|
Knob-scaled Lizard
Xenosauridae is a family of anguimorph lizards whose only living representative is the genus ''Xenosaurus'', which is native to Central America. Xenosauridae also includes the extinct genera ''Exostinus'' and '' Restes''. Also known as knob-scaled lizards, they have rounded, bumpy scales and osteoderms. Most living species prefer humid, rocky habitats, although they are widespread within their native regions, with some inhabiting semi-arid scrub environments. They are carnivorous or insectivorous, and give birth to live young. ''Shinisaurus'', the Chinese crocodile lizard, was once also regarded as a member of Xenosauridae, but most recent studies of the evolutionary relationships of anguimorphs consider ''Shinisaurus'' to be more closely related to monitor lizards and helodermatids than to ''Xenosaurus''. Xenosauridae is part of a larger clade or evolutionary grouping called Carusioidea, which, in addition to xenosaurids, includes the extinct genus ''Carusia ''Carusia'' is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenosaurus Platyceps
''Xenosaurus platyceps'', the flathead knob-scaled lizard, is a lizard found in the Sierra Madre Oriental of Mexico. Its natural habitat is dry scrub forest and oak savanna. The species is endangered due to habitat fragmentation for the development of tourism and agriculture as well as predation by feral cats. Currently, the flathead knob-scaled lizard does not live in a protected area. Temperature plays a large part in growth rates of Xenosaurus Platyceps along with genetic factors. It has been found that the flathead knob-scaled lizards living in lower elevation, in a more tropical environment, grow virtually twice as fast as those from higher elevations, in a more temperate environment. References Xenosauridae Reptiles described in 1968 Endemic reptiles of Mexico Fauna of the Sierra Madre Oriental {{lizard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinisaurus
The Chinese crocodile lizard (''Shinisaurus crocodilurus'') is a semiaquatic anguimorph lizard found only in cool forests in southeastern China and northeastern Vietnam. The Chinese crocodile lizard spends much of its time in shallow water or in overhanging branches and vegetation, where it hunts its prey of insects, snails, tadpoles, and worms. Individuals in captivity may be fed baby mice.Chinese Crocodile Lizard (''Shinisaurus crocodilurus''). The Sacramento Zoological Society. A rare and little-studied lizard, it is listed in Appendix II, which regulates international trade of specimens. This is the only species in the |
Taxa Named By Edward Drinker Cope
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard Families
This is a list of the extant lizard families. Lizards are an paraphyly, informal group of Squamata, squamates. Taxonomy There are five infraorders which separate the lizards, these are- Diploglossa, Gekkota, Iguania, Platynota and Scincomorpha. This separation is based mainly on morphological similarities between family groups. The Diploglossans and Platynotans are two closely related infraorders which are very diverse families. Very few generalisations can be placed upon these families morphologically. Many species are limbless, while others have fully formed limbs. It is believed that these lizards are the closest lizard relation to the snakes. The Gekkotans are the second most diverse group of lizards. They can be morphologically distinguished by the absence of temporal arches, which allows greater moveability of the head. Most species also have cloacal sacs and fixed eyelids. The Iguanians are another diverse group of lizards. All iguanians are fully limbed. Most species amb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenosauridae
Xenosauridae is a family of anguimorph lizards whose only living representative is the genus '' Xenosaurus'', which is native to Central America. Xenosauridae also includes the extinct genera '' Exostinus'' and '' Restes''. Also known as knob-scaled lizards, they have rounded, bumpy scales and osteoderms. Most living species prefer humid, rocky habitats, although they are widespread within their native regions, with some inhabiting semi-arid scrub environments. They are carnivorous or insectivorous, and give birth to live young. '' Shinisaurus'', the Chinese crocodile lizard, was once also regarded as a member of Xenosauridae, but most recent studies of the evolutionary relationships of anguimorphs consider ''Shinisaurus'' to be more closely related to monitor lizards and helodermatids than to ''Xenosaurus''. Xenosauridae is part of a larger clade In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is compose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carusia
''Carusia'' is an extinct genus of lizards from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It is a close relative of the family Xenosauridae, which includes living knob-scaled lizards. Fossils of the type and only species ''Carusia intermedia'' come from the late-Campanian age Barun Goyot Formation and have been found in the Flaming Cliffs, Ukhaa Tolgod, and Kheerman Tsav fossil localities. ''Carusia'' was first described in 1985 under the name ''Carolina intermedia'', but since the name ''Carolina'' was preoccupied by a genus of scarab beetles that had been named in 1880, it was renamed ''Carusia intermedia''. ''Carusia'' had initially been known from fragmentary skull material, complicating efforts to determine its evolutionary relationships with other lizards; it had variously been described as an indeterminate scincomorph, a xenosaurid, or some other type of autarchoglossan lizard convergent with xenosaurids. However, the discovery of 35 complete skulls in the 1990s, three of whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carusioidea
Carusioidea is a clade of lizards that includes the family Xenosauridae (knob-scaled lizards) from Central America and the extinct genus '' Carusia'' from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It was named in 1998 after a sister-group relationship was found between ''Carusia'' and Xenosauridae. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that Carusioidea is the most basal clade within Anguimorpha. Features that help define Carusioidea include closely spaced orbits or eye sockets separated by fused frontal bones, a connection between the jugal and squamosal bones below the supratemporal arch, and a covering of bony osteoderms over the skull roof. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ... showing the phylogenetic relationships of carusioids from Gao and Norell (1998): ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
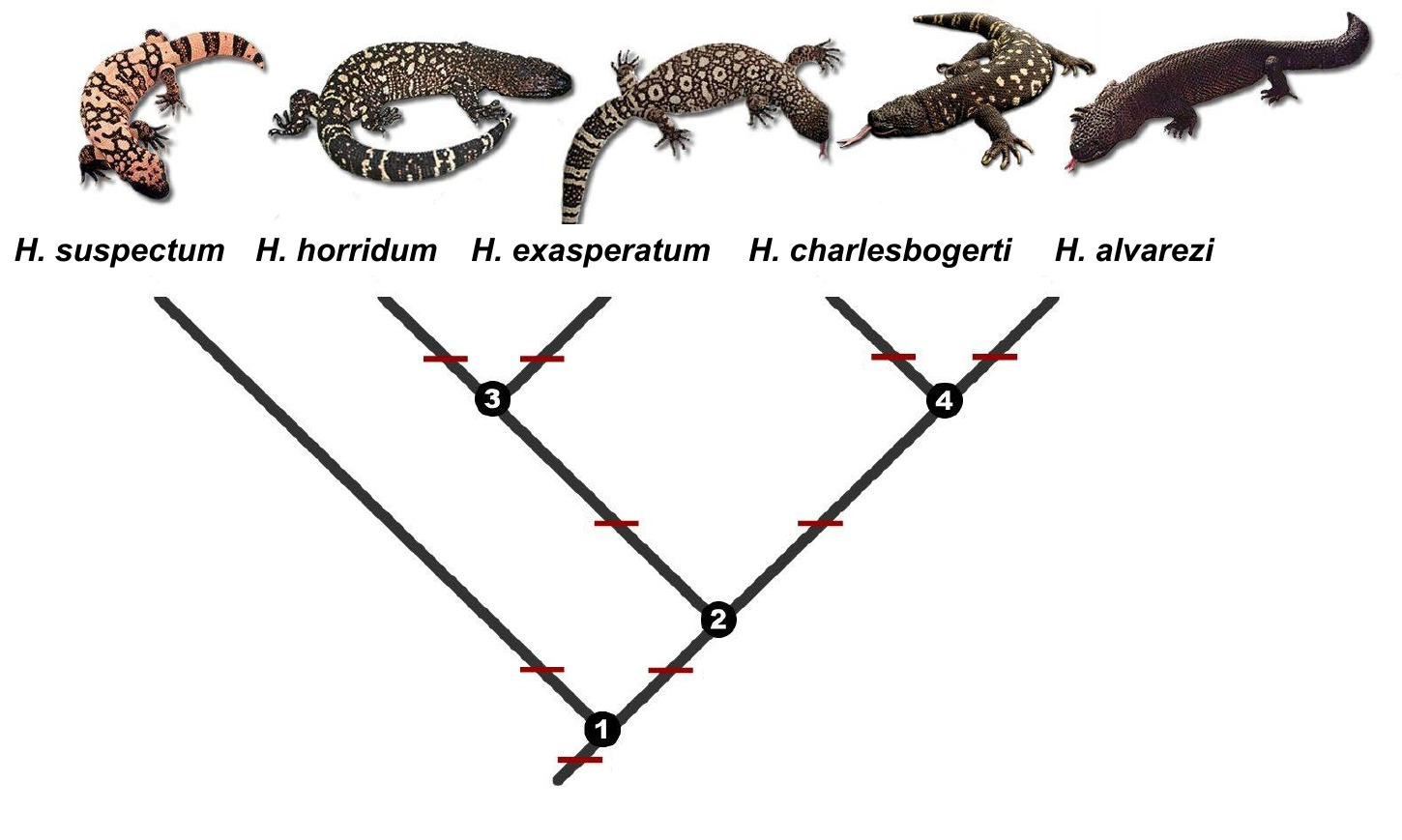
Helodermatid
''Heloderma'' is a genus of toxicoferan lizards that contains five species, all of which are venomous. It is the only extant genus of the family Helodermatidae. Description The genus ''Heloderma'' contains the Gila monster (''H. suspectum'') and four species of beaded lizards. Their eyes are immobile and fixed in their heads. The Gila monster is a large, stocky, mostly slow-moving reptile that prefers arid deserts. Beaded lizards are seen to be more agile and seem to prefer more humid surroundings. The tails of all species of ''Heloderma'' are used as fat-storage organs. The scales of the head, back, and tail are bead-like, containing osteoderms for better protection. The scales of the belly are free from osteoderms. Most species are dark in color, with yellowish or pinkish markings. Venom The venom glands of ''Heloderma'' are located at the end of the lower jaws, unlike snakes' venom glands, which are located behind the eyes. Also, unlike snakes, the Gila monster and beaded li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor Lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and West African Nile monitor, one species is also found in south America as an invasive species. About 80 species are recognized. Monitor lizards have long necks, powerful tails and claws, and well-developed limbs. The adult length of extant species ranges from in some species such as ''Dampier Peninsula monitor, Varanus sparnus'', to over in the case of the Komodo dragon, though the extinct megalania (''Varanus priscus'') may have reached lengths of more than . Most monitor species are terrestrial locomotion, terrestrial, but many are also arboreal or semiaquatic. While most monitor lizards are carnivorous, eating smaller reptiles, fish, birds, insects, small mammals, and eggs, a few species also eat fruit and vegetation. Etymology The genus, generic name ''Varanus'' is derived from the Arabic (language), Arabic word ''waral'' [St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans (armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes of amniotes and are an exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontology, paleontologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist, herpetology, herpetologist, and ichthyology, ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, he distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested in science, publishing his first scientific paper at the age of 19. Though his father tried to raise Cope as a gentleman farmer, he eventually acquiesced to his son's scientific aspirations. Cope had little formal scientific training, and he eschewed a teaching position for field work. He made regular trips to the Western United States, American West, prospecting in the 1870s and 1880s, often as a member of United States Geological Survey, U.S. Geological Survey teams. A personal feud between Cope and paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh led to a period of intense fossil-finding competition now known as the Bone Wars. Cope's financial fortunes soured after failed mining ventures i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |