|
Koppány (bishop)
Koppány, also known as Cupan or Cuppan (died 1099), was a Hungarian cleric in the late 11th century, active during the reigns of Ladislaus I then Coloman. Some historians argue he is the author of the ''Urgesta'', the first Hungarian chronicle. Ancestry According to a note – "''The aforesaid Vecellin begot Radi, Radi begot Miska, Miska begot Koppány and Martin''" – from the 14th-century ''Illuminated Chronicle'', Koppány was a great-grandson of German knight Vecelin of Wasserburg, who, in 997 or 998, played a decisive role in the defeat of Koppány, who contested the legitimacy of Stephen I, Grand Prince of the Hungarians. Koppány's father was a certain Miska (Michael or Mika). He had a brother Martin. The chronicle also states that the ''gens'' (clan) Ják descended from Vecelin, thus Koppány also belonged to this kindred, as it was first identified by historian János Karácsonyi. However, Benedictine historian Lajos J. Csóka proved that, instead of the Jáks, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
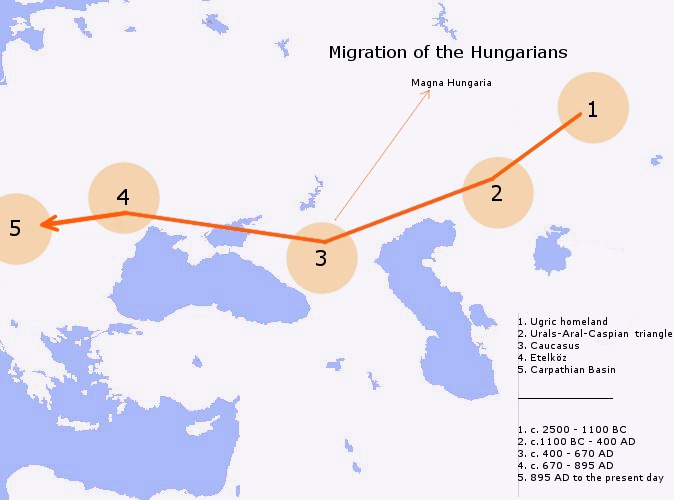
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Archdiocese Of Zagreb
The Metropolitan Archdiocese of Zagreb (; ) is the central Latin Church archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Croatia, centered in the capital city Zagreb. It is the metropolitan see of Croatia, and the present archbishop is Dražen Kutleša. It encompasses the northwestern continental areas of Croatia. Background The territory of the present-day Archdiocese of Zagreb was part of the Roman province of Pannonia Savia, centered around the busy river port of Sisak. Christianity started to spread in Pannonia in the 3rd century. The capital of province, Sisak got its first bishop in the second half of the 3rd century. Bishop Castus was mentioned for the first time in 249 A.D. during Emperor Decius’s reign. One of the more notable bishops is Quirinus of Sescia, who suffered during the persecutions of Diocletian. Later, the Councils of Split confirmed the Archbishopric of Split as the archepiscopal see having the right to govern all parishes on Croatian territory. History The dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffragan Bishop
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations. In the Catholic Church, a suffragan bishop leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led by the suffragan is called a suffragan diocese. In the Anglican Communion, a suffragan bishop is a bishop who is subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop (bishop ordinary) and so is not normally jurisdictional in their role. Suffragan bishops may be charged by a metropolitan to oversee a suffragan diocese and may be assigned to areas which do not have a cathedral. Catholic Church In the Catholic Church, a suffragan is a bishop who heads a diocese. His suffragan diocese, however, is part of a larger ecclesiastical province, nominally led by a metropolitan archbishop. The distinction between metropolitans and suffragans is of limited practical importance. Both are diocesan bishops possessing ordinary jurisdiction over thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Przemyśl
Przemyśl () is a city in southeastern Poland with 56,466 inhabitants, as of December 2023. Data for territorial unit 1862000. In 1999, it became part of the Podkarpackie Voivodeship, Subcarpathian Voivodeship. It was previously the capital of Przemyśl Voivodeship. Przemyśl owes its long and rich history to the advantages of its geographic location. The city lies in an area connecting mountains and lowlands known as the Przemyśl Gate (Brama Przemyska), with open lines of transport, and fertile soil. It also lies on the navigable San River. Important trade routes that connect Central Europe from Przemyśl ensure the city's importance. The Old Town of Przemyśl is listed as a List of Historic Monuments (Poland), Historic Monument of Poland. Since the start of the Russian invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022, Przemyśl has been a point of refuge for many Ukrainians, as it is located near the Poland–Ukraine border and serves as the end point of the Lviv–Przemyśl railway jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The highest peaks in the Carpathians are in the Tatra Mountains, exceeding , closely followed by those in the Southern Carpathians in Romania, exceeding . The range stretches from the Western Carpathians in Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Poland, clockwise through the Eastern Carpathians in Ukraine and Romania, to the Southern Carpathians in Romania and Serbia.About the Carpathians – Carpathian Heritage Society [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sviatopolk II Of Kiev
Sviatopolk II Iziaslavich (; 8 November 1050 – 16 April 1113) was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1093 to 1113. He was not a popular prince, and his reign was marked by incessant rivalry with his cousin Vladimir Monomakh. Early life Sviatopolk was the son of Iziaslav Iaroslavich by his concubine. During his brother Iaropolk's life, Sviatopolk was not regarded as a potential claimant to the throne of Kiev. In 1069 he was sent to Polotsk, a city briefly taken by his father from the local ruler Vseslav, and then he spent ten years (1078–88) ruling Novgorod. Upon his brother's death he succeeded him in Turov, which would remain in possession of his descendants until the 17th century. Reign When Vsevolod Iaroslavich died in 1093, Sviatopolk was acknowledged by other princes as the senior son of the grand prince and permitted to ascend the Kievan throne. Although he participated in the princely congresses organized by Vladimir Monomakh, he is sometimes charged with encouraging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,. * was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavs, East Slavic, Norsemen, Norse, and Finnic peoples, Finnic, it was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, founded by the Varangians, Varangian prince Rurik.Kievan Rus , Encyclopædia Britannica Online. The name was coined by Russian historians in the 19th century to describe the period when Kiev was preeminent. At its greatest extent in the mid-11th century, Kievan Rus' stretched from the White Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south and from the River source, headwaters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Archdiocese Of Eger
The Archdiocese of Eger () is a Latin Church archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Northern Hungary, its centre is the city of Eger. History * 1000: Established as Diocese of Eger * August 9, 1804: Promoted as Metropolitan Archdiocese of Eger with four suffragan dioceses: Satu Mare (until 1930), Spiš (until 1937), Košice (until 1977) and Rožňava (until 1977) * 1993: It received two new suffragan dioceses, Debrecen-Nyíregyháza (then created) and Vác Ordinaries, in reverse chronogical order Archbishops of Eger * Csaba Ternyák (2007-present) * István Seregély (1987–2007) * László Kádár, O. Cist. (1978–1986) * József Bánk (1974–1978) * Pál Brezanóczy (1969–1972) * Gyula Czapik (1943–1956) * Lajos Szmrecsányi (1912–1943) * József Samassa (1873–1912) (Cardinal in 1905) * Béla Bartakovics (1850–?) * Ladislaus Pyrker, O.Cist. (1827–1847) * István Fisher (1807–1822) * Ferenc Fuchs (1804–?) Bishops of Eger * Tamás Pálffy (1660– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonhalma Archabbey
The Benedictine Pannonhalma Archabbey or Territorial Abbey of Saint Martin on Mount Pannonhalma (lat. ''Archiabbatia'' or ''Abbatia Territorialis Sancti Martini in Monte Pannoniae'') is a medieval building in Pannonhalma and is one of the oldest historical monuments in Hungary. Founded in 996, it is located near the town, on top of a hill (282 m). Saint Martin of Tours is believed to have been born at the foot of this hill, hence its former name, Mount of Saint Martin (), from which the monastery occasionally took the alternative name of Márton-hegyi Apátság. This is the second largest territorial abbey in the world, after the one in Monte Cassino. Its sights include the Basilica with the Crypt (built in the 13th century), the Cloisters, the monumental Library with 360,000 volumes, the Baroque Refectory (with several examples of ''trompe-l'œil'') and the Archabbey Collection (the second biggest in the country). Because of the exceptional architectural evolution of the abbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bálint Hóman
Bálint Hóman (29 December 1885 – 2 June 1951) was a Hungarian scholar and politician who served as Minister of Religion and Education twice: between 1932 and 1938 and between 1939 and 1942. He died in prison in 1951 for his support of the fascistic invasion of the Soviet Union and antisemitic legislation activity as part of the Axis alliance in World War II. Academic career He was born into a Roman Catholic family. He finished his studies in Budapest. He started his career when he was still a student, working for the University Library of Budapest. He was appointed director of the National Széchényi Library in 1922, and of the Hungarian National Museum in 1923, a position he held until 1932. Hóman produced several serious scholarly works. The centre of his research was the history of the Hungarian nation during the Middle Ages. Initially he dealt with economic history, social history and the auxiliary sciences of history. He wrote about Hungarian towns during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tihany Abbey
The Tihany Abbey is a Benedictine monastery established in Tihany in the Kingdom of Hungary in 1055. Its patrons are the Virgin Mary and Saint Aignan of Orleans. Foundation The Benedictine monastery in Tihany was established in 1055 by King Andrew I of Hungary (r. 1046–1060). It was dedicated to the Holy Virgin and to Saint Bishop Aignan of Orleans. King Andrew was buried in the church of the monastery in 1060. His tomb in the crypt of the church is the only grave of a medieval King of Hungary which has been preserved up until now. The church's ceiling is decorated with frescoes by Károly Lotz, depicting Faith, Hope and Love. Gallery Tihany drón panoráma.jpg Tihany, Apátság 4.jpg A tihanyi apátság.jpg Tihanycivertanlegi2.jpg Tihanycivertanlegi6.jpg Tihanycivertanlegi4.jpg Tihanycivertanlegi5.jpg Interior of Tihany Abbey.JPG Apátsági templom (10483. számú műemlék) 6.jpg See also * Establishing charter of the abbey of Tihany The establishing charter of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |