|
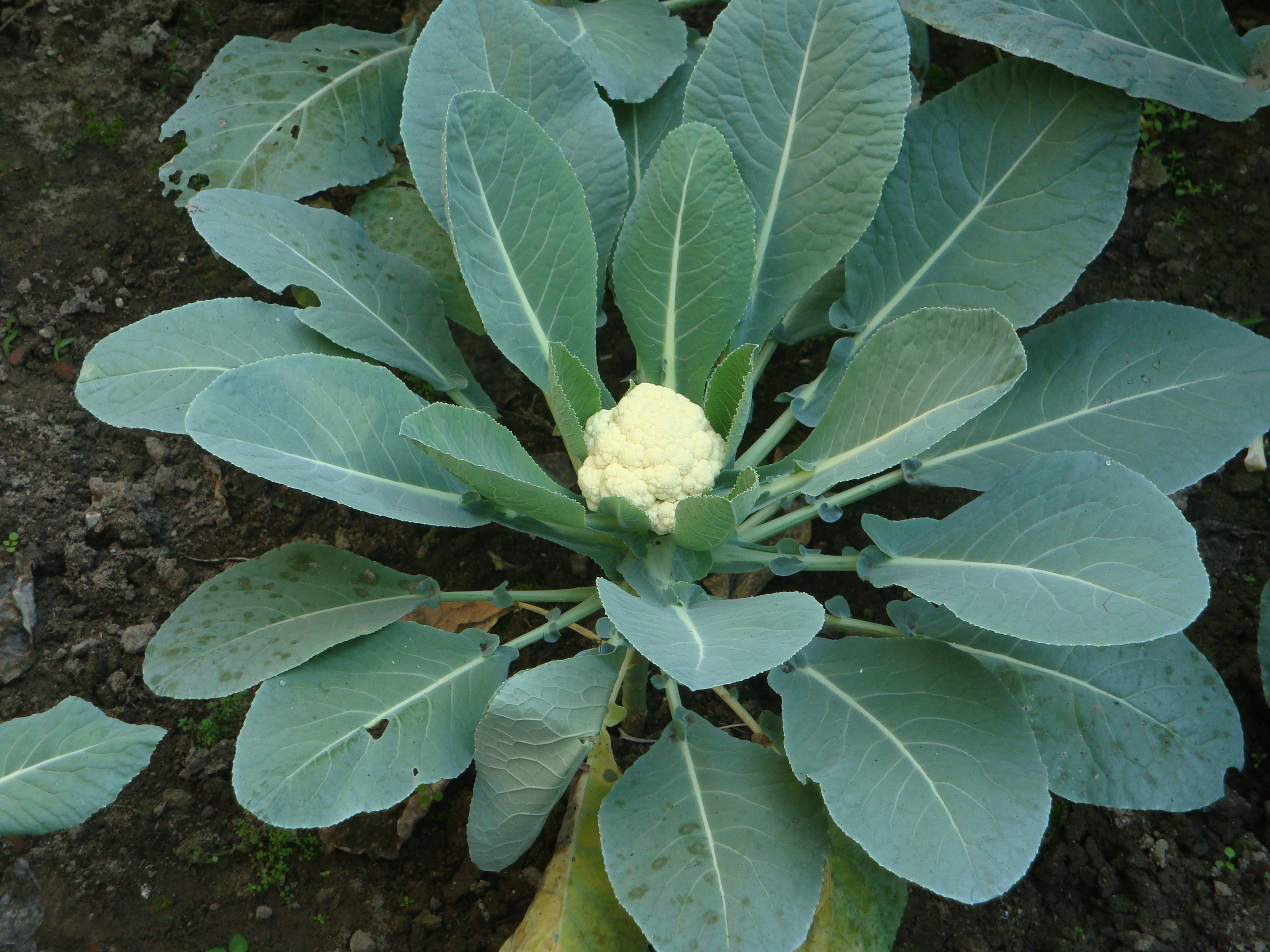
Kohlrabi
Kohlrabi (; pronounced in English; scientific name ''Brassica oleracea'' Gongylodes Group (horticulture), Group), also called German turnip or turnip cabbage, is a Biennial plant, biennial vegetable, a low, stout cultivar of wild cabbage. It is a cultivar of the same species as cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, collard greens, Savoy cabbage, and gai lan. It can be raw foodism, eaten raw or cooked. Edible preparations are made with both the stem and the leaves. Despite its common names, it is not the same species as turnip, although both are in the genus ''Brassica''. Etymology The name comes from the German language, German ("cabbage") plus ''Rübe'' ~ ''Rabi'' (Swiss German variant) ("turnip"), because the swollen stem resembles the latter. Its Group (horticulture), Group name Gongylodes (or lowercase and italicized ''gongylodes'' or ''gongyloides'' as a variety (botany), variety name) means "roundish" in Greek, from (, 'round'). History The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brassica Oleracea
''Brassica oleracea'', also known as wild cabbage in its uncultivated form, is a plant of the family Brassicaceae. The species originated from feral populations of related plants in the Eastern Mediterranean, where it was most likely first cultivated. It has many common cultivars used as vegetables, including cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprout, Collard (plant), collard, Savoy cabbage, kohlrabi, and gai lan. Description Wild ''B. oleracea'' is a tall biennial plant, biennial or perennial plant that forms a stout Rosette (botany), rosette of large leaves in the first year. The grayish-green leaves are fleshy and thick, helping the plant store water and nutrients in difficult environments. In its second year, a woody spike grows up to tall, from which branch off stems with long clusters of yellow four-petaled flowers. Taxonomy Origins According to the Triangle of U theory, ''B. oleracea'' is very closely related to five other species of the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , ,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no #Conventions, defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others; ) is any of the Alemannic German, Alemannic dialects spoken in the German-speaking Switzerland, German-speaking part of Switzerland, and in some Alps, Alpine communities in Northern Italy bordering Switzerland. Occasionally, the Alemannic dialects spoken in other countries are grouped together with Swiss German as well, especially the dialects of Liechtenstein and Austrian Vorarlberg, which are closely associated to Switzerland's. Linguistically, Alemannic is divided into Low Alemannic German, Low, High Alemannic German, High and Highest Alemannic German, Highest Alemannic, varieties all of which are spoken both inside and outside Switzerland. The only exception within German-speaking Switzerland is the municipality of Samnaun, where a Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect is spoken. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper In Biology
Copper is an essential trace element that is vital to the health of all living things (plants, animals and microorganisms). In humans, copper is essential to the proper functioning of organs and metabolic processes. Also, in humans, copper helps maintain the nervous system, immune system, brain development, and activates genes, as well as assisting in the production of connective tissues, blood vessels, and energy. The human body has complex homeostatic mechanisms which attempt to ensure a constant supply of available copper, while eliminating excess copper whenever this occurs. However, like all essential elements and nutrients, too much or too little nutritional ingestion of copper can result in a corresponding condition of copper excess or deficiency in the body, each of which has its own unique set of adverse health effects. Daily dietary standards for copper have been set by various health agencies around the world. Standards adopted by some nations recommend different copp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Vitamin C may be taken by mouth or by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Various health claims exist on the basis that moderate vitamin C deficiency increases disease risk, such as for the common cold, cancer or COVID-19. There are also claims of benefits from vitamin C supplementation in excess of the recommended d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Value
In the U.S. and Canada, the Reference Daily Intake (RDI) is used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products to indicate the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy individuals in every demographic in the United States. While developed for the US population, it has been adopted by Canada. The RDI is used to determine the Daily Value (DV) of foods, which is printed on nutrition facts labels (as %DV) in the United States and Canada, and is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and by Health Canada, respectively. The labels "high", "rich in", or "excellent source of" may be used for a food if it contains 20% or more of the DV. The labels "good source", "contains", or "provides" may be used on a food if it contains between 10% and 20% of the DV, and "low source" applies if the %DV is 5% or lower. The Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) were a set of nutrition recommenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius (or one kelvin). The small calorie or gram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to cause the same increase in one milliliter of water. Thus, 1 large calorie is equal to 1,000 small calories. In nutrition and food science, the term ''calorie'' and the symbol ''cal'' may refer to the large unit or to the small unit in different regions of the world. It is generally used in publications and package labels to express the energy value of foods in per serving or per weight, recommended dietary caloric intake, metabolic rates, etc. Some authors recommend the spelling ''Calorie'' and the symbol ''Cal'' (both with a capital C) if the large calorie is meant, to avoid confusion; however, this convention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein (nutrient)
Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body. They are one of the constituents of Tissue (biology), body tissue and also serve as a Fuel, fuel source. As fuel, proteins have the same energy density as carbohydrates: 17 Joule, kJ (4 Calories, kcal) per gram. The defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid composition. Proteins are polymer chains made of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. During human digestion, proteins are broken down in the stomach into smaller polypeptide chains via hydrochloric acid and protease actions. This is crucial for the absorption (small intestine), absorption of the essential amino acids that cannot be biosynthesized by the body. There are nine essential amino acids that humans must obtain from their diet to prevent protein–energy malnutrition, protein-energy malnutrition and resulting death. They are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroponic
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water-based mineral nutrient solutions in an artificial environment. Terrestrial or aquatic plants may grow freely with their roots exposed to the nutritious liquid or the roots may be mechanically supported by an inert medium such as perlite, gravel, or other substrates. Despite inert media, roots can cause changes of the rhizosphere pH and root exudates can affect rhizosphere biology and physiological balance of the nutrient solution when secondary metabolites are produced in plants. Transgenic plants grown hydroponically allow the release of pharmaceutical proteins as part of the root exudate into the hydroponic medium. The nutrients used in hydroponic systems can come from many different organic or inorganic sources, including fish excrement, duck manure, purchased chemical fertilizers, or artificial standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels Sprout
The Brussels sprout is a member of the Gemmifera cultivar group of cabbages (''Brassica oleracea''), grown for its edible buds. Etymology Though native to the Mediterranean region with other cabbage species, Brussels sprouts first appeared in northern Europe during the 5th century; they were later cultivated in the 13th century near Brussels, Belgium, from which their name derives. The group name Gemmifera (or lowercase and italicized ''gemmifera'' as a variety name) means "bud-bearing". Description The leaf vegetables are typically in diameter and resemble miniature cabbages. Cultivation History Predecessors to modern Brussels sprouts were probably cultivated in Ancient Rome. Brussels sprouts as they are now known were grown possibly as early as the 13th century in what is now Belgium. The first written reference dates to 1587. During the 16th century, they enjoyed a popularity in the southern Netherlands that eventually spread throughout the cooler parts of Northern E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |