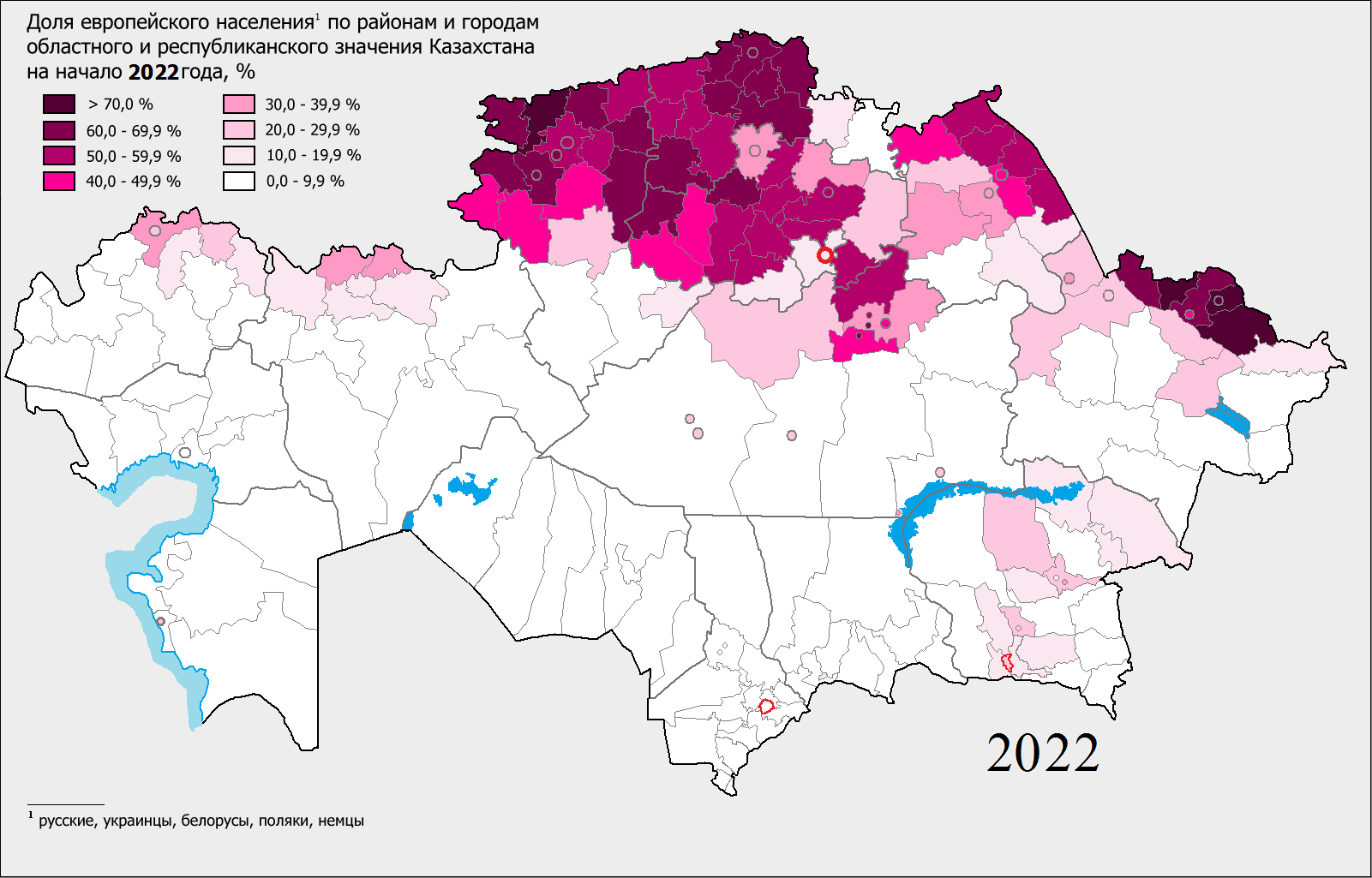
Kostanay Region (; ) is a region of Kazakhstan. Its administrative center is the city of Kostanay. The population of the region is 835,686. The population living in Kostanay is 207,000 which is equivalent to 23% of the region. Geography Kostanay Region is adjacent to the Russian federal subjects Orenburg Oblast, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Kurgan Oblast, and is near the Ural Mountains. It also touches four other Kazakh regions: Aktobe Region to the southwest, Karaganda Region to the south, Akmola Region to the southeast, and North Kazakhstan Region to the northeast. The Tobol (Tobyl) River, a tributary of the Irtysh River, starts in and flows through the region on its way to Russia. Kostanay Region's area is 197,000 square kilometers, making it the sixth largest of the Kazakh regions. Flora and fauna Resources of an animal and flora of Kostanay Region are suitable for the organization and development of zones and objects of civilized fishery and a hunt, lake-commodity fish cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan is divided into 17 regions (; ; ; ) and 4 cities. The regions are further subdivided into districts of Kazakhstan, districts (; ; ; ). The four cities, Almaty, Baikonur, Shymkent, and the capital city Astana, do not belong to their surrounding regions. Initially there were 14 regions. On 16 March 2022, President of Kazakhstan, Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev announced that three new regions would be created. Abai Region was created from East Kazakhstan Region with its capital in Semey. Ulytau Region was created from Karaganda Region with its capital in Jezkazgan. Jetisu Region was created from Almaty Region with its capital in Taldykorgan; Almaty Region's capital was moved from Taldykorgan to Qonayev. __TOC__ Regions Demographic statistics In 2022, three new regions were created - Abai (from part of East Kazakhstan), Jetisu (from part of Almaty Region) and Ulytau (from part of Karaganda Region). In the following table, the 2009 population totals ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhmet Baitursynov
Ahmet Baitursynuly (, , romanized: ''Ahmed Baitūrsynūly'', ; Russified: Ахмет Байтурсынов) ( 5 September 1872 — 8 December 1937) was a Kazakh intellectual who worked in the fields of politics, poetry, linguistics and education. Baitursynuly reformed the Kazakh alphabet. In 1912, he excluded all the purely Arabic letters not used in the Kazakh language and added letters specific to the Kazakh language. Baitursynuly's orthographic reform resulted in a script that functions like a true phonetic alphabet, with one letter for every sound in the Kazakh language, compared to the basic Arabic abjad. The new alphabet, named ''Tote jazu'' (meaning ''straight writing''), is still used by Kazakhs living in China, Afghanistan, and in Iran. Baitursynuly also developed the basics of Kazakh and the scientific terminology for the definition of Kazakh grammar. In 1937, he was executed by a firing squad during the Great Purge. Early life, education Ahmet Baitursynuly was born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokshetau
Kokshetau (; , ; rus, Кокшета́у, p=kəkʂɛ'taʊ; ), formerly known as Kokchetav (; ) between 1868 and 1993, is a lakeside city in northern Kazakhstan and the capital of Akmola Region. It stretches along the southern shore of Lake Kopa, lying in the north of Kokshetau Hills, a northern subsystem of the Kokshetau Uplands ( Saryarka) and the southern edge of the Ishim Steppe. It is named after Mount Kokshe. Kokshetau is the 17th-most populous city in Kazakhstan, the 4th-most populous city in northern part of the country, and the largest city in Akmola Region. It was the administrative center of Kokshetau Region (oblast) from 1944 to 1991 as part of the Soviet Union and from 1991 as part of Kazakhstan to 1997 when it was abolished. It is also situated at the junction of the Trans-Kazakhstan and South Siberian railways. Kokshetau lies at an elevation of approximately above sea level. The climate of Kokshetau features hot summers and cold winters. It has 176,849 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ybyrai Altynsarin
Ybyrai (Ibrahim) Altynsarin (, ''Ybyrai Altynsarin''; ; – ) was a major figure in pre-Soviet Kazakh history. He was the most prominent Kazakh educator of the 19th century, at the period of Russian colonization of and cultural influence in Kazakhstan. Ibrahim Altynsarin was born in the Araqaraghai region of Turgay Oblast (now Kostanay Province) of modern-day Kazakhstan and in his early career he was an inspector of Torghai schools. Like all ethnic Kazakhs, Ibrahim was raised in an Islamic family that valued tradition and religion over many other aspects of life. Because of the influx of Russian influence in the area, though, he developed more progressive views for Kazakh society to westernize and accelerate. This allowed him to come up with multiple ways to modernize Kazakh society. Ibrahim Altynsarin is best known for introducing the transition from the Perso-Arabic alphabet to the Cyrillic alphabet for the Kazakh language, and was a proponent of teaching in the Wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia/Qostanay
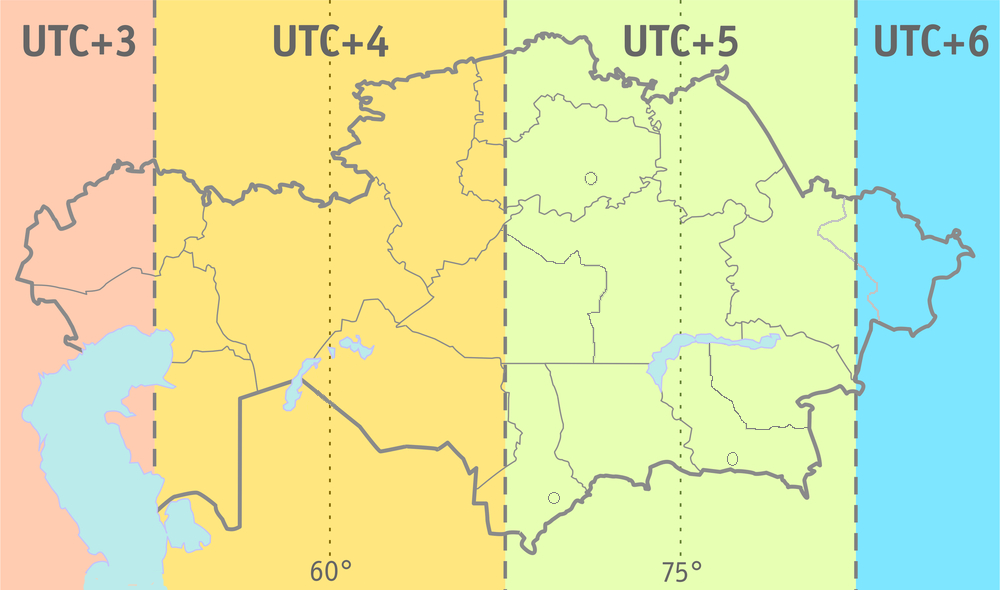
Time in Kazakhstan is regulated by the Decree "On the Procedure for Calculating Time on the Territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan", according to which time zone is applied: UTC+05:00 (from March 1, 2024); Daylight Saving Time is not observed, having been abolished in 2005. Even though the territory of Kazakhstan spans four geographical time zones (from UTC+03:00 to UTC+06:00), it observes UTC+05:00 year round. The difference in geographical longitude between the extreme eastern and western points of Kazakhstan is 40°45′, which corresponds to the difference in local solar time of 2 hours 43 minutes. IANA time zone database The tz database identifies seven zones for Kazakhstan. Data in columns marked * are from the file zone.tab This is a list of time zones from release of the tz database. Legend Type * Canonical - The primary, preferred zone name. * Link - An alternative name (alias) which links to a canonical zone. * Link - A standard Link (as above). The dag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobol River
The Tobol (, ) is a river in Western Siberia (in Kazakhstan and Russia) and the main (left) tributary of the Irtysh. Its length is , and the area of its drainage basin is . History The Tobol River was one of the four important rivers of the Siberia Khanate. In 1428 the khan was killed in a battle with the forces of Abu'l-Khayr Khan at the Battle of Tobol. In the 16th century, the Tobol was the eastern terminus of the portage route leading westward to the rivers Vishera and Kama. Cities and towns on the Tobol * Lisakovsk in Kazakhstan * Rudni in Kazakhstan * Kostanay (formerly Nikolaevsk) in Kazakhstan * Kurgan in the Russian Federation * Yalutorovsk in the Russian Federation * Tobolsk in the Russian Federation, where the Tobol joins the Irtysh Main tributaries The largest tributaries of the Tobol are, from source to mouth: * Syntasty (left) * Ayat (left) * Uy (left) * Ubagan (right) * Iset (left) * Tura (left) * Tavda (left) References Rivers of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus (burial mound) constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons, and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asia and Eastern, Southeast, Western, and Northern Europe during the third millennium BC. The earliest kurgans date to the fourth millennium BC in the Caucasus, and some researchers associate these with the Indo-Europeans. Kurgans were built in the Eneolithic, Bronze, Iron, Antiquity, and Middle Ages, with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia. Etymology According to the Etymological dictionary of the Ukrainian language the word "kurhan" is borrowed directly from the Kipchak, part of the Turkic languages, and means: fortress, embankment, high grave. The word has two possible etymologies, either from the Old Turkic root ''qori-'' "to close, to block, to guard, to protect", or ''qur-'' " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg (, ; ), alternatively Romanization of Russian, romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( ; 1924–1991), is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia. The city is located on the Iset River between the Idel-Ural, Volga-Ural region and Siberia, with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the list of cities and towns in Russia by population, fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in the Ural Federal District, and one of Russia's main cultural and industrial centres. Yekaterinburg has been dubbed the "Third capital of Russia", as it is ranked third by the size of its economy, culture, transportation and tourism. Yekaterinburg was founded on 18 November 1723 and named after the Orthodox name of Catherine I of Russia, Catherine I (born Marta Helena Skowrońska), the wife of Russian Emperor Peter the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troitsk, Chelyabinsk Oblast
Troitsk () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located east of the southern Ural Mountains and approximately south of Chelyabinsk on the Kazakhstan–Russia border, border with Kazakhstan. It stands on the east-flowing Uy River (Tobol basin), Uy River, a branch of the Tobol River. Population: 83,862 (Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census); Geography and climate The Uy and Uvelka Rivers merge within the town boundaries and form a water body which serves as a reservoir for the nearby power station. The landscape around the town is flat, although river valleys are hilly. The town is situated on the border of a forest-steppe zone. The climate is continental. The average temperature in January is , and in July. History Troitsk was founded in 1743 by Ivan Neplyuyev as a head fortress of the Orenburg Line of forts during the Bashkir rebellion of 1735–1740, Bashkir War of 1735-1740 and to protect the southern borders of Russia. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard. Originally, mosques were simple places of prayer for the early Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than elaborate buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture (650–750 CE), early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets, from which the Adhan, Islamic call to prayer was issued on a daily basis. It is typical of mosque buildings to have a special ornamental niche (a ''mihrab'') set into the wall in the direction of the city of Mecca (the ''qibla''), which Muslims must face during prayer, as well as a facility for ritual cleansing (''wudu''). The pulpit (''minbar''), from which public sermons (''khutbah'') are delivered on the event of Friday prayer, was, in earlier times, characteristic of the central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz TMA-06M Crew Members Are Greeted At The Kustanay Airport
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |