|
Kosmos 869
Kosmos 869 ( meaning ''Cosmos 869'') was an uncrewed spacecraft, uncrewed military Soyuz spacecraft, Soyuz 7K-S test. It was a somewhat successful mission. This was the third and final test flight of a new Soyuz spacecraft type 7K-S. It was designed to be a spaceship for military solo missions. At the time of the launch the program had already been discontinued. The completed spaceships were launched as uncrewed test flights: Kosmos 670, Kosmos 772 and Kosmos 869. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S. *Mass: 6800 kg. *Crew: None. *Launched: November 29, 1976. *Landed: December 17, 1976 10:31 UTC. *Perigee: 209 km. *Apogee: 289 km. *Inclination: 51.7 deg. *Duration: 17.99 days. Maneuver Summary *196 km X 290 km orbit to 187 km X 335 km orbit. Delta V: 15 m/s. *187 km X 335 km orbit to 259 km X 335 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Soyuz
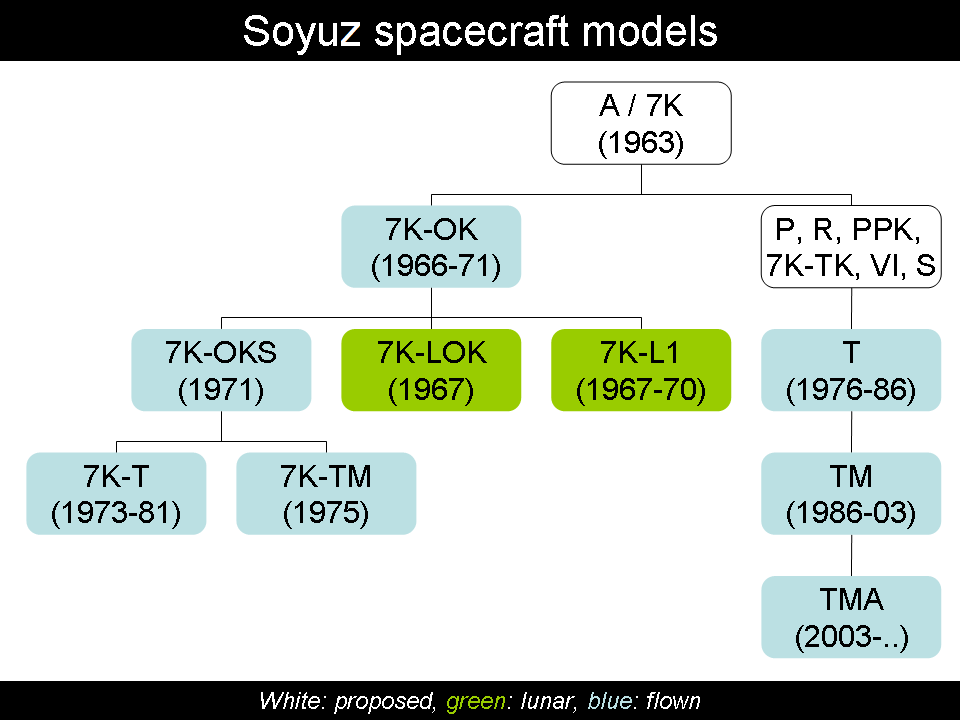
file:Soyuz 7K-OK(A) drawing.png, Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft with an active docking unit The Soviet Union planned several military Soyuz spacecraft models. These versions were named Soyuz P, Soyuz PPK, Soyuz R, Soyuz 7K-VI, and Soyuz OIS (Orbital Research Station). However, none of the spacecraft ever flew in space. Soyuz P, R and PPK Soyuz P The Soyuz P (''Perekhvatchik'', Interceptor) space interceptor and Soyuz R (''Razvedki'', intelligence) command-reconnaissance spacecraft was proposed in December 1962 by Sergei Korolev. In the initial draft project, the Soyuz P would use the Soyuz-B, Soyuz 9K rocket stage and Soyuz-V, Soyuz 11K tanker spacecraft to conduct a series of dockings and re-fueling operations. The complete complex would then conduct intercepts of enemy satellites in orbits up to 6,000 km in altitude. Soyuz P was cancelled in 1963. Soyuz R The Soyuz-R system (1963-1966) consisted of two separately launched spacecraft, including the small orbital station 11F7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 772
Kosmos 772 ( meaning ''Cosmos 772'') was an uncrewed military Soyuz 7K-S test. It was an unsuccessful mission as only one transmitter worked. Only the 166 MHz frequency transmitter operated, all of the other normal Soyuz wavelengths transmitters failed. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S *Mass: 6750 kg *Crew: None *Launched: September 29, 1975 *Landed: October 3, 1975 4:10 UTC *Perigee: 154 km *Apogee An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides perta ...: 245 km *Inclination: 51.8 deg *Duration: 3.99 days Maneuver Summary *193 km X 270 km orbit to 195 km X 300 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s. *196 km X 300 km orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 In The Soviet Union
The following lists events that happened during 1976 in the Soviet Union, Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Incumbents * General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union: Leonid Brezhnev * Premier of the Soviet Union: Alexei Kosygin * Chairman of the Russian SFSR: Mikhail Solomentsev Events January February * February 24 — 25th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union March April May June * June 1 — The Philippine government opens relations with the Soviet Union. July September October November December Births *January 10 — Valery Chekalov, Russian mercenary leader (d. 2023 in Russia, 2023) *February 27 — Sergei Semak, Russian football player and coach *April 5 — Natascha Ragosina, Russian boxer *April 12 — Andrei Lipanov, Russian ice skater *April 21 — Elisabet Reinsalu, Estonian actress *May 28 — Alexei Nemov, former Russian artistic gymnast *June 4 — Alexei Navalny, Russian lawyer and activist (d. 2024 in Russia, 2024) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Uncrewed Test Flights
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз ( Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Military Spacecraft
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the largest country by area, extending across eleven time zones and sharing borders with twelve countries, and the third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, its government and economy were highly centralized. As a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), it was a flagship communist state. Its capital and largest city was Moscow. The Soviet Union's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917. The new government, led by Vladimir Lenin, established the Russian SFSR, the world's first constitutionally communist state. The revolution was not accepted by all wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |