|
Kit Hood
Christopher "Kit" Hood (24 March 1943 – 20 January 2020) was an English-born Canadian filmmaker who co-created the '' Degrassi'' television franchise and its first three entries: ''The Kids of Degrassi Street'' (1979–86), '' Degrassi Junior High'' (1987–89), and '' Degrassi High'' (1989-91), as well serving as the writer and/or director of the majority of their episodes. As a director, Hood won a Gemini Award in 1987 for the ''Degrassi Junior High'' episode " It's Late". Born in London, he emigrated to Canada in 1969 and worked as a freelance editor before meeting ex-schoolteacher Linda Schuyler, with whom he founded the company Playing With Time in 1976. Outside of ''Degrassi'', the company produced educational films and documentaries. He split from Schuyler in the early 1990s and was not involved with '' Degrassi: The Next Generation'' or '' Degrassi: Next Class'', having retired in 1998. Career Christopher "Kit" Hood was born in London, England in 1943, the son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Gemini Awards
The 3rd Gemini Awards were held in 1988 to honour achievements in Television in Canada, Canadian television. The ceremonies were sponsored by the Academy of Canadian Cinema and Television and held at the Metro Toronto Convention Centre on 29 and 30 November. It was broadcast on CBC Television, CBC. Awards Programs Actors Journalism and sports Directing Writing Craft awards Special awards * Earle Grey Award: Kate Reid * Academy of Canadian Cinema and Television Diversity Award, Multiculturalism Award: ''Degrassi Junior High'' * TV Guide Most Popular Program Award: ''Night Heat'' * John Drainie Award: Davidson Dunton * Margaret Collier Award: M. Charles Cohen References {{Gemini Awards Gemini Awards, 03 1988 in Canadian television, Gemini Awards, 1988 1988 television awards, Gemini Awards, 1988 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ida Makes A Movie
''Ida Makes a Movie'' is a 1979 Canadian after school special short film produced by Kit Hood and Linda Schuyler for the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, who aired the film on December 8, 1979. The story was adapted from the 1974 children's picture book ''Ida Makes a Movie'', which was written by Kay Chorao. Schuyler, a former media teacher at Earl Grey Senior Public School, was introduced to the book via the school's librarian, and purchased the film rights from Chorao for $200. The film led to a series of further short films that aired on the CBC, which later developed into ''The Kids of Degrassi Street'', the first series in the '' Degrassi'' teen drama franchise. Plot 9-year-old Ida Lucas and her 6-year-old friend, Cookie, are having a day in the park on Degrassi Street. Ida is upset by the amount of litter around the park, despite the signs posted. After Ida has the disgusting experience of stepping on someone's discarded sandwich, Cookie (who cannot read) points o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OWL/TV
OWL/TV is a Canadian children's educational television series that aired on CBC, from 1985 to 1990, and then later on CTV, from 1990 to 1994. It focused on nature and science discovery, emphasizing to viewers how they can affect their own environment. Segments Each half-hour program presented cartoon segments mixed with serious themes and contains segments from several recurring themes: * ''Mighty Mites'': Three kids who possess the magical ability to shrink in size in order to discover microscopic environments. * ''Animals Close Up'': Discovers other aspects of animal life. Kids meet the animals first-hand and see on-the-spot interviews with zoologists and experts on animal behaviour. * ''Tomorrow Today'': Looks at the future from a kid's point of view, brings kids into working laboratories. * ''Real Kids'' features youths who are actively involved in trying to develop their environment. These are kids who are not afraid to try. Real Kids nurtures the idea that individuals o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslieville
Leslieville is a neighbourhood in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, situated east of the Don River. It is bounded by the Canadian National railway line and Gerrard Street to the north, McGee Street to the west, Eastern Avenue to south, and Coxwell Avenue to the east. History This east-end neighbourhood forms part of the broader neighbourhood of South Riverdale. Leslieville began as a small village in the 1850s, which grew up around the Toronto Nurseries owned by George Leslie (1804-1893) and sons, after whom the community is named. Most of Leslieville's residents were gardeners or were employed at one of the brick-making factories in the area. Leslie's home at Queen and Leslie no longer exists but the general store remains on Queen east of Jones Avenue. Alexander Muir, the composer of ''The Maple Leaf Forever'', was the first principal of the Leslieville Public School, one of the first buildings in the village. Muir was inspired when a brilliant maple leaf fell on his jacket fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joey Jeremiah
Joseph "Joey" Jeremiah is a fictional character from the ''Degrassi'' teen drama franchise. He is portrayed by Pat Mastroianni. He debuted in the first episode of ''Degrassi Junior High'' and appeared throughout ''Degrassi Junior High'', ''Degrassi High'', and the first five seasons of '' Degrassi: The Next Generation.'' As one of the main focus characters of the original two series, his role primarily concerns his friendship with Archie "Snake" Simpson ( Stefan Brogren) and Derek "Wheels" Wheeler ( Neil Hope), his on-and-off romantic relationship with Caitlin Ryan ( Stacie Mistysyn), and in ''The Next Generation'', his relationship with his stepson Craig Manning ( Jake Epstein). Characterized as a class clown and a slacker in the original series, Joey was known for his trademark fedora and Hawaiian shirts and humorous, immature attitude. However, he shows a more sensitive, caring side when his friends are in a crisis, such as his attempts to comfort Wheels after his parents' de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pat Mastroianni
Pasquale Mastroianni (born December 22, 1971), known professionally as Pat Mastroianni, is a Canadian actor who is best known for his role as Joey Jeremiah in the ''Degrassi'' television franchise, playing the role as a student in ''Degrassi Junior High'' (1987–89) and '' Degrassi High'' (1989–91), and reprising the role as an adult on '' Degrassi: The Next Generation'' (2001–06). In 1988, he received a Gemini Award for ''Degrassi Junior High''. Biography Mastroianni grew up in Toronto, the son of Angela and Angelo Mastroianni. He is of Italian heritage. He later recalled that he had first heard about the audition of ''Degrassi'' over his school's PA system. Mastroianni was among the cast of ''Degrassi'' that were named UNICEF Goodwill Ambassadors by the Ontario branch of UNICEF Canada in 1989. Along with cast member Amanda Stepto, Mastroianni visited the Headquarters of the United Nations in New York City. After '' Degrassi High'' ended in 1992, Mastroianni worked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
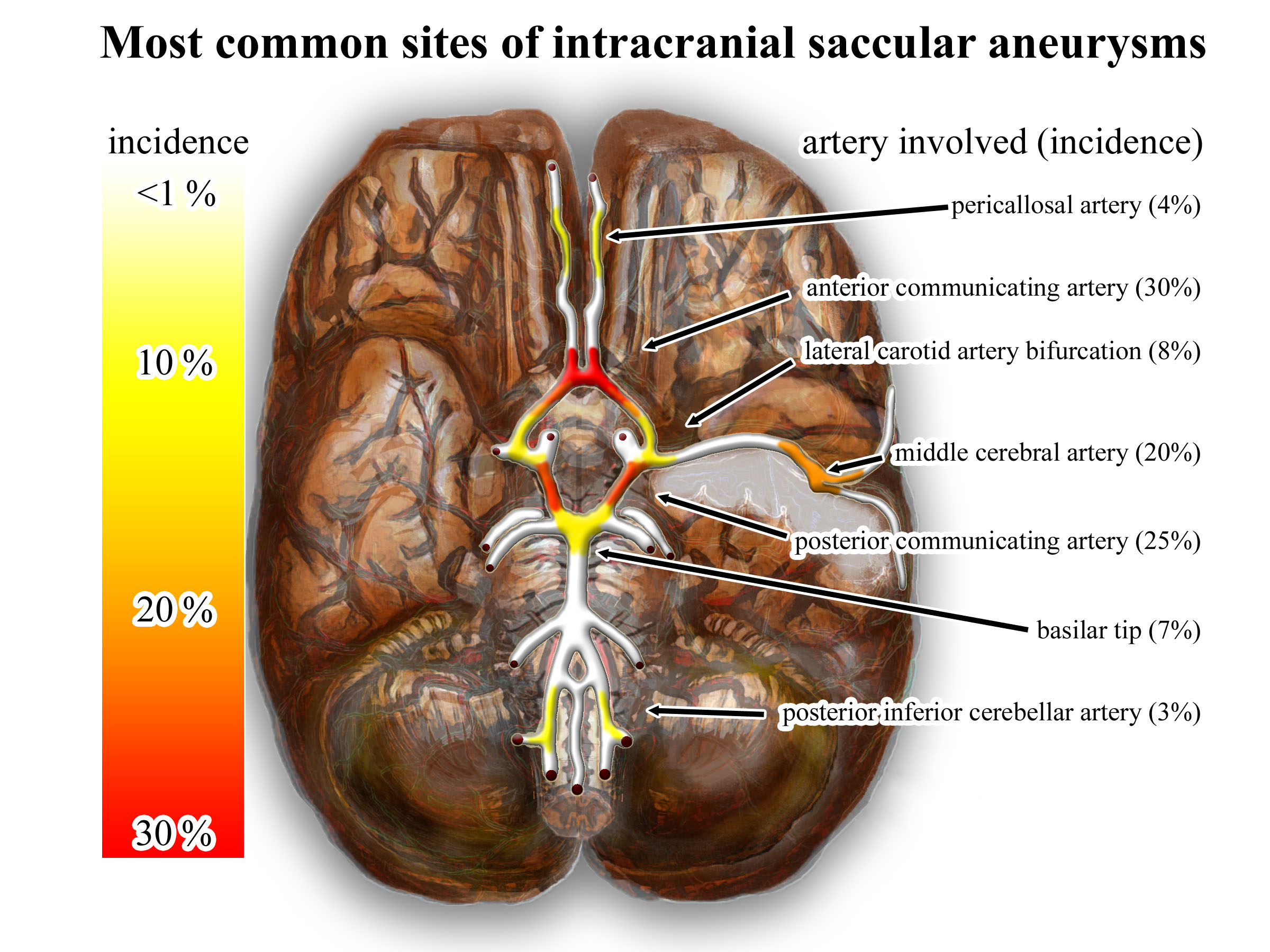
Intracranial Aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder characterized by a localized dilation or ballooning of a blood vessel in the brain due to a weakness in the vessel wall. These aneurysms can occur in any part of the brain but are most commonly found in the arteries of the cerebral arterial circle. The risk of rupture varies with the size and location of the aneurysm, with those in the posterior circulation being more prone to rupture. Cerebral aneurysms are classified by size into small, large, giant, and super-giant, and by shape into saccular (berry), fusiform, and microaneurysms. Saccular aneurysms are the most common type and can result from various risk factors, including genetic conditions, hypertension, smoking, and drug abuse. Symptoms of an unruptured aneurysm are often minimal, but a ruptured aneurysm can cause severe headaches, nausea, vision impairment, and loss of consciousness, leading to a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Treatm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stacie Mistysyn
Stacie Moana Mistysyn (born July 23, 1971) is an American and Canadian actress who is best known for her role as Caitlin Ryan throughout multiple incarnations of the ''Degrassi'' teen drama franchise, from ''Degrassi Junior High'' through '' Degrassi: The Next Generation''. She previously played Lisa Canard in ''The Kids of Degrassi Street'' from 1982 to 1986. She won a Gemini Award for ''Degrassi Junior High'' in 1989 and was nominated in 1987 and 1990. She was also named in a Young Artist Award for Outstanding Young Ensemble Cast nomination in 1990. Biography Mistysyn was born in Los Angeles to American parents, and was raised in Toronto. As of 2005, she had dual American and Canadian citizenship, but considered herself Canadian. She auditioned for ''The Kids of Degrassi Street'' at the age of 10 after coming across an audition flyer at her school. She played the role of Lisa Canard from 1982 to 1986, when development began on ''Degrassi Junior High'', where she opted to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battered Women's Shelter
A women's shelter, also known as a women's refuge and battered women's shelter, is a place of temporary protection and support for women escaping domestic violence and intimate partner violence of all forms. The term is also frequently used to describe a location for the same purpose that is open to people of all genders at risk. Representative data samples done by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that one in three women in the U.S. will experience physical violence during their lifetime.Breiding MJ, Chen J, Black MC. Intimate Partner Violence in the United States – 2010. Atlanta, GA: National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2014. One in ten will experience sexual violence. Women's shelters help individuals escape these instances of domestic violence and intimate partner violence and act as a place for protection as they choose how to move forward. Additionally, many shelters offer a variety of other ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Stohn
John Stephen Stohn, (born May 8, 1948) is an American-born Canadian entertainment lawyer and television producer. He is best known for his involvement with the '' Degrassi'' teen drama franchise, particularly as an executive producer on '' Degrassi: The Next Generation''. Until 2018 he was the president of Epitome Pictures Inc., which he and his wife Linda Schuyler founded in 1992 and was sold to DHX Media in 2014. On June 7, 2019, he was installed as Chancellor of Trent University in Peterborough, Ontario. Career Stohn's work in the entertainment industry commenced with part-time appearances as a performing artist, continuing with active work as a songwriter (including two songs that reached the Canadian Top-10, ''Maybe Your Heart'' and ''Once In A Long Time'', co-written with Christopher Ward), and a primary career as an entertainment and copyright lawyer since he was called to the Ontario Bar in 1979. Trent University had barely been built when Stohn attended there sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitome Pictures
Epitome Pictures Inc. (later known as DHX Studios Toronto) was a Canadian film and television production company based in Toronto, Ontario. Founded by Linda Schuyler and Stephen Stohn in 1992, the company is best known for producing '' Degrassi: The Next Generation'' and '' Degrassi: Next Class'', the fourth and fifth respective entries of the '' Degrassi'' teen drama franchise, of which was co-created by Schuyler. Other television series produced by Epitome include '' Liberty Street,'' '' Riverdale'', and '' The L.A. Complex.'' Epitome was acquired by DHX Media in 2014. History Linda Schuyler and Stephen Stohn founded Epitome Pictures in 1992, and purchased its first studio building in 1995, to film ''Riverdale''. At the time, the studio was allegedly "in a sorry state, with snow melting on the leaking roof and cans catching the water". Its main headquarters were located on a 100,000 square-foot lot in Bartley Drive in Toronto, Ontario. In April 2014, the company and its libr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School's Out (1992 Film)
''School's Out'' (also referred to on home video as ''Degrassi High: School's Out'') is a Canadian drama television film based on the ''Degrassi'' teen drama franchise created by Linda Schuyler and Kit Hood in 1979. It was directed by Hood and written by Yan Moore, based on a story by Moore, Schuyler and Hood. It aired on CBC Television on January 5, 1992, and served as a finale to the series ''Degrassi High'' and its predecessor ''Degrassi Junior High,'' which are collectively known as the ''Degrassi Classic'' era of the franchise. The movie, centered on the Degrassi students during their first summer post-graduation, primarily focuses on the relationship between Joey Jeremiah (Pat Mastroianni) and Caitlin Ryan (Stacie Mistysyn); after Caitlin politely rejects Joey's marriage proposal, he begins becoming romantically involved with Tessa Campanelli (Kirsten Bourne), while also still being involved with Caitlin; he has sex with both, with Tessa being first, and brags about it with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |