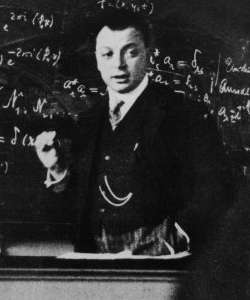|
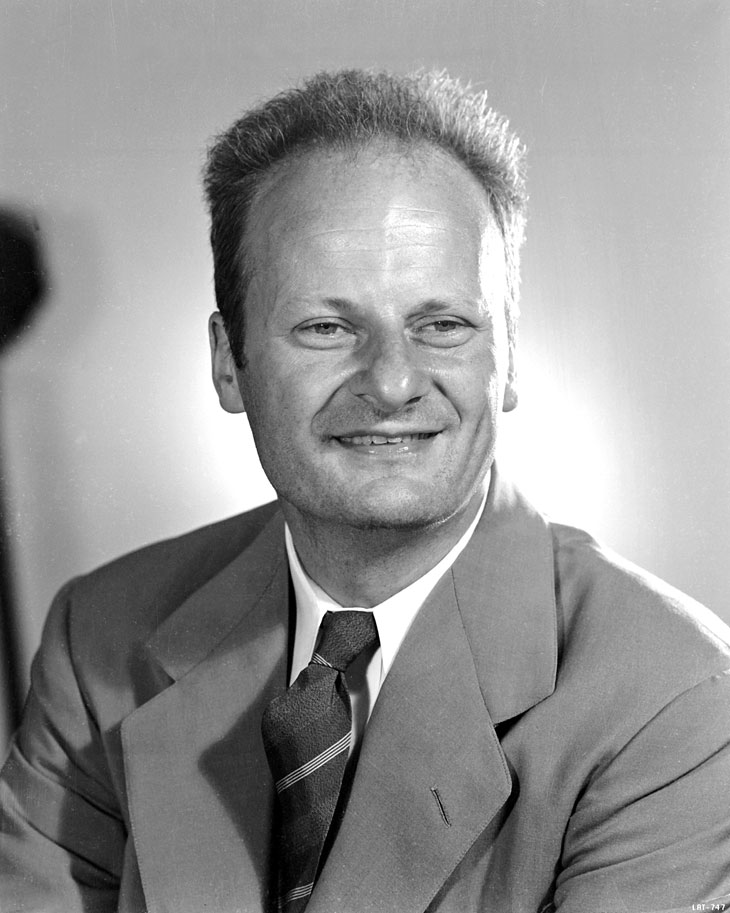
Konrad Bleuler
Konrad Bleuler (; 23 September 1912, Herzogenbuchsee – 1 January 1992, Königswinter) was a Swiss physicist who worked in the field of theoretical particle physics and quantum field theory. He is known for his work on the quantisation of the photon, the Gupta–Bleuler formalism. Education and career Bleuler was born in Herzogenbuchsee, Switzerland on 23 September 1912. He received his doctorate for the mathematical work titled "On the Rolle's theorem for the operator Δu + λu and related properties of the Green's function" from the ETH Zurich in 1942. His thesis advisor was Michel Plancherel. From 1960 to 1980 he was a professor at the University of Bonn, where he founded the Institute of Theoretical Nuclear Physics, which is now the Helmholtz Institute for Radiation and Nuclear Physics. Even after his retirement, he was active and remained there until his death. 1971 Bleuler organized the first "International Conference on Differential Geometric Methods in Theoretical Physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herzogenbuchsee
Herzogenbuchsee is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the Oberaargau (administrative district), Oberaargau administrative district in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Bern (canton), Bern in Switzerland. The population is 7055 (2011), counting the villages in the Oberaargau. The traditional name was ''Buchsi''. History Herzogenbuchsee is built on a moraine of the Rhone Glacier. The area has been settled for at least 10,000 years, with ancient settlements around the Inkwilersee and Burgäschisee. There is also evidence of Roman buildings from approximately 200 CE near the current Reformed Church. The first documented use of the name ''puhsa'' (pronounced ''Buchsa'', in Latin ''buxum'', meaning "Buxus, box") is found in the writings of Saint Gallus in 886 CE. In 1220 it was mentioned as ''Buchse'' and to distinguish it from Münchenbuchsee, in 1301 it was first mentioned as ''Herzogenbuchze''. It was ruled by Duchy of Burgundy, Burgundy, the Zähringer, the Hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suraj N
Suraj may refer to: People Arts and entertainment *Suraj Jagan, Indian playback singer * Suraj Mani, Indian musical artist *Suraj Sharma (born 1993), Indian actor * Suraj Pawar, Indian actor *Suraj Chavan, Indian actor and internet personality *Suraj Singh Thakuri, Nepali presenter, director and producer *Suraj Venjaramoodu (born 1976), Malayalam film actor and mimicry artist *Suraj (director), Indian director Sport * Suraj Lata Devi (born 1981), former captain of the India women's national hockey team * Suraj Narredu (born 1985), Indian jockey * Suraj Randiv (born 1985), Sri Lankan international cricketer * Suraj Singh (footballer) (active from 2014), Indian footballer * Sodiq Suraj (born 1988), Nigerian football player who currently plays for Prime F.C. Other fields *Suraj Bhan (born 1928), Indian politician *Suraj Bhan (archaeologist) (1931—2010), Indian archaeologist * Suraj N. Gupta (1924–2021), Indian-born American theoretical physicist *Surajmal Jat (1707–1763), rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Physicists
In physics, a quantum (: quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light of a specific frequency (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom. Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact (quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Nuclear Physicists
Swiss most commonly refers to: * the adjectival form of Switzerland *Swiss people Swiss may also refer to: Places *Swiss, Missouri * Swiss, North Carolina * Swiss, West Virginia *Swiss, Wisconsin Other uses * Swiss Café, an old café located in Baghdad, Iraq *Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports *Swiss International Air Lines **Swiss Global Air Lines, a subsidiary *Swissair, former national air line of Switzerland * .swiss alternative TLD for Switzerland See also *Swiss made, label for Swiss products *Swiss cheese (other) *Switzerland (other) *Languages of Switzerland, none of which are called "Swiss" *International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, in graphic design *Schweizer (other), meaning Swiss in German *Schweitzer, a family name meaning Swiss in German *Swisse Swisse is a vitamin, supplement, and skincare brand. Founded in Australia in 1969 and globally headquartered in Melbourne, and was sold to Health & Happin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Oberaargau District
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1992 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912 Births
This year is notable for Sinking of the Titanic, the sinking of the ''Titanic'', which occurred on April 15. In Albania, this leap year runs with only 353 days as the country achieved switching from the Julian to Gregorian Calendar by skipping 13 days. Friday, 30 November ''(Julian Calendar)'' immediately turned Saturday, 14 December 1912 ''(in the Gregorian Calendar)''. Events January * January 1 – The Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China is established. * January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens. * January 6 ** German Geophysics, geophysicist Alfred Wegener first presents his theory of continental drift. ** New Mexico becomes the 47th U.S. state. * January 8 – The African National Congress is founded as the South African Native National Congress, at the Waaihoek Wesleyan Church in Bloemfontein, to promote improved rights for Black people, black South Africans, with Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lillian Hoddeson
Lillian Hartman Hoddeson (born 20 December 1940, in New York City) is an American historian of science, specializing in the history of physics and technology during the 2nd half of the 20th century. Education and career Hoddeson received in 1957 a high school diploma from the Bronx High School of Science, in 1961 a bachelor's degree in physics from Barnard College, and in 1966 a Ph.D. in physics from Columbia University with a dissertation on solid-state physics. She was an assistant professor of physics from 1967 to 1970 at Barnard College and from 1971 to 1976 at Rutgers University. In 1974–1975 she was a visiting fellow at Princeton University and took Thomas Kuhn's "History of Quantum Mechanics" graduate course. From 1977 to 1992 she held various academic positions at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, before becoming there an associate professor from 1993 to 2000 and a full professor from 2000 until her retirement. Since 1978 she has held the position of Fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolf Nevanlinna
Rolf Herman Nevanlinna (né Neovius; 22 October 1895 – 28 May 1980) was a Finnish mathematician who made significant contributions to complex analysis. Background Nevanlinna was born Rolf Herman Neovius, becoming Nevanlinna in 1906 when his father changed the family name. The Neovius-Nevanlinna family contained many mathematicians: Edvard Engelbert Neovius (Rolf's grandfather) taught mathematics and topography at a military academy; Edvard Rudolf Neovius (Rolf's uncle) was a professor of mathematics at the University of Helsinki from 1883 to 1900; Lars Theodor Neovius-Nevanlinna (Rolf's uncle) was an author of mathematical textbooks; and Otto Wilhelm Neovius-Nevanlinna (Rolf's father) was a physicist, astronomer and mathematician. After Otto obtained his Ph.D. in physics from the University of Helsinki, he studied at the Pulkovo Observatory with the German astronomer Herman Romberg, whose daughter, Margarete Henriette Louise Romberg, he married in 1892. Otto and Margarete the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ( ; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli exclusion principle, Pauli Principle". The discovery involved Spin (physics), spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the Matter#Structure, structure of matter. To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, he posited the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi. The neutrino was detected in 1956. Early life Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his Godparent, godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent Jewish families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter. Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the atom as a whole, including its electrons. Discoveries in nuclear physics have led to applications in many fields such as nuclear power, nuclear weapons, nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, industrial and agricultural isotopes, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology. Such applications are studied in the field of nuclear engineering. Particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and the two fields are typically taught in close association. Nuclear astrophysics, the application of nuclear physics to astrophysics, is crucial in explaining the inner workings of stars and the origin of the chemical elements. History The history of nuclear physics as a discipline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Electrodynamics
In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the Theory of relativity, relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomenon, phenomena involving electric charge, electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum mechanics, quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction. In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory (quantum mechanics), perturbation theory of the electromagnetic Quantum vacuum state, quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it "the jewel of physics" for its precision tests of QED, extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |