|
Kishor Phadke
Kishor Moreshwar Phadke (20 February 1936 - 31 January 2022), also known as K. M. Phadke, was an Indian psychologist, practitioner and trainer in Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT). He held M.A. degree in psychology from Pune University. He is first Indian psychologist who enjoys the unique distinction of being a fellow and supervisor of the Albert Ellis Institute in New York City. He is best known as a pioneer of REBT in India. Due to his distinguished contributions to REBT, Indian psychologists consigned a unique title to his therapy – Ellis-Phadke therapy. He has authored nine Marathi books, several popular articles and papers and co-authored five English books. Family and education Kishor was born on 20 February 1936 in a Maharashtrian family. The origin of his family can be traced to Haripant Phadke, who was a lieutenant general in the Darbar of Peshwas. His father was a general practitioner (MBBS) in Pune whereas his mother was a housewife. The couple had fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mumbai, Maharashtra
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second-most populous city in India after Delhi and the eighth-most populous city in the world with a population of roughly 20 million (2 crore). As per the Indian government population census of 2011, Mumbai was the most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 12.5 million (1.25 crore) living under the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation. Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23 million (2.3 crore). Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an alpha world city. It has the highest number of millionaires and billionaires among all cities in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later, under the Bhat family, they became the ''de facto'' leaders of the Maratha Confederacy, with the Chhatrapati becoming a nominal ruler. During the last years of the Maratha Empire, the Peshwas themselves were reduced to titular leaders, and remained under the authority of the Maratha nobles and the British East India Company. All Peshwas during the rule of Shivaji, Sambhaji and Rajaram belonged to Deshastha Brahmin community. The first Peshwa was Moropant Pingle, who was appointed as the head of the Ashta Pradhan (council of eight ministers) by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, the founder of the Maratha Empire. The initial Peshwas were all ministers who served as the chief executives to the king. The later Peshwas held the highest admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about social order and social change. While some sociologists conduct research that may be applied directly to social policy and welfare, others focus primarily on refining the theoretical understanding of social processes and phenomenological method. Subject matter can range from micro-level analyses of society (i.e. of individual interaction and agency) to macro-level analyses (i.e. of social systems and social structure). Traditional focuses of sociology include social stratification, social class, social mobility, religion, secularization, law, sexuality, gender, and deviance. As all spheres of human activity are affected by the interplay between social structure and individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and laws. Modern political science can generally be divided into the three subdisciplines of comparative politics, international relations, and Political philosophy, political theory. Other notable subdisciplines are Public administration, public policy and administration, Domestic politics, domestic politics and government, political economy, and political methodology. Furthermore, political science is related to, and draws upon, the fields of economics, Legal education, law, sociology, history, philosophy, human geography, political anthropology, and psychology. Political science is methodologically diverse and appropriates many methods originating in psychology, social research, and political philosophy. Approaches include positivism, Vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include oral literature, much of which has been transcribed. Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment, and can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role. Literature, as an art form, can also include works in various non-fiction genres, such as biography, diaries, memoir, letters, and the essay. Within its broad definition, literature includes non-fictional books, articles or other printed information on a particular subject.''OED'' Etymologically, the term derives from Latin ''literatura/litteratura'' "learning, a writing, grammar," originally "writing formed with letters," from ''litera/littera'' "letter". In spite of this, the term has also been applied to spok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat University
The Gujarat University is a public state university located at Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. The university is an affiliating university at the under-graduate level and a teaching university at the postgraduate level. It is accredited B++ by NAAC. It was established in 23rd November 1949. History Many leaders like Mahatma Gandhi, Sardar Patel, Anandshankar Dhruv, Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar and Kasturbhai Lalbhai recommended formation of the university in the 1920s, and the university was established soon after the independence of India. Gujarat University was evolved out of Ahmedabad Education Society, a major educational organisation of Gujarat then. Gujarat University was formed under the Gujarat University Act of the Government of Gujarat in 1949 as a teaching and affiliating university. It was established under the recommendation of a committee headed by Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar for rearrangement of university education in Bombay State. Many universities were establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
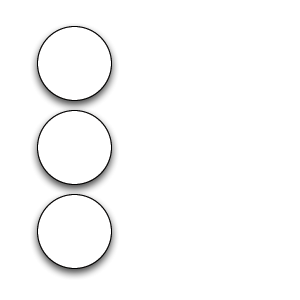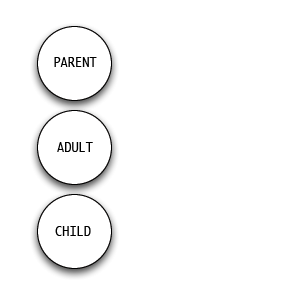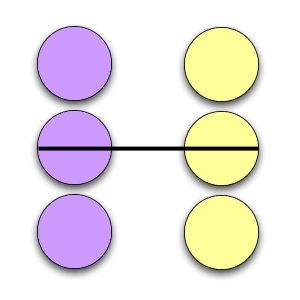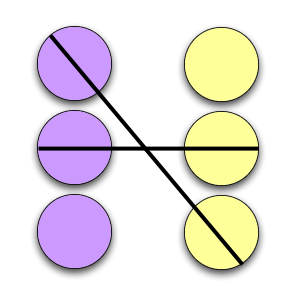
Transactional Analysis
Transactional Analysis (TA) is a psychoanalytic theory and method of therapy wherein social interactions (or “transactions”) are analyzed to determine the ego state of the communicator (whether parent-like, childlike, or adult-like) as a basis for understanding behavior. In transactional analysis, the communicator is taught to alter the ego state as a way to solve emotional problems. The method deviates from Freudian psychoanalysis which focuses on increasing awareness of the contents of subconsciously held ideas. Eric Berne developed the concept and paradigm of transactional analysis in the late 1950s. History Eric Berne presented Transactional Analysis to the world as a phenomenological approach, supplementing Freud's philosophical construct with observable data. His theory built on the science of Wilder Penfield and René Spitz along with the neo-psychoanalytic thought of people such as Paul Federn, Edoardo Weiss, and Erik Erikson. By moving to an interpersonal motiva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mumbai University
The University of Mumbai is a collegiate, state-owned, public research university in Mumbai. The University of Mumbai is one of the largest universities in the world. , the university had 711 affiliated colleges. Ratan Tata is the appointed head of the advisory council. History In accordance with " Wood's despatch", drafted by Sir Charles Wood in 1854, the University of Bombay was established in 1857 after the presentation of a petition from the Bombay Association to the British colonial government in India. The University of Mumbai was modelled on similar universities in the United Kingdom, specifically the University of London. The first departments established were the Faculty of Arts at Elphinstone College in 1835 and the Faculty of Medicine at Grant Medical College in 1845. Both colleges existed before the university was founded and surrendered their degree-granting privileges to the university. The first degrees awarded in 1862 were Bachelor of Arts and Licentiate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldsmiths, University Of London
Goldsmiths, University of London, officially the Goldsmiths' College, is a constituent research university of the University of London in England. It was originally founded in 1891 as The Goldsmiths' Technical and Recreative Institute by the Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths in New Cross, London. It was renamed Goldsmiths' College after being acquired by the University of London in 1904 and specialises in the arts, design, humanities and social sciences. The main building on campus, known as the Richard Hoggart Building, was originally opened in 1792 and is the site of the former Royal Naval School. According to Quacquarelli Symonds (2021), Goldsmiths ranks 12th in Communication and Media Studies, 15th in Art & Design and is ranked in the top 50 in the areas of Anthropology, Sociology and the Performing Arts. In 2020, the university enrolled over 10,000 students at undergraduate and postgraduate levels. 37% of students come from outside the United Kingdom and 52% of all undergrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmedabad Textile Industry's Research Association
The Ahmedabad Textile Industry's Research Association (commonly known as ATIRA) is an autonomous non-profit association for textile research located in the Navarangpura area of Ahmedabad, India. It is the largest association for textile research and allied industries in India. Established on 13 December 1947, and started in 1949, ATIRA was recognized by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research under the Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India. It was later linked to the Ministry of Textiles. Establishment The idea of ATIRA was conceived by Vikram Sarabhai, Kasturbhai Lalbhai and Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar. ATIRA was founded in 1947. Vikram Sarabhai served as its first honorary director. ATIRA Complex The foundation stone for the ATIRA complex was laid by Vallabhbhai Patel on 1 November 1950 which was inaugurated by the then Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru on completion on 10 April 1954. The architect of the ATIRA building is Achyut Kanvinde. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)