|
Korg PS-3300
The Korg PS-3300 is a polyphonic analog synthesizer released by Korg in 1977. It was released alongside the PS-3100, a more compact variant featuring a complete synthesizer voice board for each of its 48 keyboard notes. The PS-3300 essentially combines three PS-3100 units, triggering all voices simultaneously with each key press and mirroring the PS-3100's overall design, featuring a total of 144 synth voices. The PS-3300 uses the PS-3010, a detachable keyboard equipped with an assignable joystick called the X-Y Manipulator. The PS series also includes the PS-3200, launched in 1978, which upgrades to two voices per key and introduces the capability to save and recall 16 presets. The PS-3200 also substitutes the resonators found in the PS-3100 and PS-3300 with a 7-band equalizer. Background At the time the PS-series synthesizers were released, creating polyphonic synthesizers posed significant difficulties for manufacturers. Truly polyphonic instruments, such as the Polymoog, Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korg
, founded as Keio Electronic Laboratories, is a Japanese multinational corporation that manufactures electronic musical instrument An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electronics, electronic circuitry. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical, electronic or digital audio signal that ultimately is ...s, audio processors and guitar pedals, recording equipment, and electronic tuners. Under the Vox brand name, they also manufacture guitar amplifiers and electric guitars. History KORG was founded in 1962 in Tokyo by Tsutomu Kato and Tadashi Osanai as ''Keio Gijutsu Kenkyujo Ltd.''. It later became because its offices were located near the Keio train line in Tokyo and Keio can be formed by combining the first letters of Kato and Osanai. Before founding the company, Kato ran a nightclub. Osanai, a Tokyo University graduate and noted accordionist, regularly performed at Kato's club accompanie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korg Polyphonic Ensemble P
The Korg PE-1000 (Polyphonic Ensemble) is a preset-based polyphonic analog synthesizer released by Korg in 1976. It was Korg's first polyphonic synthesizer and was marketed in the US as the Univox K4. Background In the mid-1970s, polyphonic synthesizers had started to emerge, with the releases of the Yamaha GX-1, Oberheim Four Voice, and Polymoog signalling a new direction in synthesis technology. Korg aiming to produce a synthesizer capable of producing true polyphonic chords, as all of their previous synthesizers had been monophonic. Constructing a polyphonic synth was prohibitively expensive at the time. Although string synthesizers had been available for a few years, they didn't offer the articulation of a true synthesizer. Korg's innovation involved integrating the basic features of a monosynth with the polyphonic sound generation system of string synthesizers, resulting in the release of two Polyphonic Ensemble keyboards. These instruments, the PE-1000 followed by the PE- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Filter
A voltage-controlled filter (VCF) is an electronic filter whose operating characteristics (primarily cutoff frequency) can be set by an input control voltage. Voltage-controlled filters are widely used in synthesizers. A music synthesizer VCF allows its cutoff frequency, and sometimes its Q factor (resonance at the cutoff frequency), to be continuously varied. The filter outputs often include a lowpass response, and sometimes highpass, bandpass or notch responses. Some musical VCFs offer a variable ''slope'' which determines the rate of attenuation outside the bandpass, often at 6 dB/octave, 12 dB/octave, 18 dB/octave or 24 dB/octave (one-, two-, three- and four-pole filters, respectively). In modular analog synthesizers, VCFs receive signal input from signal sources, including oscillators and noise, or the output of other processors. By varying the cutoff frequency, the filter passes or attenuates partials of the input signal. In some popular elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrato
Vibrato (Italian language, Italian, from past participle of "wikt:vibrare, vibrare", to vibrate) is a musical effect consisting of a regular, pulsating change of pitch (music), pitch. It is used to add expression to vocal and instrumental music. Vibrato is typically characterized in terms of two factors: the amount of pitch variation ("extent of vibrato") and the speed with which the pitch is varied ("rate of vibrato"). In singing, it can occur spontaneously through variations in the larynx. The vibrato of a string instrument and wind instrument is an imitation of that vocal function. Vibrato can also be reproduced mechanically (Leslie speaker) or electronically as an Audio signal processing, audio effect close to Chorus (audio effect), chorus. Terminology History Descriptions of what would now be characterised as vibrato go back to the 16th century. However, no evidence exists of authors using the term vibrato before the 19th century. Instead, authors used various descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawtooth Wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ramp waveform. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse (or inverse) sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. The equivalent piecewise linear functions x(t) = t - \lfloor t \rfloor x(t) = t \bmod 1 based on the floor function of time ''t'' is an example of a sawtooth wave with period 1. A more general form, in the range −1 to 1, and with period ''p'', is 2\left( - \left\lfloor + \right\rfloor\right) This sawtooth function has the same phase as the sine function. While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave's sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying period). PWM is useful for controlling the average power or amplitude delivered by an electrical signal. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by switching the supply between 0 and 100% at a rate faster than it takes the load to change significantly. The longer the switch is on, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of controlling the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching. The goal of PWM is to control a load; however, the PWM switching frequency must be sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions between minimum and maximum are instantaneous. The square wave is a special case of a pulse wave which allows arbitrary durations at minimum and maximum amplitudes. The ratio of the high period to the total period of a pulse wave is called the duty cycle. A true square wave has a 50% duty cycle (equal high and low periods). Square waves are often encountered in electronics and signal processing, particularly digital electronics and digital signal processing. Its stochastic counterpart is a two-state trajectory. Origin and uses Square waves are universally encountered in digital switching circuits and are naturally generated by binary (two-level) logic devices. They are used as timing references or "clock signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
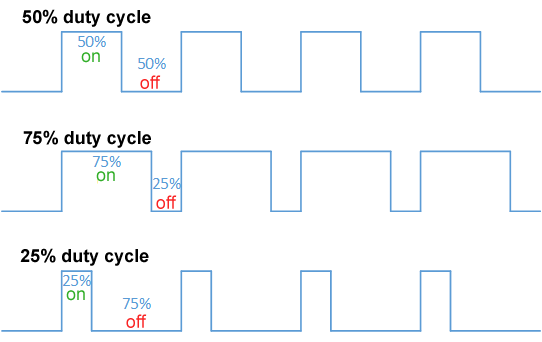
Pulse Wave
A pulse wave or pulse train or rectangular wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform that is the periodic version of the rectangular function. It is held high a percent each cycle ( period) called the duty cycle and for the remainder of each cycle is low. A duty cycle of 50% produces a square wave, a specific case of a rectangular wave. The average level of a rectangular wave is also given by the duty cycle. A pulse wave is used as a basis for other waveforms that modulate an aspect of the pulse wave. In pulse-width modulation (PWM) information is encoded by varying the duty cycle of a pulse wave. Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) encodes information by varying the amplitude. Frequency-domain representation The Fourier series expansion for a rectangular pulse wave with period T, amplitude A and pulse length \tau is x(t) = A \frac + \frac \sum_^ \left(\frac \sin\left(\pi n\frac\right) \cos\left(2\pi nft\right)\right) where f = \frac. Equivalently, if duty cycle d = \frac is used, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Wave
A triangular wave or triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function. Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse). Definitions Definition A triangle wave of period ''p'' that spans the range , 1is defined as x(t) = 2 \left, \frac - \left\lfloor \frac + \frac \right\rfloor \, where \lfloor\ \rfloor is the floor function. This can be seen to be the absolute value of a shifted sawtooth wave. For a triangle wave spanning the range the expression becomes x(t)= 2 \left , 2 \left( \frac - \left\lfloor \frac + \frac \right\rfloor \right) \ - 1. A more general equation for a triangle wave with amplitude a and period p using the modulo operation and absolute value is y(x) = \frac \left, \left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) by applying a modulation, modulating signal to the control input. A VCO is also an integral part of a phase-locked loop. VCOs are used in synthesizers to generate a waveform whose Pitch (music), pitch can be adjusted by a voltage determined by a musical keyboard or other input. A voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC) is a special type of VCO designed to be very linear in frequency control over a wide range of input control voltages. Types VCOs can be generally categorized into two groups based on the type of waveform produced. * ''Linear'' or ''harmonic oscillators'' generate a sinusoidal waveform. Harmonic oscillators in electronics usually consist of a resonator with an amplifier that re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Synthesizer
Modular synthesizers are synthesizers composed of separate modules for different functions. The modules can be connected together by the user to create a patch. The outputs from the modules may include audio signals, analog control voltages, or digital signals for logic or timing conditions. Typical modules are voltage-controlled oscillators, voltage-controlled filters, voltage-controlled amplifiers and envelope generators. History The first modular synthesizer was developed by German engineer Harald Bode in the late 1950s. The 1960s saw the introduction of the Moog synthesizer and the Buchla Modular Electronic Music System, created around the same period. The Moog was composed of separate modules which created and shaped sounds, such as envelopes, noise generators, filters, and sequencers, connected by patch cords. The Japanese company Roland released the Roland System 100 in 1975, followed by the System 700 in 1976 and the System 100m in 1979. In the late 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moog Modular Synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer ( ) is a modular synthesizer invented by the American engineer Robert Moog in 1964. Moog's company, R. A. Moog Co., produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer and established the analog synthesizer concept. The Moog synthesizer consists of separate modules which create and shape sounds, which are connected via patch cords. Modules include voltage-controlled oscillators, amplifiers, Voltage-controlled filter, filters, envelope generators, noise generators, ring modulators, triggers and mixers. The synthesizer can be played using controllers including musical keyboard, keyboards, joysticks, pedals and ribbon controllers, or controlled with Music sequencer, sequencers. Its oscillators produce waveforms, which can be modulated and filtered to shape their sounds (subtractive synthesis) or used to control other modules (low-frequency oscillation). Moog developed the synthesizer in response to demand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |