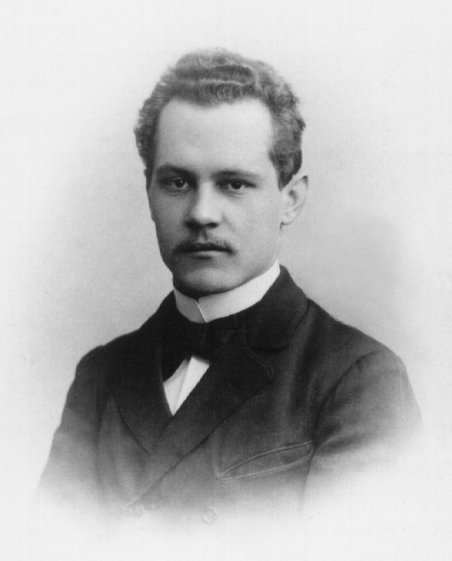|
Klein Paradox
In relativistic quantum mechanics, the Klein paradox (also known as Klein tunneling) is a quantum phenomenon related to particles encountering high-energy potential barriers. It is named after physicist Oskar Klein who discovered in 1929. Originally, Klein obtained a paradoxical result by applying the Dirac equation to the familiar problem of electron scattering from a potential barrier. In nonrelativistic quantum mechanics, electron tunneling into a barrier is observed, with exponential damping. However, Klein's result showed that if the potential is at least of the order of the electron mass Ve\approx mc^2 (where ''V'' is the electric potential, ''e'' is the elementary charge, ''m'' is the electron mass and ''c'' is the speed of light), the barrier is nearly transparent. Moreover, as the potential approaches infinity, the reflection diminishes and the electron is always transmitted. The immediate application of the paradox was to Rutherford's proton–electron model for neutral p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
In physics, relativistic quantum mechanics (RQM) is any Poincaré- covariant formulation of quantum mechanics (QM). This theory is applicable to massive particles propagating at all velocities up to those comparable to the speed of light ''c'', and can accommodate massless particles. The theory has application in high-energy physics, particle physics and accelerator physics, as well as atomic physics, chemistry and condensed matter physics. ''Non-relativistic quantum mechanics'' refers to the mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics applied in the context of Galilean relativity, more specifically quantizing the equations of classical mechanics by replacing dynamical variables by operators. ''Relativistic quantum mechanics'' (RQM) is quantum mechanics applied with special relativity. Although the earlier formulations, like the Schrödinger picture and Heisenberg picture were originally formulated in a non-relativistic background, a few of them (e.g. the Dirac or path-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines Field theory (physics), field theory and the principle of relativity with ideas behind quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and in condensed matter physics to construct models of quasiparticles. The current standard model of particle physics is based on QFT. History Quantum field theory emerged from the work of generations of theoretical physicists spanning much of the 20th century. Its development began in the 1920s with the description of interactions between light and electrons, culminating in the first quantum field theory—quantum electrodynamics. A major theoretical obstacle soon followed with the appearance and persistence of various infinities in perturbative calculations, a problem only resolved in the 1950s with the invention of the renormalization procedure. A second major barrier came with QFT's apparent inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl David Anderson
Carl David Anderson (September 3, 1905 – January 11, 1991) was an American particle physicist who shared the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics with Victor Francis Hess for his discovery of the positron. Biography Anderson was born in New York City, the son of Swedish immigrants. He studied physics and engineering at Caltech ( B.S., 1927; Ph.D., 1930). Under the supervision of Robert A. Millikan, he began investigations into cosmic rays during the course of which he encountered unexpected particle tracks in his (modern versions now commonly referred to as an Anderson) cloud chamber photographs that he correctly interpreted as having been created by a particle with the same mass as the electron, but with opposite electrical charge. This discovery, announced in 1932 and later confirmed by others, validated Paul Dirac's theoretical prediction of the existence of the positron. Anderson first detected the particles in cosmic rays. He then produced more conclusive proof by shootin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igor Tamm
Igor Yevgenyevich Tamm (; 8 July 1895 – 12 April 1971) was a Soviet Union, Soviet physicist who received the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov and Ilya Mikhailovich Frank, for their 1934 discovery and demonstration of Cherenkov radiation. He also predicted the quasi-particle of sound: the phonon; and in 1951, together with Andrei Sakharov, proposed the Tokamak, Tokamak system. Biography Igor Tamm was born in 1895 in Vladivostok into the family of Eugene Tamm, a civil engineer, and his wife Olga Davydova. According to Russian sources, Tamm had German people, German noble descent on his father's side through his grandfather Theodor Tamm, who emigrated from Thuringia. Although his surname "Tamm (surname), Tamm" is rather common in Estonia, other sources state he was Jewish people, Jewish or had Jewish ancestry. He studied at a Gymnasium (school), gymnasium in Elisavetgrad (now Kropyvnytskyi, Ukraine). In 1913–1914 he studied at the Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (born Julius Robert Oppenheimer ; April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physicist who served as the director of the Manhattan Project's Los Alamos Laboratory during World War II. He is often called the "father of the atomic bomb" for his role in overseeing the development of the first nuclear weapons. Born in New York City, Oppenheimer obtained a degree in chemistry from Harvard University in 1925 and a doctorate in physics from the University of Göttingen in Germany in 1927, studying under Max Born. After research at other institutions, he joined the physics faculty at the University of California, Berkeley, where he was made a full professor in 1936. Oppenheimer made significant contributions to physics in the fields of quantum mechanics and nuclear physics, including the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for molecular wave functions; work on the theory of positrons, quantum electrodynamics, and quantum field theory; and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protons
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' ( elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one dalton, are jointly referred to as '' nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Weyl
Hermann Klaus Hugo Weyl (; ; 9 November 1885 – 8 December 1955) was a German mathematician, theoretical physicist, logician and philosopher. Although much of his working life was spent in Zürich, Switzerland, and then Princeton, New Jersey, he is associated with the University of Göttingen tradition of mathematics, represented by Carl Friedrich Gauss, David Hilbert and Hermann Minkowski. His research has had major significance for theoretical physics as well as purely mathematical disciplines such as number theory. He was one of the most influential mathematicians of the twentieth century, and an important member of the Institute for Advanced Study during its early years. Weyl contributed to an exceptionally wide range of fields, including works on space, time, matter, philosophy, logic, symmetry and the history of mathematics. He was one of the first to conceive of combining general relativity with the laws of electromagnetism. Freeman Dyson wrote that Weyl alone bore comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Sauter
Fritz Eduard Josef Maria Sauter (; 9 June 1906 – 24 May 1983) was an Austrian-German physicist who worked mostly in quantum electrodynamics and solid-state physics. Education From 1924 to 1928, Sauter studied mathematics and physics at the Leopold-Franzens-Universität Innsbruck. He received his doctorate in 1928 under Arthur March, with a thesis on Kirchhoff’s theory of diffraction. After graduation, he did postdoctoral studies with Arnold Sommerfeld and was his assistant at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. In January 1931, Sommerfeld recommended Sauter to Max Born, director of the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Göttingen.Hentschel, 1996, Appendix F; see the entry for Fritz Sauter.Kroemer – Nobel Prize Laureate Career From 1931 to 1934, Sau ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld (; 5 December 1868 – 26 April 1951) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in Atomic physics, atomic and Quantum mechanics, quantum physics, and also educated and mentored many students for the new era of theoretical physics. He served as doctoral advisor and Postdoctoral researcher, postdoc advisor to seven Nobel Prize winners and supervised at least 30 other famous physicists and chemists. Only J. J. Thomson's record of mentorship offers a comparable list of high-achieving students. He introduced the second quantum number, azimuthal quantum number, and the third quantum number, magnetic quantum number. He also introduced the fine-structure constant and pioneered X-ray wave theory. Early life and education Sommerfeld was born in 1868 to a family with deep ancestral roots in Prussia. His mother Cäcilie Matthias (1839–1902) was the daughter of a Potsdam builder. His father Franz Sommerfeld (1820� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin (physics)
Spin is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, and thus by List of particles#Composite particles, composite particles such as hadrons, atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, and atoms. Spin is quantized, and accurate models for the interaction with spin require relativistic quantum mechanics or quantum field theory. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The relativistic spin–statistics theorem connects electron spin quantization to the Pauli exclusion principle: observations of exclusion imply half-integer spin, and observations of half-integer spin imply exclusion. Spin is described mathematically as a vector for some particles such as photons, and as a spinor or bispinor for other particles such as electrons. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Dirac
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac ( ; 8 August 1902 – 20 October 1984) was an English mathematician and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who is considered to be one of the founders of quantum mechanics. Dirac laid the foundations for both quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge and a professor of physics at Florida State University. Dirac shared the 1933 Nobel Prize in Physics with Erwin Schrödinger for "the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory". Dirac graduated from the University of Bristol with a first class honours Bachelor of Science degree in electrical engineering in 1921, and a first class honours Bachelor of Arts degree in mathematics in 1923. Dirac then graduated from the University of Cambridge with a PhD in physics in 1926, writing the first ever thesis on quantum mechanics. Dirac made fundamental contributions to the early development of both quantum mechanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, Annus Mirabilis papers#Special relativity, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just Postulates of special relativity, two postulates: # The laws of physics are Invariant (physics), invariant (identical) in all Inertial frame of reference, inertial frames of reference (that is, Frame of reference, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see ''Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |