|
Koporye
Koporye (; Finnish: ''Kaprio''; ) is a historic village ('' selo'') in Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located about west of St. Petersburg and south of the Koporye Bay of the Baltic Sea. Its population in 2017 was 1,603. History The first wooden fortress on the coast of the Koporye Bay was built by the Teutonic Knights in the winter of 1240, only to be destroyed by Alexander Nevsky the next year. The second fortress was built in stone by Alexander's son Dmitry Alexandrovich in 1280. Enraged by the prince's independence, the Novgorodians razed the fortress two years later. The Swedes took advantage of the lack of a fortress and occupied the banks of the Narva River. The Novgorodians had to restore the stone fort in 1297. Koporye was the strongest stronghold in the region and survived numerous attacks during the Swedish–Novgorodian Wars. In the 14th and 15th centuries, the town was given several times to mercenary princes invited by Novgorodians to protect the northern te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomonosovsky District, Leningrad Oblast
Lomonosovsky District () is an administrativeOblast Law #32-oz and municipalLaw #117-oz district (raion), one of the administrative divisions of Leningrad Oblast, seventeen in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It is located in the west of the oblast and borders with Petrodvortsovy District, Petrodvortsovy and Krasnoselsky District, Saint Petersburg, Krasnoselsky Districts of the Federal city of Saint Petersburg in the east, Gatchinsky District in the southeast, Volosovsky District in the south, Kingiseppsky District in the southwest, and the city of oblast significance of Sosnovy Bor in the west. In the north, the district is bounded by the Gulf of Finland. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, town of Lomonosov, Russia, Lomonosov (which is not a part of Leningrad Oblast and is located on the territory of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg). Population: 65,297 (Russian Census (2002), 2002 Census) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Ingria
Swedish Ingria (, ‘land of Ingrians’) was a dominion of the Swedish Empire from 1583 to 1595 and then again from 1617 to 1721 in what is now the territory of Russia. At the latter date, it was ceded to the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Nystad, at the end of the Great Northern War between the two empires. History Ingria had fallen to Sweden in the 1580s and as a consequence of the Treaty of Plussa (1583), Sweden kept the Ingrian towns of Ivangorod (Ivanslott), Jamburg (Jama/Jamo) and Koporye (Kaprio) together with their hinterland. Russia only kept a narrow passage to the Baltic Sea at the estuary of the Neva River, between Strelka and Sestra Rivers. The region was returned to Russia by the Treaty of Teusina (1595), and again ceded together with the remainder of Ingria and the County of Kexholm to Sweden in the Treaty of Stolbovo (1617) that concluded the Ingrian War. The area ran along the basin of the Neva River, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
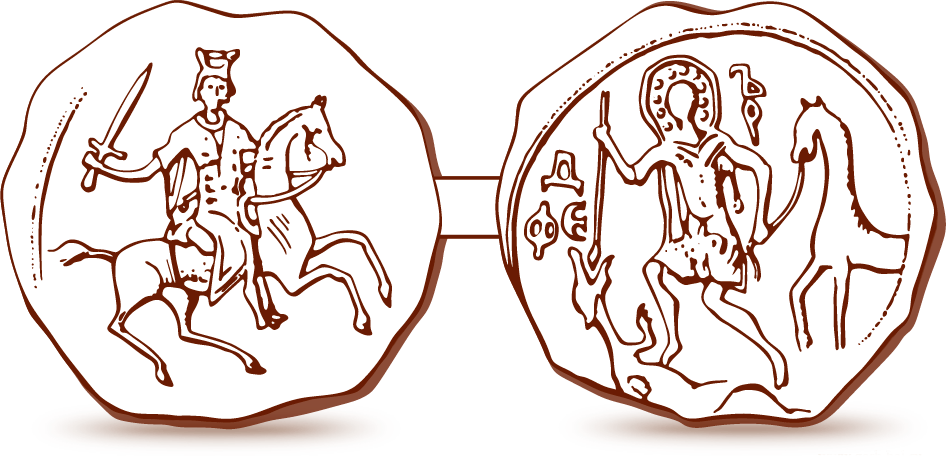
Dmitry Of Pereslavl
Dmitry Alexandrovich (; 1250–1294) was Grand Prince of Vladimir from 1276 to 1281, and again from 1283 until 1293. Biography Dmitry was the second son of Alexander Nevsky. When his elder brother Vasily died young, Dmitry remained the chief heir to his illustrious father. As early as 1259, he was left by Alexander in charge of Novgorod. Upon Alexander's death in 1264, however, the Novgorodians expelled Dmitry to his native Pereslavl-Zalessky, citing his youth as a pretext. Four years later, when Dmitry had turned 18, he was welcomed back to Novgorod and — together with his future son-in-law, Daumantas of Pskov — led a local militia against Livonian Knights in the Battle of Rakvere. During the following decade, he struggled for control of Novgorod against his uncles, Yaroslav III and Vasily of Kostroma. In 1276, when his elders died, he finally ascended the coveted thrones of Vladimir and Novgorod. Two years later, he founded a great fortress of Koporye, which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (; ; monastic name: ''Aleksiy''; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) was Prince of Novgorod (1236–1240; 1241–1256; 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1249–1263), and Grand Prince of Vladimir (1252–1263). Commonly regarded as a key figure in medieval Russian history, Alexander was a grandson of Vsevolod the Big Nest and rose to legendary status on account of his military victories in northwestern Russia over Swedish invaders in the 1240 Battle of the Neva, as well as German crusaders in the 1242 Battle on the Ice. He preserved Eastern Orthodoxy, agreeing to pay tribute to the powerful Golden Horde. Metropolitan Macarius of Moscow canonized Alexander Nevsky as a saint of the Russian Orthodox Church in 1547. Early life Born in Pereslavl-Zalessky around the year 1220, Alexander was the second son of Prince Yaroslav Vsevolodovich. His mother was , daughter of Mstislav Mstislavich The Bold. From the ''Tales of the Life and Courage of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census, 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina. The oblast was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Saint Petersburg, Leningrad. In 1991, the city restored its original name, Saint Petersburg, but the oblast retains the name of Leningrad. It overlaps the historical region of Ingria, and is bordered by Finland (Kymenlaakso and South Karelia) in the northwest and Estonia (Ida-Viru County) in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia in the northeast, Vologda Oblast in the east, Novgorod Oblast in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koporye Bay
The Koporye Bay ( Russian: Копорская губа, ''Koporskaya Guba'') is a 12 km-long bay on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland. It is up to 26 km wide and 20 meters deep. The shore is low and rocky; the hinterland is woody. It is part of Russia's Leningrad Oblast Leningrad Oblast (, ; ; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). The oblast has an area of and a population of 2,000,997 (2021 Russian census, 2021 Census); up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Russian census .... The only major settlement is the town of Sosnovy Bor. The Voronka and Sista Rivers drain into the bay. It is named after the medieval fortress of Koporye, which lies slightly to the south. Bays of the Baltic Sea Bays of Leningrad Oblast {{LeningradOblast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingria
Ingria (; ; ; ) is a historical region including, and adjacent to, what is now the city of Saint Petersburg in northwestern Russia. The region lies along the southeastern shore of the Gulf of Finland, bordered by Lake Ladoga on the Karelian Isthmus in the north and by the Narva river on the current international border with Estonia in the west. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were indigenous Finnic peoples, primarily the ancestors of modern Izhorians and Votians, who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity during the late Middle Ages. They were later joined by the Ingrian Finns, descendants of 17th century Lutheran Finnish immigrants. At that time, Ingria, the Karelian Isthmus, Estonia, and what is now Finland were all part of the Kingdom of Sweden. Ingria as a whole never formed a separate state; however, North Ingria was an independent state for just under two years in 1919–1920. The inhabitants of Ingria cannot be said to have comprised a distinct n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Tyavzino
The Treaty of Teusina (, Russian: ''Тя́взинский ми́рный догово́р'') was concluded by Russian diplomats under the boyar Afanasiy Pushkin and ambassadors of the Swedish king at the village of (, ) in Ingria on 18 May 1595 to end the Russo-Swedish War (1590–1595). The treaty revised provisions of the Truce of Plussa in 1583. It restored all territory ceded to Sweden back to Russia, except for Narva. Russia received Kexholm County with Korela Fortress and most of Ingria, with the towns of Ivangorod, Yama, Koporye. The treaty restored the borders predating the Livonian War. The Swedish-Russian border was delineated from the outstream of the Systerbäck river into the Gulf of Finland, over the lakes Saimaa and Inari, the settlement of Neiden and up to the Barents Sea. Russia had to renounce all claims on Estonia, including Narva, and they had to accept Swedish sovereignty over Estonia. Background The Armistice of 1593 Sweden and Russia had signe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) concerned control of Terra Mariana, Old Livonia (in the territory of present-day Estonia and Latvia). The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom of Sweden (1523–1611), Kingdom of Sweden, and the Polish–Lithuanian union, Union (later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Commonwealth) of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland. From 1558 to 1578, Russia dominated the region with early military successes at Tartu, Dorpat (Tartu) and Narva. The Russian dissolution of the Livonian Confederation brought Poland–Lithuania into the conflict, and Sweden and Denmark-Norway intervened between 1559 and 1561. Swedish Estonia was established despite constant invasion from Russia, and Frederick II of Denmark, Frederick II of Denmark-Norway bought the old Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, which he placed under the control of his brother Magnus of Holstein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish–Novgorodian Wars
The Swedish–Novgorodian Wars were a series of armed conflicts during the 12th and 13th centuries, fought between the Novgorod Republic and medieval Sweden over control of the Gulf of Finland. Part of the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, the area was vital to the Hanseatic League. The clashes between Catholic Swedes and Orthodox Novgorodians had religious overtones, but before the 14th century there is no knowledge of official crusade bulls issued by the pope. Background Scandinavians maintained trade relations and other links with Novgorod from the Viking Age onwards. Merchants from Gotland operated both their own trading house (Gutagård) and Saint Olaf's Church in Novgorod. Scandinavians also carried out isolated raids on Novgorod. Eiríkr Hákonarson raided Staraya Ladoga, Ladoga in 997, and his brother Sveinn Hákonarson followed suit in 1015. After the marriage of Yaroslav the Wise, Yaroslav I (Grand Prince of Novgorod and Kiev) to Ingegerd Olofsdotter of Sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in and in Latin . Thus the term "T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601,911 residents as of 2021, with more than 6.4 million people living in the Saint Petersburg metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As the former capital of the Russian Empire, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |