|
Kock (biologist)
Kock is a town in eastern Poland, about north of Lublin and south-east of Warsaw. It lies in Lublin Voivodeship, in Lubartów County. It is the capital of the administrative district Gmina Kock. Historically Kock belongs to the Polish province of Lesser Poland and is located in its northeastern corner. , its population numbered 3,509. Name and location Kock is located a few kilometers north of the Wieprz river, approximately 150 meters above sea level, near the ''Łuków Lowland'' (''Równina Łukowska''). In 1952–1954 it was the seat of Gmina Białobrzegi. The town first appears in chronicles in 1258 as ''Cocsk''. In the 15th century, it was called ''Kocsko'' or ''Koczsko'', and in 1787, its name was spelled ''Kocko''. Current form has been in use since the 19th century, and the word Kock either comes from the last name or a nickname ''Kot'' (a person named so founded the town), or from a plant called kocanka ( Helichrysum arenarium), which grows abundantly in the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The administrative divisions of Poland, Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 subdivisions of the Polish People's Republic, former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło ()He is known under a number of names: lt, Jogaila Algirdaitis; pl, Władysław II Jagiełło; be, Jahajła (Ягайла). See also: Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło. was Grand Duke of Lithuania (1377–1434) and then King of Poland (1386–1434), first alongside his wife Jadwiga until 1399, and then sole ruler of Poland. Born a pagan, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and was baptized as Władysław in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His own reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-five years, and laid the foundation for the centuries-long Polish–Lithuanian union. He was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty in Poland that bears his name and was previously also known as the Gediminid dynasty in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Square
The market square (or sometimes, the market place) is a square meant for trading, in which a market is held. It is an important feature of many towns and cities around the world.The World's Best Squares PPS website, Making Places, December 2005 A market square is an open area where s are traditionally set out for trading, commonly on one particular day of the week known as ''market day''. A typical market square consists of a square or rectangular area, or sometimes just a widening of the main street. It is usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapieha Family
The House of Sapieha (; be, Сапега, ''Sapieha''; lt, Sapiega) is a Polish-Lithuanian noble and magnate family of Lithuanian and Ruthenian origin,Энцыклапедыя ВКЛ. Т.2, арт. "Сапегі" descending from the medieval boyars of Smolensk and Polotsk. Vernadsky, George. ''A History of Russia''. New Haven. Connecticut: Yale University Press. 1961online/ref> The family acquired great influence and wealth in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the 16th century. History The first confirmed records of the Sapieha family date back to the 15th century, when Semen Sopiha ( be, Сямён Сапега) was mentioned as a writer (scribe) of the then King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, Casimir IV Jagiellon ( pl, Kazimierz IV Jagiellończyk) for the period of 1441–49. Semen had two sons, Bohdan and Iwan. Possibly, the family of Semen Sopiha owned the village of Sopieszyno near Gdansk, which they left because of the Teutonic invasion. Sopies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many Proto-Protestantism, earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the ''Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firlej Family
Firlej (plural: Firlejowie) was a Polish szlachta (nobility) family. Magnates in the 15th and 17th century. History According to Kasper Niesiecki, Ostafi of Lewart coat of arms came from Franconia, Germany, to Poland, in 1317, to serve Polish king Władysław Łokietek. He was nicknamed Firlej, and the name became his family name. From the 15th to 17th centuries, the Firlej family was a powerful magnate family in the Lesser Poland (''Małopolska'') region. A branch of the family became a vocal supporter of Protestantism in Poland. The family became extinct in the 18th century. Notable members * Piotr Firlej z Dąbrowicy (died 1499), judge and notary of Lublin, married to Jadwiga Osmólska h. Bończa ** Mikołaj Firlej (died 1526), Great Hetman of the Crown, married to Anna z Mielca h. Gryf ***Piotr Firlej (died 1553), voivode of Ruthenia, married Katarzyna Tęczyńska h. Topór **** Jan Firlej (1521-1571), Grand Marshal of the Crown, married Barbara Mniszech h. Mniszech, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandomierz Voivodeship
Sandomierz Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo Sandomierskie, la, Palatinatus Sandomirensis) was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Poland region. Originally Sandomierz Voivodeship also covered the area around Lublin, but in 1474 its three eastern counties were organized into Lublin Voivodeship. In the 16th century, it had 374 parishes, 100 towns and 2586 villages. The voivodeship was based on the Sandomerz '' ziemia'', which earlier was the Duchy of Sandomierz. The Duchy of Sandomierz was created in 1138 by King Bolesław III Wrymouth, who in his testament divided Poland into five principalities. One of them, with the capital at Sandomierz, was assigned to Krzywousty's son, Henry of Sandomierz. Later on, with southern part of the Seniorate Province (which emerged into the Duchy of Krakow), the Duchy of Sandomierz created Lesser Poland, divided into Kraków and Sandomierz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the medieval rulers of the Romanian-inhabited states and of governors and military commanders of Hungarian, Balkan or some Slavic-speaking populations. In the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, ''voivode'' was interchangeably used with '' palatine''. In the Tsardom of Russia, a voivode was a military governor. Among the Danube principalities, ''voivode'' was considered a princely title. Etymology The term ''voivode'' comes from two roots. is related to warring, while means 'leading' in Old Slavic, together meaning 'war leader' or 'warlord'. The Latin translation is for the principal commander of a military force, serving as a deputy for the monarch. In early Slavic, ''vojevoda'' meant the , the military leader in battle. The term has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders. Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military commander in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from the 16th to 18th centuries. Throughout much of the history of Romania and the Moldavia, hetmans were the second-highest army rank. In the modern Czech Republic the title is used for regional governors. Etymology The term ''hetman'' was a Polish borrowing, probably from the German – captain or a borrowing of the comparable Turkic title '' ataman'' (literally 'father of horsemen'). Hetmans of Poland and Lithuania The Polish title ''Grand Crown Hetman'' ( pl, hetman wielki koronny) dates from 1505. The title of ''Hetman'' was given to the leader of the Polish Army. Until 1581 the hetman position existed only during specific campaigns and wars. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikołaj Firlej (?-1526) , voivode of Sandomierz (wojewoda sandomierski)
{{hndis, Firlej, Mikolaj ...
Mikołaj Firlej may refer to several members of the Firlej family: * Mikołaj Firlej (?-1526), hetman, voiode of Sandomierz (wojewoda sandomierski) * Mikołaj Firlej (?-1588), voivode of Lublin (wojewoda lubelski) * Mikołaj Firlej (?-1601), voivode of Kraków (wojewoda krakowski), Grand Marshal of the Crown * Mikołaj Firlej (1588-1635) Mikołaj Firlej may refer to several members of the Firlej family: * Mikołaj Firlej (?-1526), hetman, voiode of Sandomierz (wojewoda sandomierski) * Mikołaj Firlej (?-1588), voivode of Lublin (wojewoda lubelski) * Mikołaj Firlej (?-1601) Mikoła ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Poland Province Of The Polish Crown
Lesser Poland Province ( pl, Prowincja małopolska, la, Polonia Minor) was an administrative division of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1795 and the biggest province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The name of the province comes from historic land of Lesser Poland. The name of the province did not imply its size, but rather seniority. It had two administrative seats one Sudova Vyshnia for Ruthenian lands, and another Nowe Miasto Korczyn for Polonian lands. The province consisted of 11 voivodeships and one duchy (see below). Polish historian Henryk Wisner in his 2002 book ''Rzeczpospolita Wazów. Czasy Zygmunta III i Władysława IV'' writes that it is not known when lands of the Polish Crown were divided into the two provinces: "Parallel to the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, provinces existed, which should be called Sejm provinces, as they became visible during its sessions; mostly during election of the Marsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lublin Voivodeship (1474–1795)
Lublin Voivodeship ( la, Palatinatus Lublinensis; pl, Województwo Lubelskie) was an administrative region of the Kingdom of Poland created in 1474 out of three eastern counties of Sandomierz Voivodeship and lasting until the Partitions of Poland in 1795. Together with Sandomierz Voivodeship and Kraków Voivodeship, it was part of historic Lesser Poland (see Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown). Lublin Voivodeship had two senators in the Senate of the Kingdom of Poland: the Voivode and the Castellan of Lublin. Local sejmiks took place in Lublin. The entire area of the voivodeship was located east of the Vistula river, and its boundaries did not change from the time of its creation (1474), until its dissolution by Austrian authorities in 1795, after the third and final partition of Poland. After 1795, the entire Lublin Voivodeship became part of Austrian province of West Galicia. In 1809, former Lublin Voivodeship was annexed by the Duchy of Warsaw (since 1815 – Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
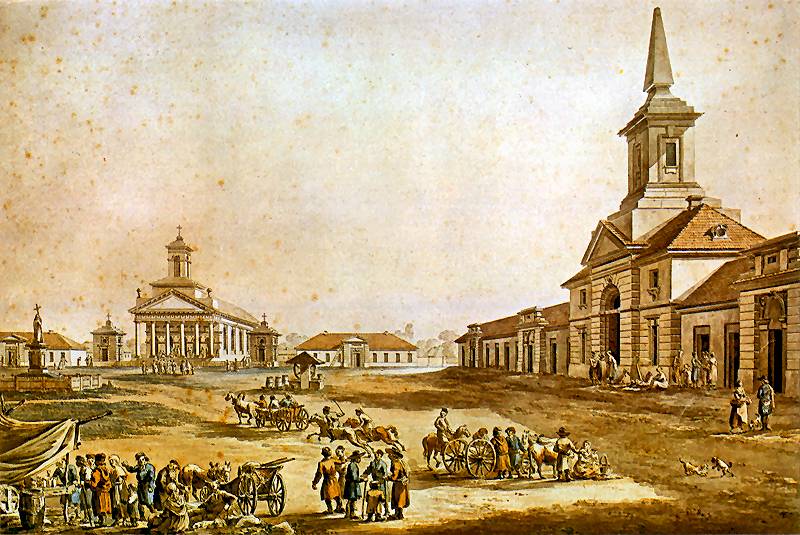

.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)
.png)
