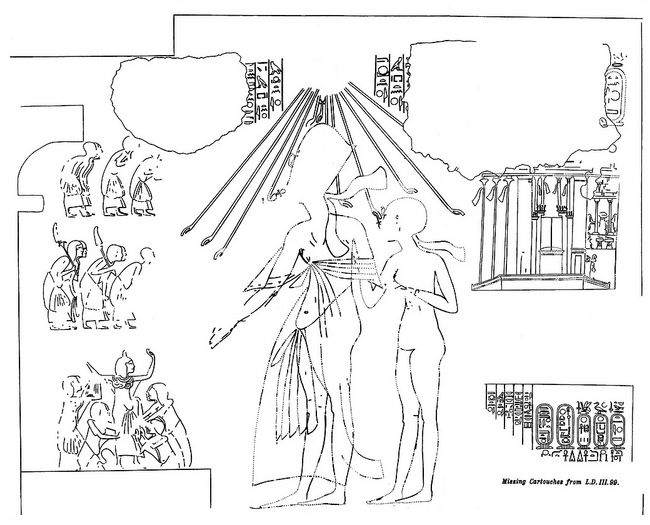
|
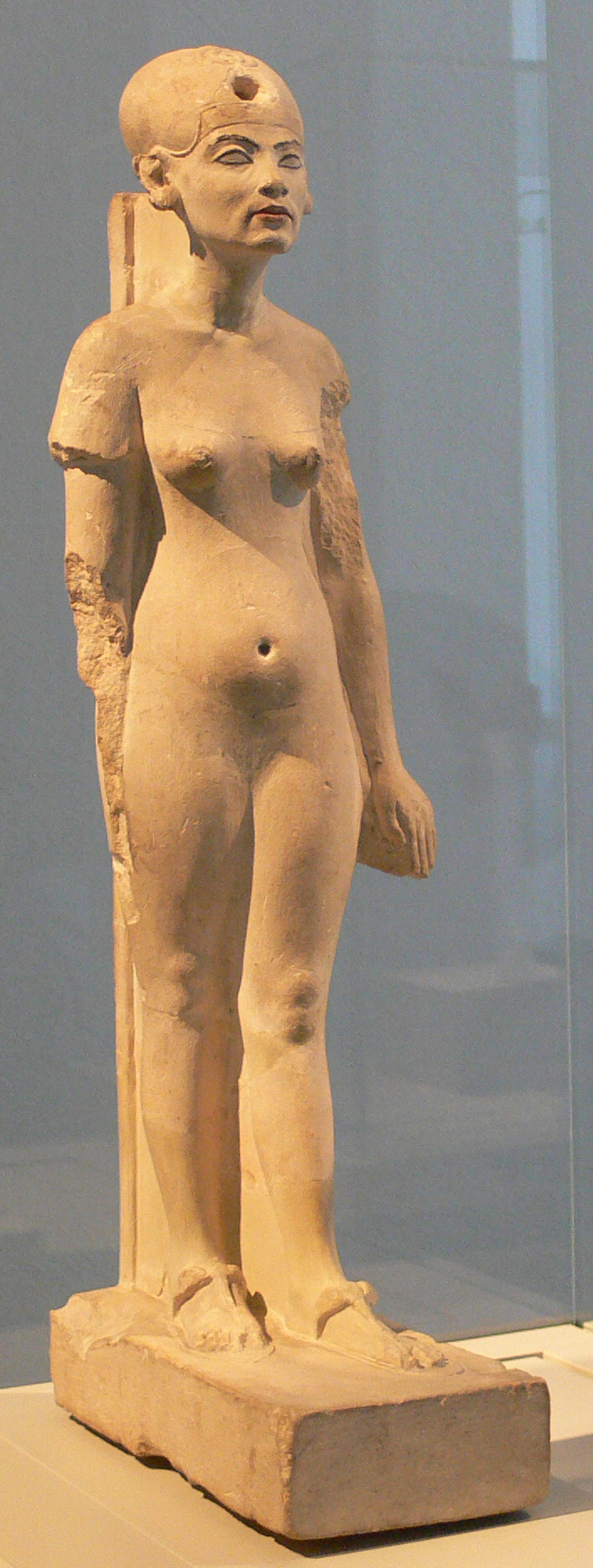
Kiya
Kiya was one of the wives of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten. Little is known about her, and her actions and roles are poorly documented in the historical record, in contrast to those of Akhenaten's 'Great royal wife', Nefertiti. Her unusual name suggests that she may originally have been a Mitanni princess.Reeves, C. Nicholas. ''New Light on Kiya from Texts in the British Museum'', p.100 The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, Vol. 74 (1988) Surviving evidence demonstrates that Kiya was an important figure at Akhenaten's court during the middle years of his reign, when she had a daughter with him.William J. Murnane. ''Texts from the Amarna Period in Egypt.'' Edited by E.S. Meltzer. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature, 1995. () Page 9, pp 90–93, pp 210–211.Aidan Dodson. Amarna Sunset: Nefertiti, Tutankhamun, Ay, Horemheb, and the Egyptian Counter Reformation. The American University in Cairo Press, 2009. () Page 17. She disappears from history a few years before her royal hus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beketaten
Beketaten () (14th century BCE) was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. Beketaten is considered to be the youngest daughter of Pharaoh Amenhotep III and his Great Royal Wife Great Royal Wife, or alternatively, Chief King's Wife () is the title that was used to refer to the Queen consort, principal wife of the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, who served many official functions. Description While most ancient Egyptians were ... Tiye, thus the sister of Pharaoh Akhenaten.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt, Thames & Hudson (2004), p.154 Her name means "Handmaid of Aten". Family Beketaten was most likely the youngest daughter of Amenhotep III and Tiye. This would mean their other children were her siblings, including Prince Thutmose, the Pharaoh Akhenaten, Sitamun, Isis, Henuttaneb, and Nebetah. Some scholars have speculated that Nebetah was identical with Beketaten. However, no evidence proves that they are the same person. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning 'Effective for the Aten'), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV (, meaning "Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning traditional ancient Egyptian religion of polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheism, monotheistic, or whether it was monolatristic, religious syncretism, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name Damnatio memoriae, excluded from regnal list, lists of rulers compiled by lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV55
KV55 is a tomb in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was discovered by Edward R. Ayrton in 1907 while he was working in the Valley for Theodore M. Davis. It has long been speculated, as well as much disputed, that the body found in this tomb was that of the famous king, Akhenaten, who moved the capital to Akhetaten (modern-day Amarna). The results of genetic and other scientific tests published in February 2010 have confirmed that the person buried there was both the son of Amenhotep III and the father of Tutankhamun. Furthermore, the study established that the age of this person at the time of his death was consistent with that of Akhenaten, thereby making it almost certain that it is Akhenaten's body.Hawass, Zahi et al. "Ancestry and Pathology in King Tutankhamun's Family" ''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (2010) p. 644 However, a growing body of work soon began to appear to dispute the assessment of the age of the mummy and the identification of KV55 as A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadukhipa
Tadukhipa (in the Hurrian language ''Tadu-Hepa''), was a princess of the Mitanni kingdom. She was the daughter of King Tushratta of Mitanni and his queen Juni, and the niece of Artashumara. Tadukhipa's aunt Gilukhipa (sister of Tushratta) had married Pharaoh Amenhotep III in his 10th regnal year. Tadukhipa was to marry Amenhotep III more than two decades later. Early life Tadukhipa was the daughter of King Tushratta of Mitanni, who is believed to have reigned c. 1382 BC–1342 BC. She is believed to have been born around Year 21 of the reign of Egyptian Pharaoh Amenhotep III (c. 1366 BC). Almost nothing is known of her early years. In approximately Year 36 of Amenhotep's reign (c. 1352), Tushratta sent her to Egypt to marry the pharaoh, who was a close ally. Relatively little is known about this princess of Mitanni. She is believed to have been born around Year 21 of the reign of Egyptian Pharaoh Amenhotep III, (c. 1366 BC). Fifteen years later, Tushratta married his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Younger Lady (mummy)
The Younger Lady is the informal name given to an ancient Egyptian mummy discovered within tomb KV35 in the Valley of the Kings by archaeologist Victor Loret in 1898. The mummy also has been given the designation KV35YL ("YL" for "Younger Lady") and 61072, and currently resides in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. Through DNA tests, this mummy was identified as the mother of the pharaoh Tutankhamun and a daughter of pharaoh Amenhotep III and his Great Royal Wife Tiye. Early speculation that this mummy was the remains of Nefertiti was argued to be incorrect, as nowhere is Nefertiti accorded the title "King's daughter" unless this mummy was in fact a cousin of Akhenaten and not a sister. Discovery The mummy was found adjacent to two other mummies in KV35: a young boy who died at the approximate age of ten and is thought to be Webensenu, and an older woman, who has been identified as Tiye by the recent DNA studies on Tutankhamun's lineage. The three mummies were found together in a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna
Amarna (; ) is an extensive ancient Egyptian archaeological site containing the ruins of Akhetaten, the capital city during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era. Name The name ''Amarna'' comes from the Beni Amran tribe that lived in the region and founded a few settlements. The ancient Egyptian name means " the horizon of the Aten".David (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meritaten
Meritaten, also spelled Merytaten, Meritaton or Meryetaten () (14th century BC), was an ancient Egyptian royal woman of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name means "She who is beloved of Aten"; Aten being the sun-deity whom her father, Pharaoh Akhenaten, worshipped. She held several titles, performing official roles for her father and becoming the Great Royal Wife to Pharaoh Smenkhkare, who may have been a brother or son of Akhenaten. Meritaten also may have served as pharaoh in her own right under the name Ankhkheperure Neferneferuaten.J. Tyldesley, ''Chronicle of the Queens of Egypt'', 2006, Thames & Hudson, pg 136–137 Family Meritaten was the first of six daughters born to Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti. Her sisters are Meketaten, Ankhesenpaaten, Neferneferuaten Tasherit, Neferneferure, and Setepenre. Meritaten is mentioned in diplomatic letters, by the name ''Mayati''. She is mentioned in a letter from Abimilki of Tyre. The reference usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meketaten
Meketaten (, meaning "Behold the Aten" or "Protected by Aten") was the second of six daughters born to the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti. She likely lived between Year 4 and Year 14 of Akhenaten's reign. Although little is known about her, she is frequently depicted with her sisters accompanying her royal parents in the first two-thirds of the Amarna Period. Biography Meketaten was born approximately in Year 4 of Akhenaten's reign to him and his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti.Tyldesley, Joyce. Nefertiti: Egypt's Sun Queen. Penguin. 1998. She had an elder sister, Meritaten, and four younger sisters: Ankhesenpaaten, Neferneferuaten Tasherit, Neferneferure and Setepenre. Tutankhaten was likely their full brother or half-brother through their father.Dodson, Aidan and Hilton, Dyan. The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2004. Her birth year is estimated based on the dates of inscriptions that reference her. The first known d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmoside Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose. Several of Egypt's most famous pharaohs were from the Eighteenth Dynasty, including Tutankhamun. Other famous pharaohs of the dynasty include Hatshepsut (c. 1479 BC–1458 BC), the longest-reigning woman pharaoh of an indigenous dynasty, and Akhenaten (c. 1353–1336 BC), the "heretic pharaoh", with his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti. The Eighteenth Dynasty is unique among Egyptian dynasties in that it had two Queen regnant, queens regnant, women who ruled as sole pharaoh: Hatshepsut and Neferneferuaten, usually identified as Nefertiti. History Early Dynasty XVIII Dynasty XVIII was founded by Ahmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV35
Tomb KV35 is the burial place of Amenhotep II, a pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, in the Valley of the Kings in Luxor, Egypt. Later, it was used as a cache for other royal mummies. It was discovered by Victor Loret in March 1898. Layout and history It has a bent axis, typical of the layout of early Eighteenth Dynasty tombs, but several features make this tomb unusual. The burial chamber is rectangular and divided into upper and lower pillared sections, with the lower part holding the cartouche-shaped royal sarcophagus of the king. This style of burial chamber became standard for royal burials in the later New Kingdom. Only the burial chamber of the tomb is decorated, albeit in an unusual style that, other than '' KV34'' (the tomb of Amenhotep II's father, Thutmose III), is not found elsewhere in the Valley of the Kings. On a yellow-tinged background (intended to resemble aged papyrus), the '' Amduat'' is traced, depicting the ancient Egyptian deities as simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nefertiti
Nefertiti () () was a queen of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the Great Royal Wife, great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for their radical overhaul of state religious policy, in which they promoted the earliest known form of monotheism, Atenism, centered on Aten, the sun disc and its direct connection to the royal household. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. After her husband's death, some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as the female pharaoh known by the throne name, Neferneferuaten and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is Neferneferuaten#Nefertiti, a matter of ongoing debate. If Nefertiti did rule as pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes, Egypt, Thebes. In the 20th century, Nefertiti was made famous by the disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provenance
Provenance () is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art, but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including archaeology, paleontology, archival science, circular economy, economy, computing, and Scientific method, scientific inquiry in general. The primary purpose of tracing the provenance of an object or entity is normally to provide contextual and circumstantial evidence for its original production or discovery, by establishing, as far as practicable, its later history, especially the sequences of its formal ownership, custody and places of storage. The practice has a particular value in helping Authentication, authenticate objects. Comparative techniques, expert opinions and the results of scientific tests may also be used to these ends, but establishing provenance is essentially a matter of documentation. The term dates to the 1780s in English. Provenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |