|
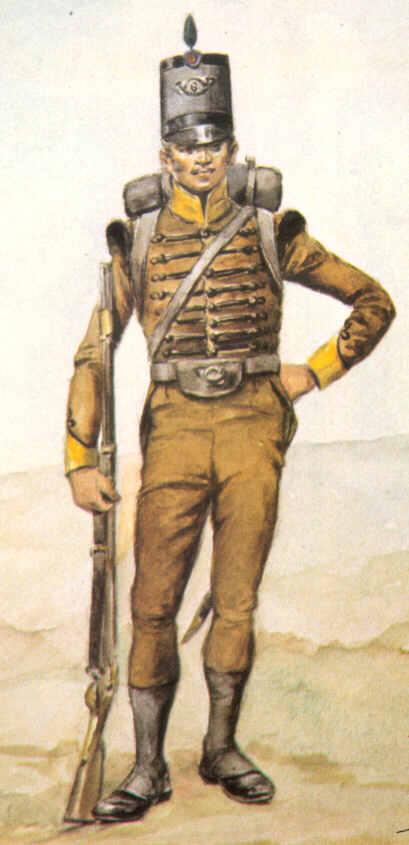
Korps Pandoeren
The Pandour Corps ( Dutch: ''Korps Pandoeren'') was a light infantry unit raised in the Dutch Cape Colony in 1793 during the French Revolutionary Wars. After the Dutch Republic became involved in the War of the First Coalition against France, the twin governors of the Cape Colony, Sebastiaan Cornelis Nederburgh and Simon Hendrik Frijkenius, raised the unit as an emergency measure to defend the colony against seaborne attack. The Pandour Corps consisted of Coloured soldiers, and was the second such unit raised in the colony after Dutch officials noted the effective skirmishing ability of Coloured troops compared to their European counterparts. Coloured soldiers of the unit were mostly servants on burgher-owned farms, and many were recruited from Christian missions in the colony. In 1795, Great Britain launched an invasion of the Cape Colony in order to secure British trade with the East Indies. After British forces landed at the colony on 11 June, the Pandour Corps fought in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought as Reconnaissance, scouts, Raid (military), raiders, and skirmishers. These are loose formations that fight ahead of the main army to harass, delay, disrupt supply lines, engage the enemy's own skirmishing forces, and generally "soften up" an enemy before the main battle. Light infantrymen were also often responsible for Screening (tactical), screening the main body of a military formation. Following World War II, the term "light infantry" has evolved to include rapid-deployment units (including commando and Airborne forces, airborne units) that emphasize speed and mobility over armor and firepower. Some units or battalions that historically held a skirmishing role retain their designation "light infantry" for the sake of tradition. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
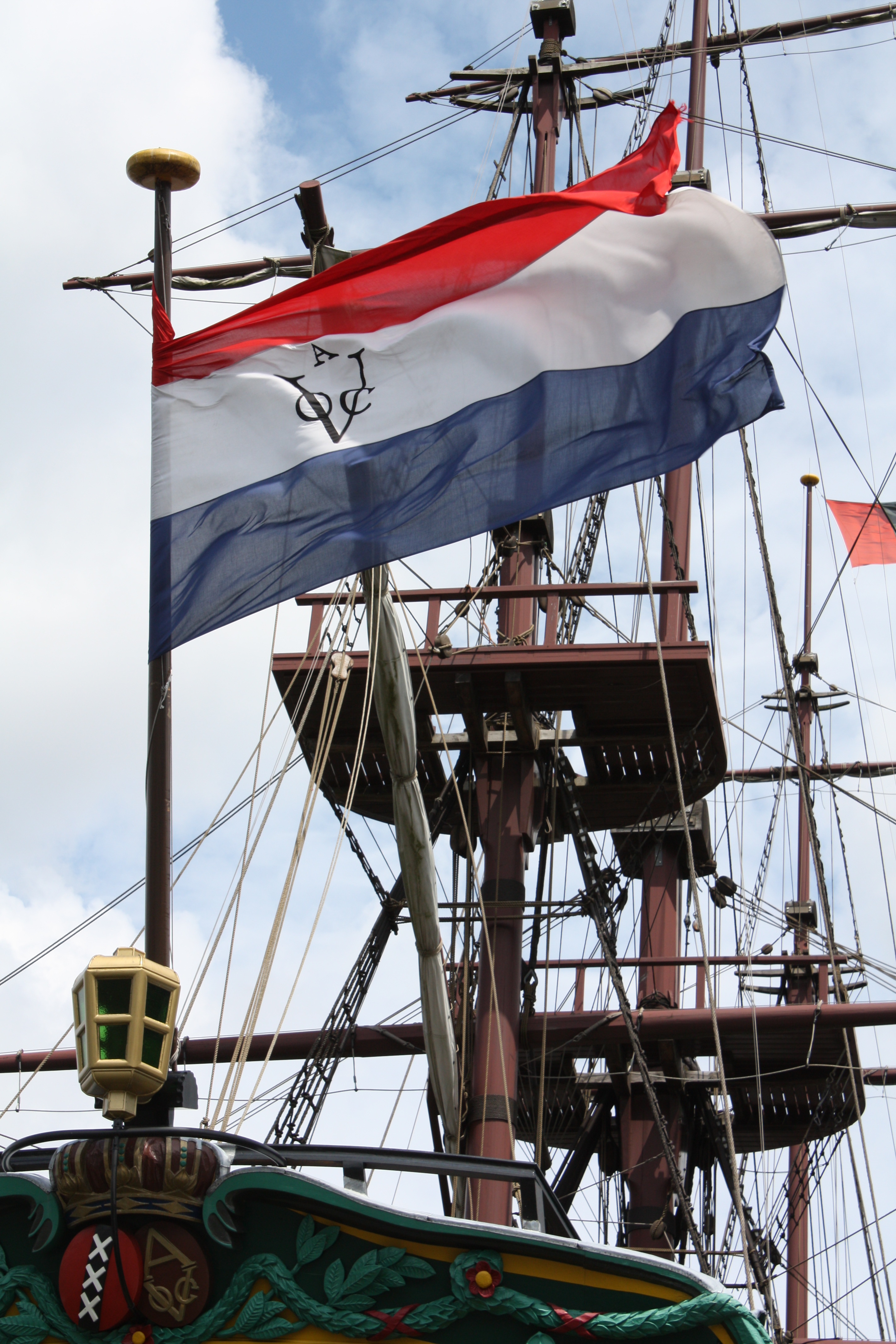
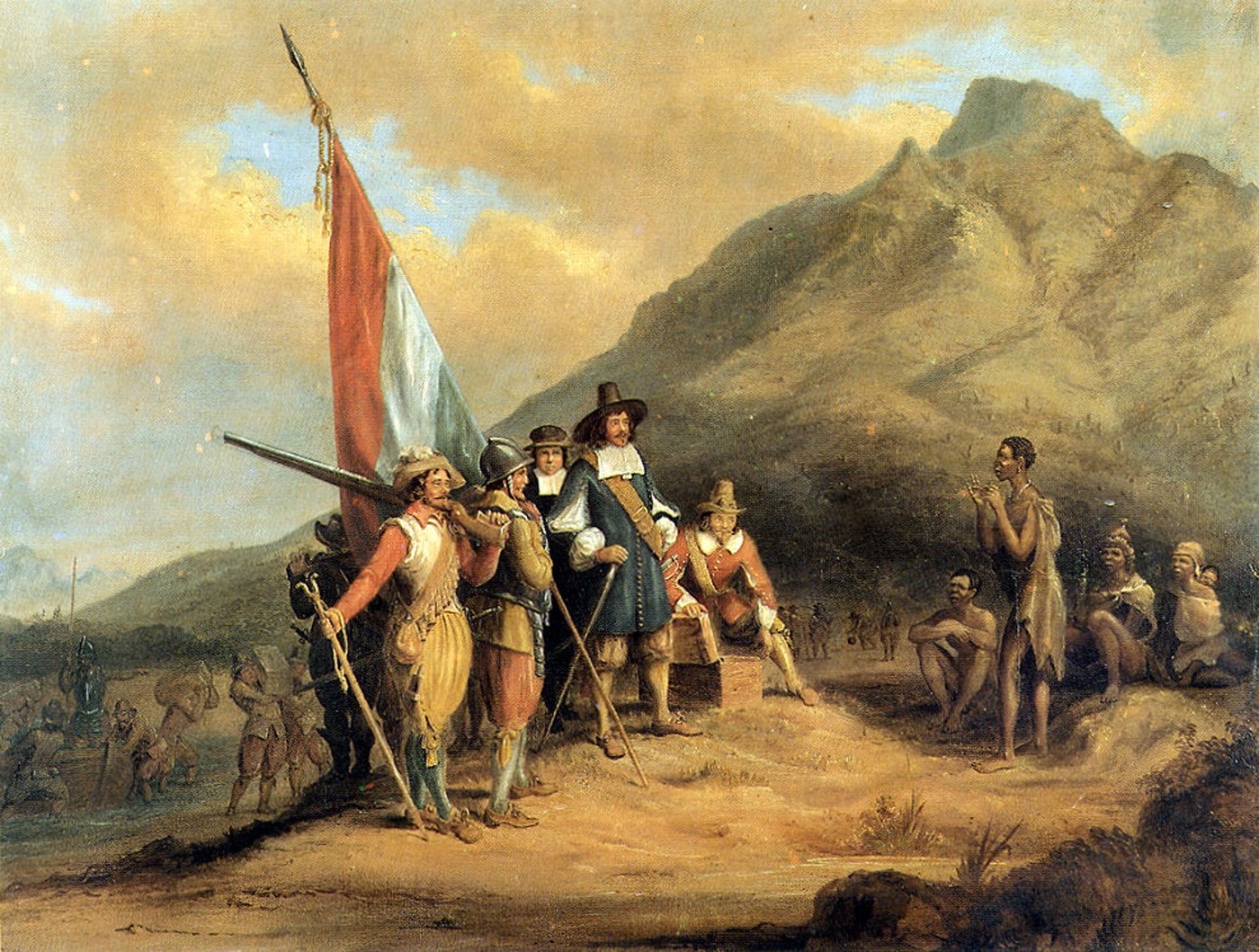
Dutch Cape Colony
The Cape of Good Hope () was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) supplystation in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original supply station and the successive states that the area was incorporated into occupied much of modern South Africa. Between 1652 and 1691, it was a Commandment, and between 1691 and 1795, a Governorate of the VOC. Jan van Riebeeck established the supply station as a re-supply and layover port for vessels of the VOC trading with Asia. The Cape came under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and from 1803 to 1806 as Dutch Cape Colony was ruled by the Batavian Republic. Much to the dismay of the shareholders of the VOC, who focused primarily on making profits from the Asian trade, the colony rapidly expanded into a settler colony in the years after its founding. As the only permanent settlement of the Dutch United East India Company serving as a trading post, it proved an ideal retirement place for employee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of The Cape Colony
The invasion of the Cape Colony, also known as the Battle of Muizenberg (), was a British military expedition launched in 1795 against the Dutch Cape Colony at the Cape of Good Hope. The Dutch colony at the Cape, established and controlled by the United East India Company in the seventeenth century, was at the time the only viable South African port for ships making the journey from Europe to the European colonies in the East Indies. It therefore held vital strategic importance, although it was otherwise economically insignificant. In the winter of 1794, during the French Revolutionary Wars, French troops entered the Dutch Republic, which was reformed into the Batavian Republic. In response, Great Britain launched operations against the Dutch Empire to use its facilities against the French Navy. The British expedition was led by Vice-Admiral Sir George Elphinstone and sailed in April 1795, arriving off Simon's Town at the Cape in June. Attempts were made to negotiate a settlem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khoekhoe
Khoikhoi ( /ˈkɔɪkɔɪ/ ''KOY-koy'') (or Khoekhoe in Namibian orthography) are the traditionally nomadic pastoralist indigenous population of South Africa. They are often grouped with the hunter-gatherer San (literally "foragers") peoples, the accepted term for the two people being Khoisan. The designation "Khoikhoi" is actually a ''kare'' or praise address, not an ethnic endonym, but it has been used in the literature as an ethnic term for Khoe-speaking peoples of Southern Africa, particularly pastoralist groups, such as the Inqua, Griqua, Gonaqua, Nama, Attequa. The Khoekhoe were once known as '' Hottentots'', a term now considered offensive."Hottentot, n. and adj." ''OED Online'', Oxford University Press, March 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/88829. Accessed 13 May 2018. Citing G. S. Nienaber, 'The origin of the name "Hottentot" ', ''African Studies'', 22:2 (1963), 65–90, . See also . The Khoekhoe are thought to have diverged from other humans 100,000 to 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khoikhoi–Dutch Wars
The Khoikhoi–Dutch Wars (or Khoekhoe–Dutch Wars) refers to a series of armed conflicts that took place in the latter half of the 17th century in what was then known as the Cape of Good Hope, in the area of present-day Cape Town, South Africa, fought primarily between Dutch colonisers, who came mostly from the Dutch Republic (today the Netherlands and Belgium) and the local African people, the indigenous Khoikhoi. Under the Dutch East India Company (VOC), and starting in 1652, colonists ( Vrijburghers) – initially and predominantly the VOC's European employees and emancipated servants, but later also including a minority of the VOC's Asian and African employees and emancipated servants and slaves – were permanently settled at the Cape of Good Hope on land which had been seized from the indigenous people, including the Khoikhoi (called Hottentots or Kaffirs by the Dutch), and the Bushmen (also known as the San), collectively referred to as the Khoisan. Though Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and the #Definitions and Usage, physical geography definition based on the physical characteristics of the land. The most restrictive definition considers the region of Southern Africa to consist of Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia, and South Africa, while other definitions also include several other countries from the area. Defined by physical geography, Southern Africa is home to several river systems; the Zambezi, Zambezi River is the most prominent. The Zambezi flows from the northwest corner of Zambia and western Angola to the Indian Ocean on the coast of Mozambique. Along the way, it flows over Victoria Falls on the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe. Victoria Falls is one of the largest waterfalls in the world and a major tourist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
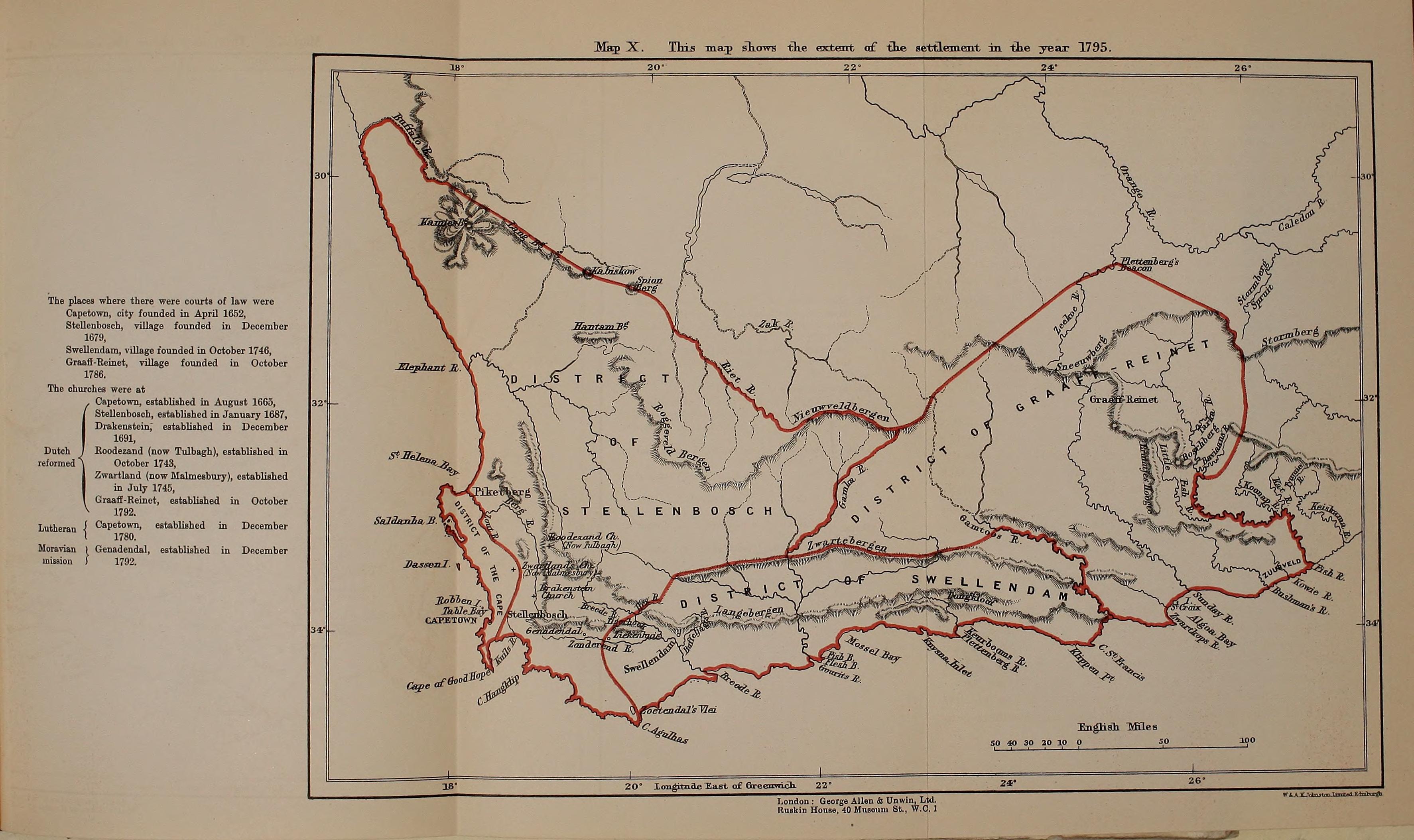
Map Of The Dutch Cape Colony In 1795
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Blaauwberg
The Battle of Blaauwberg (also known as the Battle of Cape Town) was a successful British amphibious operation during the War of the Third Coalition which lasted from 8–18 January 1806 and resulted in the capture of the Dutch Cape Colony. After defeating their Batavian Republic, Batavian opponents, the British signed a treaty under the Treaty Tree in Woodstock, Cape Town which established Britain's control over the Cape Colony. The colony later became a permanent part of the British Empire following the Congress of Vienna that marked the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1814. Due to establishing permanent British rule over the Cape Colony, the battle would have many ramifications for southern Africa during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. A bi-centennial commemoration of the battle was held in January 2006. Background In 1795, the Kingdom of Great Britain, British carried out a successful invasion of the Cape Colony during the War of the First Coalition, capturing the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France, the Spanish Empire, and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it set the stage for the Napoleonic Wars. Britain gave up most of its recent conquests; France was to evacuate Naples and Egypt. Britain retained Ceylon (Sri Lanka) and Trinidad. It was signed in the Hôtel de Ville (City Hall) of Amiens on 25 March 1802 (4 Germinal X in the French Revolutionary calendar) by Joseph Bonaparte and Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis as a "Definitive Treaty of Peace". The consequent peace lasted only one year (18 May 1803) and was the only period of general peace in Europe between 1793 and 1814. Under the treaty, Britain recognised the French Republic. Together with the Treaty of Lunéville (1801), the Treaty of Amiens marked the end of the Second Coalition, which had waged war against Revolutionary F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xhosa Wars
The Xhosa Wars (also known as the Cape Frontier Wars or the Kaffir Wars) were a series of nine wars (from 1779 to 1879) between the Xhosa Kingdom and the British Empire as well as Trekboers from the Dutch colonial empire in what is now the Eastern Cape in South Africa. These events were the longest-running military resistance against European colonialism in Africa. The reality of the conflicts between the Europeans and Xhosa involves a balance of tension. At times, tensions existed between the various Europeans in the Cape region, tensions between Empire administration and colonial governments, and tensions within the Xhosa Kingdom, e.g. chiefs rivaling each other, which usually led to Europeans taking advantage of the situation to meddle in Xhosa politics. A perfect example of this is the case of chief Ngqika and his uncle, chief Ndlambe. The conflicts between the Xhosa and British were covered extensively in the metropolitan British press, generating increased demand a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Corps
The Cape Corps and its predecessor units were the main military organisations in which the Coloured members of South Africa's population served. History As one of the military units of South Africa with one of the longest histories, the Cape Corps reflects the history of South Africa's Coloured population to a great extent. Pre-history 1770s In the 1770s, the Dutch authorities established the first Coloured military unit, the Free Corps. The unit consisted solely of Coloured recruits and no white people were allowed to join except as officers, marking the beginning of racially segregated units in the military history of South Africa. 1781–1782 The second Coloured unit to be formed was the Bastard Hottentot Corps (Afrikaans: "Corps Bastaard Hottentoten"), which was organised in 1781 by the Dutch Cape Colony, Dutch colonial administration of the time. Based in Cape Town and drawing its members from men of mixed Hottentot and White ancestry, this unit had about 400 me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |