|
Kolomea
Kolomyia (, ), formerly known as Kolomea, is a city A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ... located on the Prut, Prut River in Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast in the west of Ukraine. It serves as the administrative centre of Kolomyia Raion, hosting the administration of Kolomyia urban hromada. The population is The city rests approximately halfway between Ivano-Frankivsk and Chernivtsi, in the centre of the historical region of Pokuttia, with which it shares much of its history. Kolomyia is a notable railroad hub, as well as an industrial centre (textiles, shoes, metallurgical plant, machine works, wood and paper industry). It is a centre of Hutsul culture. Until 1925 the town was the most populous town in the region. Before the The Holocaust, Holocaust about half the town’s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolomyia 1892
Kolomyia (, ), formerly known as Kolomea, is a city located on the Prut, Prut River in Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast in the west of Ukraine. It serves as the administrative centre of Kolomyia Raion, hosting the administration of Kolomyia urban hromada. The population is The city rests approximately halfway between Ivano-Frankivsk and Chernivtsi, in the centre of the historical region of Pokuttia, with which it shares much of its history. Kolomyia is a notable railroad hub, as well as an industrial centre (textiles, shoes, metallurgical plant, machine works, wood and paper industry). It is a centre of Hutsul culture. Until 1925 the town was the most populous town in the region. Before the The Holocaust, Holocaust about half the town’s population was Jews, Jewish. Etymology The city has alternative names for it in other languages: * ; * ; * ; * . According to Ukrainian etymological dictionaries, the name ''Kolomyia'' is a compound word formed from the roots of the noun ''kolo'' ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast
Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast (), also referred to as Ivano-Frankivshchyna () or simply Frankivshchyna, is an administrative divisions of Ukraine, oblast (region) in western Ukraine. Its administrative center is the city of Ivano-Frankivsk. It has a population of The area, also known as Prykarpattia, was part of the historical region of Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia, where the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia flourished. After World War I, the area became part of the Second Polish Republic and was administered as part of Stanisławów Voivodeship until the invasion of Poland. The area was annexed by the Soviet Union and was known as Stanislav Oblast until 1962, when its administrative center was renamed after the Ukrainian writer Ivan Franko. Kolomyia was a historical center of the oblast and remains a major cultural center of Pokuttia, the traditional name for the southern part of the oblast. Name On November 9, 1962, a decree was issued by the Presidium of the Verkhovna Rada of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
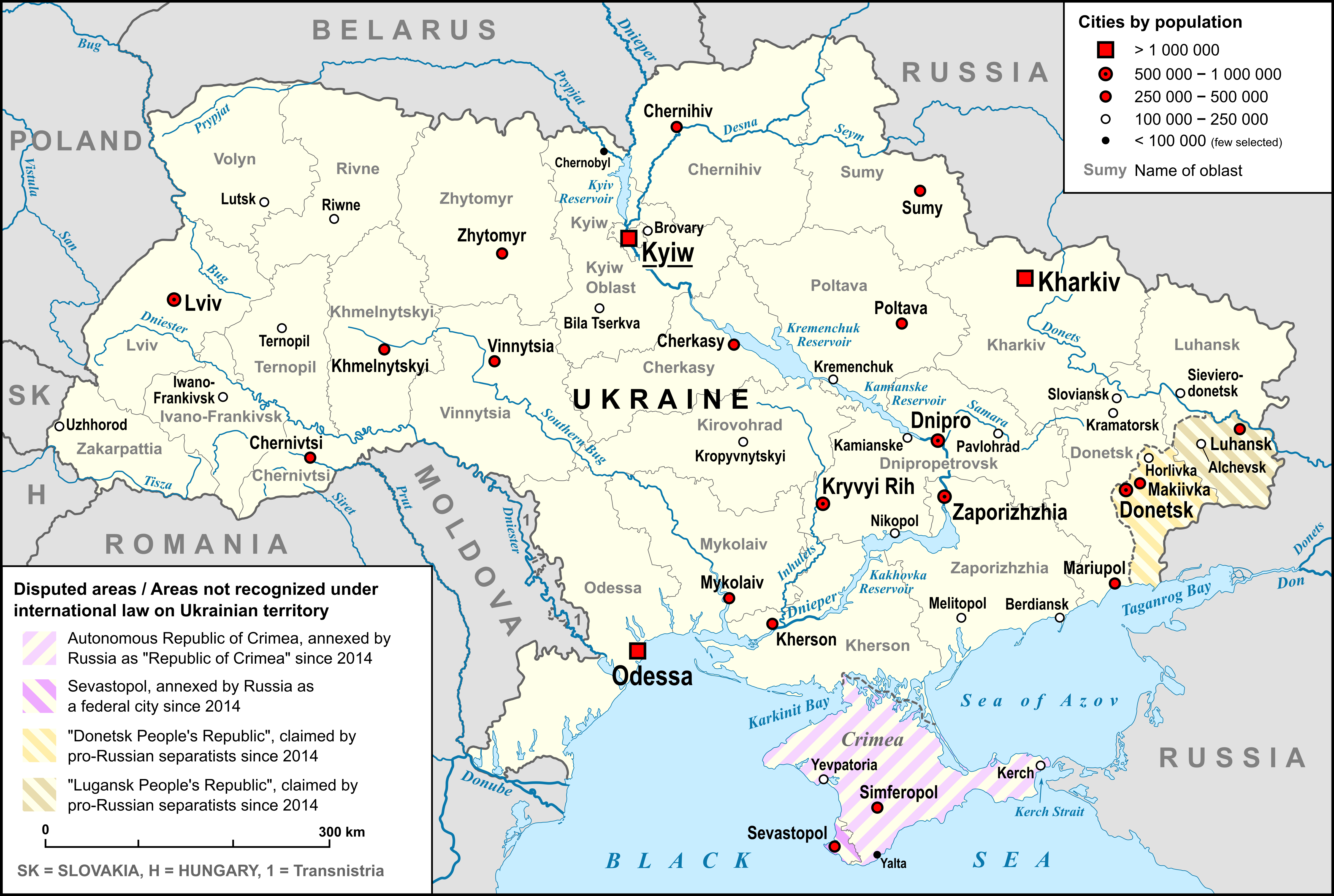
List Of Cities In Ukraine
There are 463 populated places in Ukraine, populated places in Ukraine that have been officially granted city status () by the Verkhovna Rada, the country's parliament, as of 23 April 2025. Settlements with more than 10,000 people are eligible for city status although the status is typically also granted to settlements of historical or regional importance. Smaller settlements are Populated places in Ukraine#Rural settlements, rural settlements () and villages (). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. In the past, cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is roughly ordered by population and the 2022 estimates are compared to the 2001 Ukrainian census, except for Chernobyl for which the population is an unofficial estimate. The City with special status, cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. The average population size is 62,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgical
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals, including the production of metals and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mineral processing, the extraction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boroldai
Boroldai (or Burulday, Borolday), also known as Burundai, (Cyrillic: ''Боролдай'') (died 1263) was a Mongol general of the mid 13th century. He participated in the Mongol invasion of Russia and Europe from 1236 to 1242 and other Mongol raids of Europe until 1263. The clan of Borolday is not clear. He was probably from one of four tribes that Genghis Khan (1162–1227) assigned to his eldest son, Jochi: the Sanchi'ud (or Salji'ud), Keniges, Uushin, and Je'ured clans. Career Serving under Jochi's successor and son, Batu Khan, Borolday's vanguard surprised and crushed the great army of Yuri II, the Grand Prince of Vladimir, at the battle of the Sit River in 1238. He also participated in the Siege of Kiev in 1240. After the conquest of Rus, the Mongols invaded Eastern Europe and parts of Central Europe. His name appears as Bujgai or Bujakh in ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', according to which, Ögedei, Khagan of the Mongol Empire, praised Subutai and Bujgai's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Successor State
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th-century diplomacy. A successor state often acquires a new international legal personality, which is distinct from a continuing state, also known as a continuator or historical heir, which despite changes to its borders retains the same legal personality and possess all its existing rights and obligations (such as a rump state). Partial and universal state succession A state succession can be characterized as either being ''universal'' or ''partial''. A universal state succession occurs when one state is completely extinguished and its sovereignty is replaced by that of one or more successor states. A partial state succession occurs when successor state(s) succeed only part of a state's land and sovereignty, which continues to exist wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,. * was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavs, East Slavic, Norsemen, Norse, and Finnic peoples, Finnic, it was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, founded by the Varangians, Varangian prince Rurik.Kievan Rus , Encyclopædia Britannica Online. The name was coined by Russian historians in the 19th century to describe the period when Kiev was preeminent. At its greatest extent in the mid-11th century, Kievan Rus' stretched from the White Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south and from the River source, headwaters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasion Of Rus'
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered much of Kievan Rus' in the mid-13th century, sacking numerous cities such as Principality of Ryazan, Ryazan, Principality of Yaroslavl, Yaroslavl, Principality of Pereyaslavl, Pereyaslavl and Vladimir-Suzdal, Vladimir, including the largest: Grand Principality of Kiev, Kiev (50,000 inhabitants) and Principality of Chernigov, Chernigov (30,000 inhabitants). The Siege of Kiev (1240), siege of Kiev in 1240 by the Mongols is generally held to mark the end of the state of Kievan Rus', which had already been undergoing Feudal fragmentation, fragmentation. Many other principalities and urban centres in the northwest and southwest escaped complete destruction or suffered little to no damage from the Mongol invasion, including Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, Galicia–Volhynia, Pskov Land, Pskov, Principality of Smolensk, Smolensk, Principality of Polotsk, Polotsk, Principality of Vitebsk, Vitebsk, and probably Vladimir-Suzdal, Rostov and Uglic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galician–Volhynian Chronicle
The ''Galician–Volhynian Chronicle'' (GVC) (, called "Halicz-Wolyn Chronicle" in Polish historiography), also known as ''Chronicle of Halych–Volhynia'' and by other names is a prominent work of Old Ruthenian literature and historiographyKotlyar, M. Galician–Volhynian Chronicle (ГАЛИЦЬКО-ВОЛИНСЬКИЙ ЛІТОПИС)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. 2004 covering 1201–1292 in the history of the Principality of Galicia–Volhynia (in modern Ukraine Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...). Textual witnesses The original chronicle completed in the late 13th century did not survive. The oldest known copy is part of the early 15th-century '' Hypatian Codex'', discovered in the Hypatian Monastery of Kostroma by the Russian historian and essayis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia'' () was a multi-purpose encyclopedia of Ukraine, issued in the USSR. First attempt Following the publication of the first volume of the in Lviv, then in Poland, in 1930, the ''Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia'' (''USE'') was commissioned by Mykola Skrypnyk. During his chairmanship in Kharkiv the editorial board of the ''USE'' was established, enlisting the help of over 100 professionals. Printing began in early 1933, but Moscow censors decried the encyclopedia as being nationalist. Of the 20 planned volumes only three were produced. In the same year Skrypnyk committed suicide, and was succeeded by Volodymyr Zatonsky. The printed copies were destroyed, and plans for the November 1934 edition of USE dissolved. First edition In early 1948, interest in the ''USE'' returned as a response the publication of the '' Encyclopedia of Ukrainian Studies'' by Volodymyr Kubijovyč; an attempt to preserve a Ukrainian national heritage believed to be und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypatian Chronicle
The ''Hypatian Codex'', also known as Hypatian Letopis or Ipatiev Letopis, is a compendium of three Rus' chronicles: the ''Primary Chronicle'', ''Kievan Chronicle'' and '' Galician-Volhynian Chronicle''. It is the most important source of historical data about Kievan Rus'. The language of this work is Old Church Slavonic with many East Slavisms. Provenance The codex was discovered in Ukraine in 1617 by Zacharias Kopystensky, and was then copied by monks in 1621. The codex later known as the ''Hypatian Codex'' was most likely acquired from the Ipatievsky Monastery (Hypatian Monastery) in Kostroma on 15 May 1767. This would have happened during the May–June 1767 Volga voyage of Empress Catherine II (), who was highly interested in reading Rus' chronicles, and collecting them all at the capital city of Saint Petersburg (one of the goals of her voyage). Count Vladimir Grigorievich Orlov (1743–1831), then director of the Academy of Sciences, accompanied the empress on the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |