|
Kola Province
The Kola Province (also known as Kola Block and Kola Domain) is an area of the Fennoscandian Shield spanning an area near the borders of Russia, Finland, and Norway, including the bulk of its namesake Kola Peninsula. The continental crust that makes up the province is a collage of Mesoarchean and Neoarchean age with some lesser amounts being of Paleoproterozoic The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ... age. References Archean geology Geography of the Republic of Karelia Geography of Murmansk Oblast Geology of European Russia Geology of Finland Geology of Norway {{russia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overview Baltic Shield
*
*
{{disambiguation ...
Overview may refer to: * Overview article, an artícle that summarizes the current state of understanding on a topic * Overview map, generalised view of a geographic area See also * Summary (other) * Outline (list) * ''A Brief Overview'' * Overview and Scrutiny * Overview effect The overview effect is a cognitive shift reported by some astronauts while viewing the Earth from space. Researchers have characterized the effect as "a state of awe with self-transcendent qualities, precipitated by a particularly striking visu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoarchean
The Neoarchean (; also spelled Neoarchaean) is the last geologic era in the Archean eon that spans from 2800 to 2500 million years ago—the period being defined chronometrically and not referencing a specific level in a rock section on Earth. The era is marked by major developments in complex life and continental formation. Complex life This era saw the rise of oxygen in the atmosphere after oxygenic photosynthesis evolved as early as the Mesoarchean era. The environmental changes that occurred in the Neoarchean such as its developing atmospheric and soil compositions drastically differentiated the era from others in its encouragement of microbial metabolisms to evolve and diversify. The era could have also seen pre-biotic organic molecules being brought to Earth through meteorites, comets, or through abiotic reactions. The growth of juvenile continental crust as well as the onset of plate tectonics in the Archean allowed for the colonization of a larger variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of European Russia
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Murmansk Oblast
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archean Geology
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic. The Earth during the Archean was mostly a water world: there was continental crust, but much of it was under an ocean deeper than today's ocean. Except for some trace minerals, today's oldest continental crust dates back to the Archean. Much of the geological detail of the Archean has been destroyed by subsequent activity. The earliest known life started in the Archean. Life was simple throughout the Archean, mostly represented by shallow-water microbial mats called stromatolites, and the atmosphere lacked free oxygen. Etymology and changes in classification The word ''Archean'' comes from the Greek word (), meaning 'beginning, origin'. It was first used in 1872, when it meant 'of the earliest geological age'. Before the Hadean Eon was recognized, the Archean sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episodes (journal)
''Episodes'' is the quarterly journal of the International Union of Geological Sciences, published in Seoul, Korea. In circulation since 1978, Episodes is an international and interdisciplinary open access and free, both to submit and download, publication journal that covers all geoscience disciplines. Episodes includes authoritative articles that reflect global research advances, evolving trends in geoscience disciplines and concise reports on the results of international meetings, conferences, and symposia. It is a high visibility journal, and is indexed in Science Citation Index (SCI), Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE; Web of Science), and Journal Citation Reports (JCR)/Science Edition, along with many other databases such as SCOPUS. Submitted manuscripts are peer-reviewed, and a first decision is provided to authors approximately within 30 days after submission. See also * List of scientific journals * List of scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences A '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's geological history. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized. Paleontological evidence suggests that the Earth's rotational rate ~1.8 billion years ago equated to 20-hour days, implying a total of ~450 days per year. Atmosphere Before the enormous increase in atmospheric oxygen, almost all existing lifeforms were anaerobic organisms whose metabolism was based on a form of cellular respiration that did not require oxygen. Free oxygen in large amounts is toxic to most anaerobic organisms. Consequently, most died when the atmospheric free oxygen levels soared in an extinction event called the Great Oxidation Event, which brought atmospheric oxygen levels to up to 10% of their current level. The only creatures that sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoarchean
The Mesoarchean (, also spelled Mesoarchaean) is a geologic era in the Archean Eon, spanning , which contains the first evidence of modern-style plate subduction and expansion of microbial life. The era is defined chronometrically and is not referenced to a specific level in a rock section on Earth. Tectonics The Mesoarchean era is thought to be the birthplace of modern-style plate subduction, based on geologic evidence from the Pilbara craton in western Australia. A convergent margin with a modern-style oceanic arc existed at the boundary between West and East Pilbara approximately 3.12 Ga. By 2.97 Ga, the West Pilbara Terrane converged with and accreted onto the East Pilbara Terrane. A supercontinent, Vaalbara, may have existed in the Mesoarchean. Environmental conditions Analysis of oxygen isotopes in Mesoarchean cherts has been helpful in reconstructing Mesoarchean surface temperatures. These cherts led researchers to draw an estimate of an oceanic temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
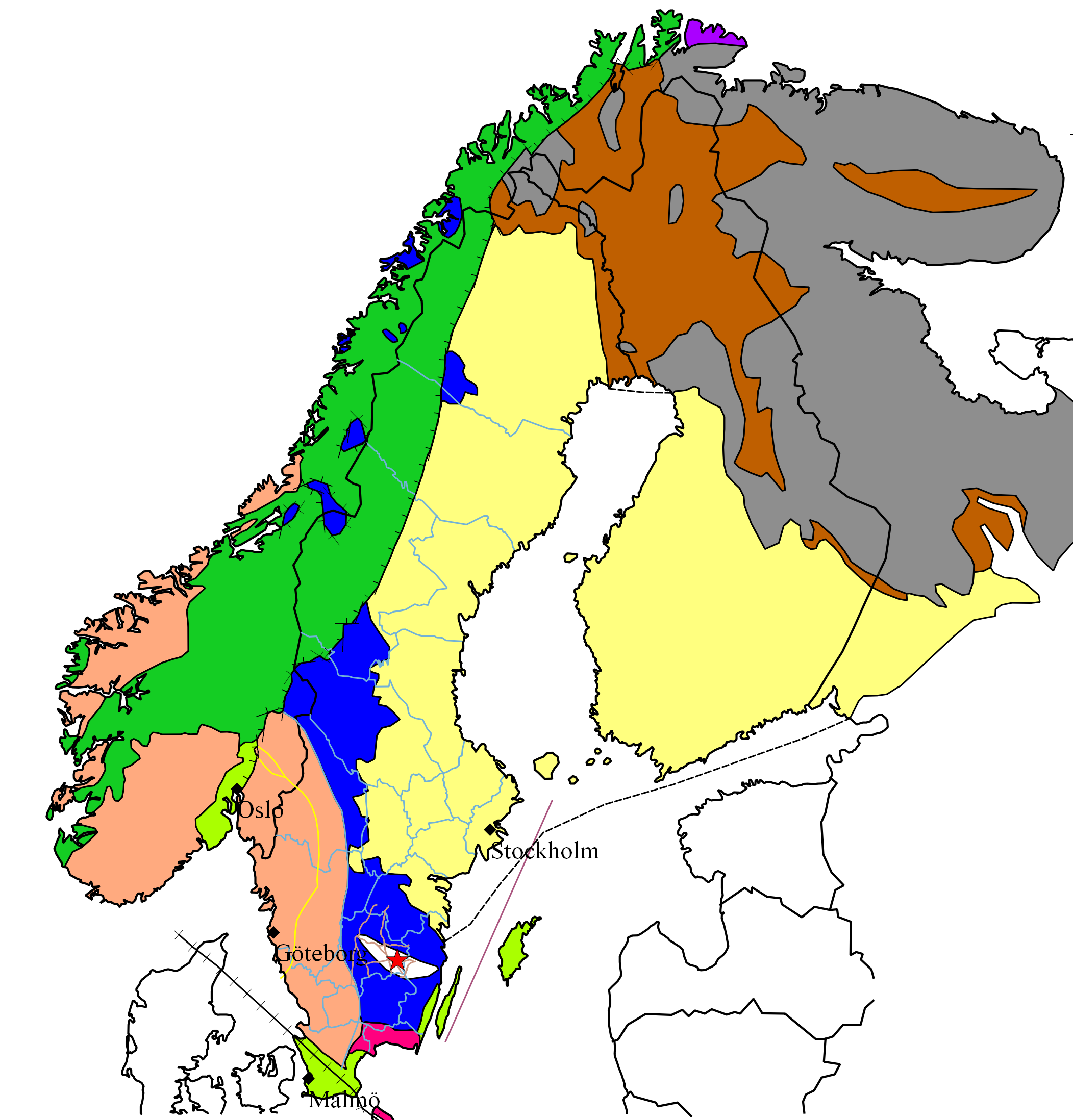
Baltic Shield
The Baltic Shield (or Fennoscandian Shield) is a segment of the Earth's crust belonging to the East European Craton, representing a large part of Fennoscandia, northwestern Russia and the northern Baltic Sea. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstone which have undergone numerous deformations through tectonic activity. It contains the oldest rocks of the European continent with a thickness of 250–300 km. The Baltic Shield is divided into five ''provinces'': the Svecofennian and Sveconorwegian (or Southwestern gneiss) provinces in Fennoscandia, and the Karelian, Belomorian and Kola provinces in Russia. The latter three are divided further into several ''blocks'' and ''complexes'' and contain the oldest of the rocks, at 2500-3100 Ma (million years) old. The youngest rocks belong to the Sveconorwegian province, at 900-1700 Ma old. Thought to be formerly part of an ancient continent, the Baltic Shield grew in size through collisions with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collage (geology)
In geology a collage is a tectonostratigraphy, tectonostratigraphic unit characterized by its heterogeneity in terms of its lithology, rock ages, or both. The term is usually applied to Precambrian tectonostratigraphic units. Collages form by plate tectonics, plate tectonic processes like accretion (geology), accretion and continental collision. Geology {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
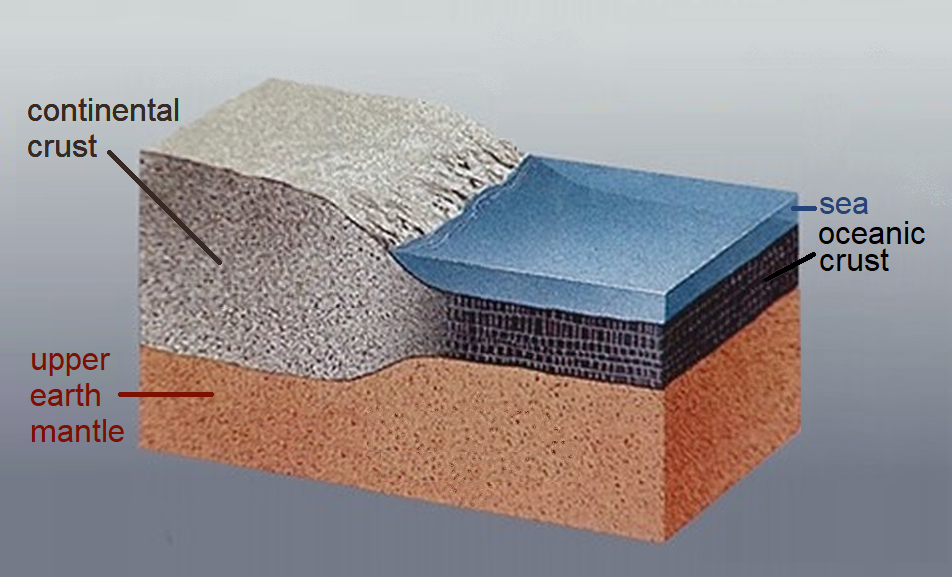
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |