|
Kok Borok
Kokborok (or Tripuri) is a Tibeto-Burman language of the Indian state of Tripura and neighbouring areas of Bangladesh. Its name comes from ''kók'' meaning "verbal" or "language" and ''borok'' meaning "people" or "human", It is one of the ancient languages of Northeast India. History Kokborok was formerly known as Tripuri and Tipra kok, with its name being changed in the 20th century. The names also refer to the inhabitants of the former Twipra kingdom, as well as the ethnicity of its speakers. According to an oral history, Kókborok has been attested since at least the 1st century AD, when the historical record of Tripuri kings began to be written down in a book called the ''Rajratnakar'' or ''Rajmala'', using a script for Kókborok called "Koloma", by the scholar and priest Durlabendra Chantai (also spelled Durlobendra Chontai). In the early 15th century, under the reign of Dharma Manikya I, two Brahmins, Sukreswar and Vaneswar, compiled a ''Rajmala'', translating it into S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of India
Languages of India belong to several list of language families, language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indian people, Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both families together are sometimes known as languages of South Asia, Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino–Tibetan, Kra–Dai languages, Tai–Kadai, Andamanese languages, Andamanese, and a few other minor language families and language isolate, isolates. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the Number of languages by country, second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (Languages of Papua New Guinea, 840). ''Ethnologue'' lists a lower number of 456. Article 343 of the Constitution of India stated that the official language of the Union is Hindi in Devanagari script, with officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhaka Division
Dhaka Division () is an Divisions of Bangladesh, administrative division of Bangladesh. Dhaka serves as the capital city of Dhaka Division, the Dhaka District and Bangladesh. The division remains as a population magnet, and covers an area of 20,508.8 km2 with a population in excess of 44 million, it is one of the fastest growing populous administrative divisions of the world, growing at a rate of 1.94% since prior count, compared with the national average of 1.22%. However, national figures may include data skewing expatriation of male labor force as gender ratio is skewed towards females. Dhaka Division borders every other division in the country except Rangpur Division. It is bounded by Mymensingh Division to the north, Barisal Division to the south, Chittagong Division to the east and south-east, Sylhet Division to the north-east, and Rajshahi Division to the west and Khulna Divisions to the south-west. Etymology The origins of the name Dhaka are uncertain. It may deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma Manikya I
Dharma Manikya I, also known as Dangar Fa, was the Maharaja of Tripura from 1431 to 1462. His reign was notable for its territorial expansions as well as for his religious and cultural contributions. Ascension The eldest of the five sons of his father Maha Manikya, Dharma was not initially intended to inherit the throne. According to court histories, he had originally decided on a monastic life, abandoning material desires and embarking on pilgrimages as an itinerant mendicant. It was while he was visiting the holy city of Benares in 1431 that he received news of his father's death, as well as of the violent struggle for the vacant throne which had ensued among his brothers and the military leaders. The story continues that accompanied by eight Brahmins, Dharma hastened back to Tripura. There he was welcomed by the people and unanimously chosen as the next ruler. Reign Early in Dharma's reign, his territories were invaded by the Sultan of Bengal, Shamsuddin Ahmad Shah, who com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twipra Kingdom
The Twipra Kingdom (), anglicized as Tipperah, was one of the largest historical kingdoms of the Tripuri people in Northeast India. Legend A list of legendary Tripuri kings is given in the Rajmala chronicle, a 15th-century chronicle in Bengali written by the court pandits of Dharma Manikya I (r. 1431). The chronicle traces the king's ancestry to the mythological Lunar Dynasty. Druhyu, the son of Yayati, became king of the land of Kirata and constructed a city named Trivega on the bank of Kapila river. His kingdom was bounded by the river Tairang on the north, Acaranga on the south, Mekhali on the east, Koch and Vanga on the west. The daughter of the King of Hedamba was married to King Trilochona of Trivega. The King of Hedamba, having no heir, made the eldest son of Trilochona the king of his land. After the death of Trilochona, his second son Daksina became King of Tripura. Daksina shared the wealth of the kingdom among his eleven brothers. Being the eldest son of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Of The World's Languages In Danger
The UNESCO ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'' was an online publication containing a comprehensive list of the world's endangered languages. It originally replaced the ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' as a title in print after a brief period of overlap before being transferred to an online-only publication. History In 1992, the International Congress of Linguists (CIPL) meeting in Canada discussed the topic of endangered languages, as a result of which it formed the Endangered Languages Committee. It held an international meeting also in 1992 in Paris to place the topic before the world and initiate action. The meeting was considered important enough to come under the authority of UNESCO. At the instigation of Stephen Wurm the committee resolved to create a research center, the International Clearing House for Endangered Languages (ICHEL) and to publish the UNESCO ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' based on the data it collected, the title being derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Official Languages Of India
, 22 languages have been classified as scheduled languages under the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. There is no national language of India. While the constitution was adopted in 1950, article 343 declared that Hindi would be the official language and English would serve as an additional official language for a period not exceeding 15 years. Article 344(1) defined a set of 14 regional languages which were represented in the Official Languages Commission. The commission was to suggest steps to be taken to progressively promote the use of Hindi as the official language of the country. The Official Languages Act, 1963, which came into effect on 26 January 1965, made provision for the continuation of English as an official language alongside Hindi. History The official languages of British India before independence were English, Hindustani language, Hindustani and Languages of India, other Indian vernaculars, with English being used for purposes at the central leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali–Assamese Script
The Bengali–Assamese script, sometimes also known as Eastern Nagri, is an eastern Brahmic script, primarily used today for the Bengali and Assamese language spoken in eastern South Asia. It evolved from Gaudi script, also the common ancestor of the Odia and Trihuta scripts. It is commonly referred to as the ''Bengali script'' by Bengalis and the ''Assamese script'' by the Assamese, while in academic discourse it is sometimes called ''Eastern-Nāgarī''. Three of the 22 official languages of the Indian Republic— Bengali, Assamese, and Meitei—commonly use this script in writing; Bengali is also the official and national language of Bangladesh. Besides, Bengali and Assamese languages, it is also used to write Bishnupriya Manipuri, Meitei, Chakma, Santali and numerous other smaller languages spoken in eastern South Asia. Historically, it was used to write various Old and Middle Indo-Aryan languages, and, like many other Brahmic scripts, is still used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boro–Garo Languages
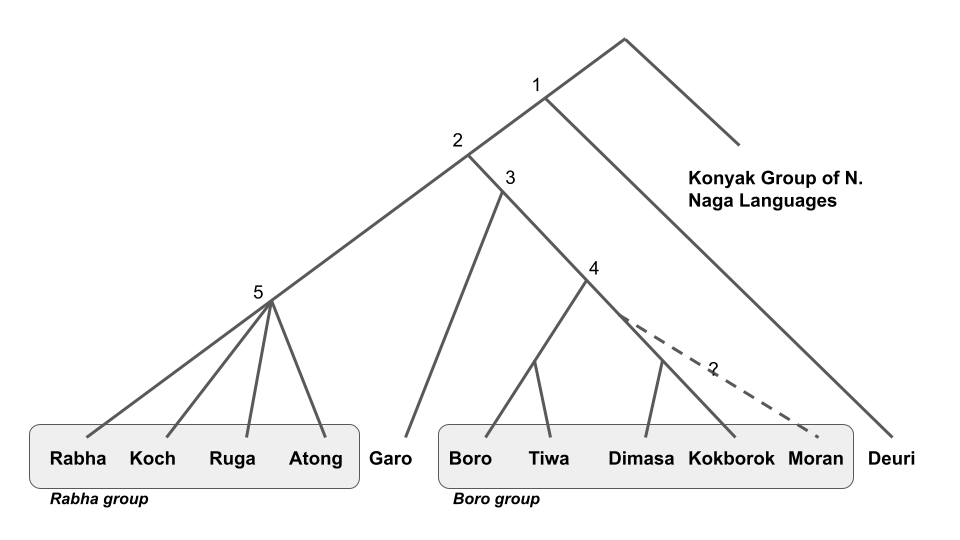
The Boro–Garo languages are a branch of Sino-Tibetan languages, spoken primarily in Northeast India and parts of Bangladesh. The Boro–Garo languages form four groups: Boro, Garo, Koch and Deori. Boro–Garo languages were historically very widespread throughout the Brahmaputra Valley and in what are now the northern parts of Bangladesh, and it is speculated that the proto-Boro-Garo language was the lingua franca of the Brahmaputra valley before it was replaced by Assamese, to which it has made major contributions. Branches The Boro-Garo languages were identified in the Grierson's Language Survey of India, and the names of the languages and their modern equivalents are given below in the table. Sub groups The Boro-Garo languages have been further divided into four subgroups by Burling. *Koch languages: Atong, Koch, Ruga, Rabha * Garo languages: Garo, Megam *Bodo languages: Bodo, Dimasa, Barman, Tiwa, Kokborok (Tripuri), Kachari, Moran * Deori language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sal Languages
The Sal languages, also known as the Brahmaputran languages, are a branch of Tibeto-Burman languages spoken in northeast India, as well as parts of Bangladesh, Myanmar (Burma), and China. Alternative names ''Ethnologue'' calls the group "Jingpho–Konyak-Garo–Bodo", while Scott DeLancey (2015) refers to it as "Bodo-Konyak-Garo-Jinghpaw" (BKJ). Glottolog lists this branch as �Brahmaputran (brah1260)��, as the languages occur around the Brahmaputra Valley. Classification within Sino-Tibetan Scott DeLancey (2015)DeLancey, Scott. 2015. "Morphological Evidence for a Central Branch of Trans-Himalayan (Sino-Tibetan)." ''Cahiers de linguistique - Asie oriental'' 44(2):122-149. December 2015. considers the Sal languages, which he refers to as Garo-''Bodo-Konyak-Jinghpaw'' (BKJ), to be part of a wider Central Tibeto-Burman group. Internal classification noted that the Bodo–Garo, Konyak, and Jingpho (Kachin) languages, as well as the extinct Chairel language, shared distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tibeto-Burman Languages
Central Tibeto-Burman or Central Trans-Himalayan is a proposed branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family proposed by Scott DeLancey (2015) on the basis of shared morphological evidence. DeLancey (2018)DeLancey, Scott (2018). ''Internal and external history of the Central branch of Tibeto-Burman/Trans-Himalayan''. Paper presented at the 28th Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society, held May 17-19, 2018 in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. considers Central Tibeto-Burman to be a linkage rather than a branch with a clearly nested internal structure. DeLancey's Central Tibeto-Burman group includes many languages in Matisoff's (2015: 1123–1127)Matisoff, James A. 2015''The Sino-Tibetan Etymological Dictionary and Thesaurus'' Berkeley: University of California.PDF proposed Northeast Indian areal group, which includes Tani, Deng (Digaro), “ Kuki-Chin–Naga”, Meitei, Mikir, Mru, and Sal. Languages DeLancey considers there to be strong morphological evidence for the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |