|
Komaki Dam
The Komaki Dam is an arch-gravity dam on the Shō River about southeast of Shogawa in Toyama Prefecture, Japan. It was constructed between 1925 and 1930. The dam has an associated 90.2 MW hydroelectric Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ... power station which was commissioned in 1930. Of the nine dams on the Shō River, it is the second-furthest downstream. See also * Shogawa Goguchi Dam – downstream * Soyama Dam – upstream References {{Dams in Toyama Prefecture Dams in Toyama Prefecture Arch–gravity dams Dams completed in 1930 Dams on the Shō River Hydroelectric power stations in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogawa, Toyama
was a town located in Higashitonami District, Toyama Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Toyama Prefecture has a population of 993,848 (1 January 2025) and has a geographic area of 4,247.61 km2 (1,640.01 sq mi). Toyama Prefecture borders Ishikawa Prefecture to the ..., Japan. As of 2003, the town had an estimated population of 7,285 and a population density, density of 236.99 persons per km2. The total area was 30.74 km2. On November 1, 2004, Shōgawa was merged into the expanded city of Tonami, Toyama, Tonami. References Dissolved municipalities of Toyama Prefecture Tonami, Toyama {{Toyama-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyama Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Toyama Prefecture has a population of 993,848 (1 January 2025) and has a geographic area of 4,247.61 km2 (1,640.01 sq mi). Toyama Prefecture borders Ishikawa Prefecture to the west, Gifu Prefecture to the south, Nagano Prefecture to the east, and Niigata Prefecture to the northeast. Toyama is the capital and largest city of Toyama Prefecture, with other major cities including Takaoka, Imizu, and Nanto. Toyama Prefecture is part of the historic Hokuriku region, and the majority of the prefecture's population lives on Toyama Bay, one of the largest bays in Japan. Toyama Prefecture is the leading industrial prefecture on the Japan Sea coast and has the advantage of cheap electricity from abundant hydroelectric resources. Toyama Prefecture contains the only known glaciers in East Asia outside of Russia, first recognized in 2012, and 30% of the prefecture's area is designated as national parks. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shō River
The has its source in Mount Eboshi (烏帽子岳 ''Eboshigatake'') in the Shōkawa-chō area of Takayama, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. After flowing for through the northern part of Gifu Prefecture and the western part of Toyama Prefecture, it empties into Toyama Bay. River communities The river passes through or forms the boundary of the communities listed below. The area through which the river flows in Gifu is referred to as Shirakawa-gō, while the area in Toyama is referred to as Gokayama. Both areas are UNESCO World Heritage Sites because of their ''gasshō-zukuri'' houses. ;Gifu Prefecture: : Takayama, Shirakawa ( Ōno District) ;Toyama Prefecture: : Nanto, Tonami, Takaoka, Imizu Tributary *Toga River *Kotori River Dams The river is extensively developed for water storage, flood control and hydroelectric power generation. There are 16 major dams in the basin, seven of them are on tributaries. The major dams collectively have an installed power generation capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tainter Gate
The Tainter gate is a type of radial arm floodgate used in dams and canal locks to control water flow. It is named for its inventor, the Wisconsin structural engineer Jeremiah Burnham Tainter. Tainter, an employee of the lumber firm Knapp, Stout and Co., invented the gate in 1886 for use on the company's dam that forms Lake Menomin in the United States. Description A side view of a Tainter gate resembles a slice of pie with the curved part of the piece facing the source or upper pool of water and the tip pointing toward the destination or lower pool. The curved face or skinplate of the gate takes the form of a wedge section of cylinder. The straight sides of the pie shape, the trunnion arms, extend back from each end of the cylinder section and meet at a trunnion which serves as a pivot point when the gate rotates. Principle Pressure forces on a submerged body act perpendicular to the body's surface. The design of the Tainter gate results in every pressure force acting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
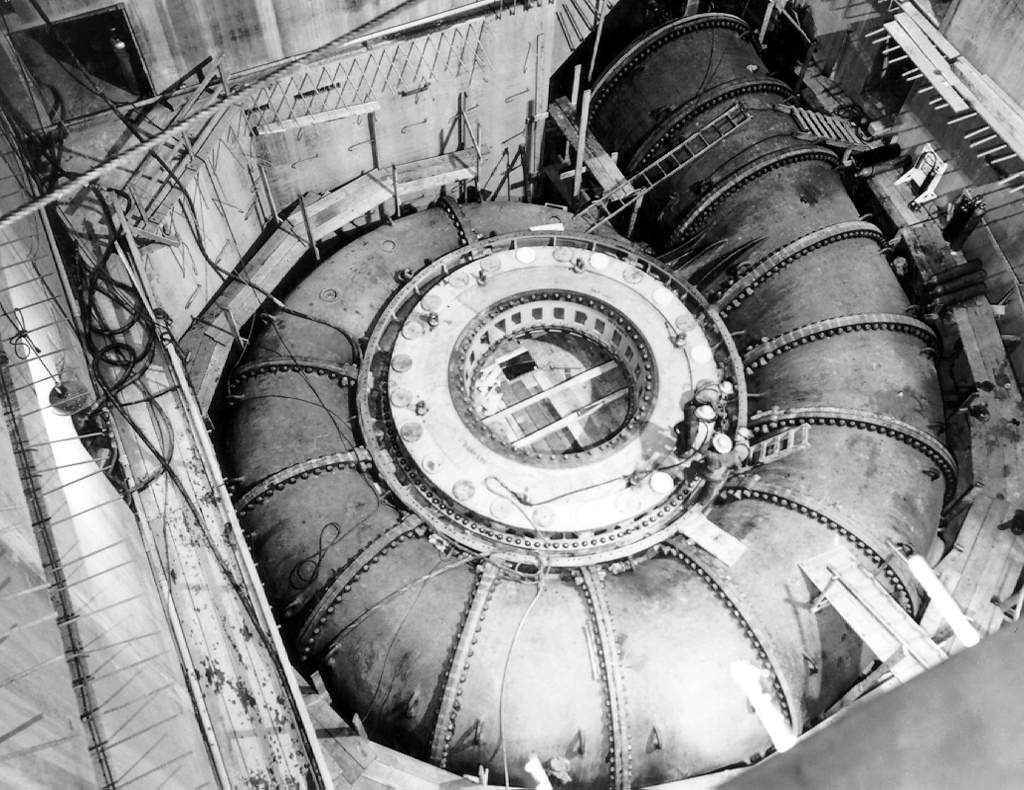
Francis-type
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogawa Goguchi Dam
The Shogawa Goguchi Dam is a gravity dam on the Shō River in Shogawa, Toyama Prefecture, Japan. It was constructed between 1934 and 1939. The dam has an associated 23.4 MW hydroelectric Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ... power station which was commissioned in two stages, December 1939 and March 1967. Of the nine dams on the Shō River it is the furthest downstream. See also * Wadagawa Dam – downstream on a tributary of the Shō River References {{Dams in Toyama Prefecture Dams in Toyama Prefecture Gravity dams Dams completed in 1939 Dams on the Shō River Hydroelectric power stations in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyama Dam
The Soyama Dam is a gravity dam on the Shō River in Soyama village about southeast of Nanto in Toyama Prefecture, Japan. It was constructed between 1927 and 1930. The dam has an associated 128.1 MW hydroelectric Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ... power station which was built in two parts. The first part of the power station (56.1 MW) was commissioned in 1930 and the second part of the power station (72 MW) was commissioned in 1967. Of the nine dams on the Shō River it is the third furthest downstream. See also * Komaki Dam – downstream * Ohara Dam – upstream References {{Dams in Toyama Prefecture Dams in Toyama Prefecture Gravity dams Dams completed in 1930 Dams on the Shō River Hydroelectric power stations in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In Toyama Prefecture
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. Ancient dams were built in Mesopotamia and the Middle East for water control. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. Egyptians also built dams, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |