|
Kinhai
Kinhai is a village located in Koregaon Taluka, Satara District in Maharashtra, India. The village is divided into Pantanchi Kinhai on the western side and Peth Kinhai to the east. It is located north of Koregaon, at above sea level. As of the 2011 Indian census, Kinhai had a population of 3,360. History In 965 CE, the village, then known as Kinhika, was donated to a Brahmin named Navashiv. It fell under the administrative unit of Ramtirthika. Kinhai was a village of the former princely state of Aundh and was included in Koregaon Taluka after the merger of the princely states. The Pratinidhi families were hereditary Kulkarnis or accountants of Kinhai and several of the neighbouring villages and it was from that position that Parashuram Trimbak raised himself till he was appointed the third Pratinidhi in 1700. In 1749, Sakhargadnivasini Temple (meaning "she who resides on top of the hill called sugar-fort") was completed. In 2014, the temple underwent a restoration effor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Q ... mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalyangad
Kalyangad Fort/Nandgiri is in the taluka Koregaonl. of Satara district of Maharashtra. The fort stands at the end of a spur of the Mahadev range running south-west from the villages of Vikhale and Bhadle, eight miles north of Koregaon and about fourteen miles north-east of Satara. Its elevation is 3,537 feet above sea level. History According to tradition the fort was built by the Silahara king Bhoj II, of Panhala. In 1673 it was surrendered, along with other Satara forts, to Shivaji. The Pratinidhi administered it until his struggle with Bajirao, the second Peshwa (1720–1740). In 1791, Major Price described it as looking like the hull of a ship of war, with another hill opposite it with some places of devotion on its summit. In the last Maratha war, it fell to the army of General Pritzler in April 1818. In 1862, it was described as a dismantled and uninhabited fort with a steep approach and a strong gateway, but no water and no supplies.Government List of Civil Forts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wainganga River
The Wainganga is a river in India originating in the Mahadeo Hills in Mundara near the village Gopalganj in Seoni, Madhya Pradesh. It is a key tributary of the Godavari River, Godavari. The river flows south in a winding course through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, roughly . After joining the Wardha River, the united stream, which is known as the Pranhita River, Pranahita River, empties into the River Godavari, Godavari River at Kaleshwaram, Telangana. Course The main stream of the Wainganga originates at Mahadev hills near Gopalganj, Seoni District, on the southern slopes of the Satpura Range of Madhya Pradesh. The river has developed extensive floodplains characterized by sweeping graceful meanders, low Alluvial plain, alluvial flats, and slip-off slopes. The river has high banks, which measure from to on either side. The northern part is surrounded by the Mahadeo Hills, Mahadeo hills and Satpura Range, with an average elevation of 625 m (2,051 ft) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO Asia Pacific Heritage Awards
UNESCO Asia Pacific Heritage Awards (since 2000) are given with as the strategic purpose of UNESCO with in the region Asia Pacific. The objective is to motivate the protection of Cultural Heritage sites, which are initiated by any individual organization under private sector or institutional organization. Award categories The Awards consist of five categories. * Award of Excellence. * Award of Distinction. * Award of Merit. * Honourable Mention. * Award for New Design in Heritage Contexts Laureates 2022 Award of Excellence: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya Museum, Mumbai, India Award of Distinction Stepwells of Golconda, Hyderabad, India Zarch Qanat, Yazd, Iran Neilson Hays Library, Bangkok, Thailand Award of Merit Topdara Stupa, Charikar, Afghanistan Nantian Buddhist Temple, Fujian, China Domakonda Fort, Telangana, India Byculla Station, Mumbai, India Sadoughi House, Yazd, Iran 25 Chivas in Kathmandu, Nepal Special Recognition for Sustai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulkarni
Kulkarni is a family name native to the Indian state of Maharashtra. The name "Kulkarni" is a combination of two words (''kula'' and ''karni''). ''Kula'' means "family", and ''Karanika'' means "archivist". Historically, Kulkarni was the title given to the village record keeper. As per the historian P.J. Marshall, both Kulkarni and Deshpande were specialized scribes who "served great households and enhanced other, familiar, administrative mechanisms at their disposal". History Before British rule, the Maharashtra region was divided into many revenue divisions. The medieval equivalent of a county or district was the pargana. The chief of the pargana was called Deshmukh and record keepers were called Deshpande. The lowest administrative unit was the village. Village society in Marathi areas included the Patil or the head of the village, collector of revenue, and Kulkarni, the village record-keeper. These were hereditary positions. The Patil usually came from the Maratha caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large ( Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from thousands of zamindari estates and jagirs. In 1947, princely states covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aundh State
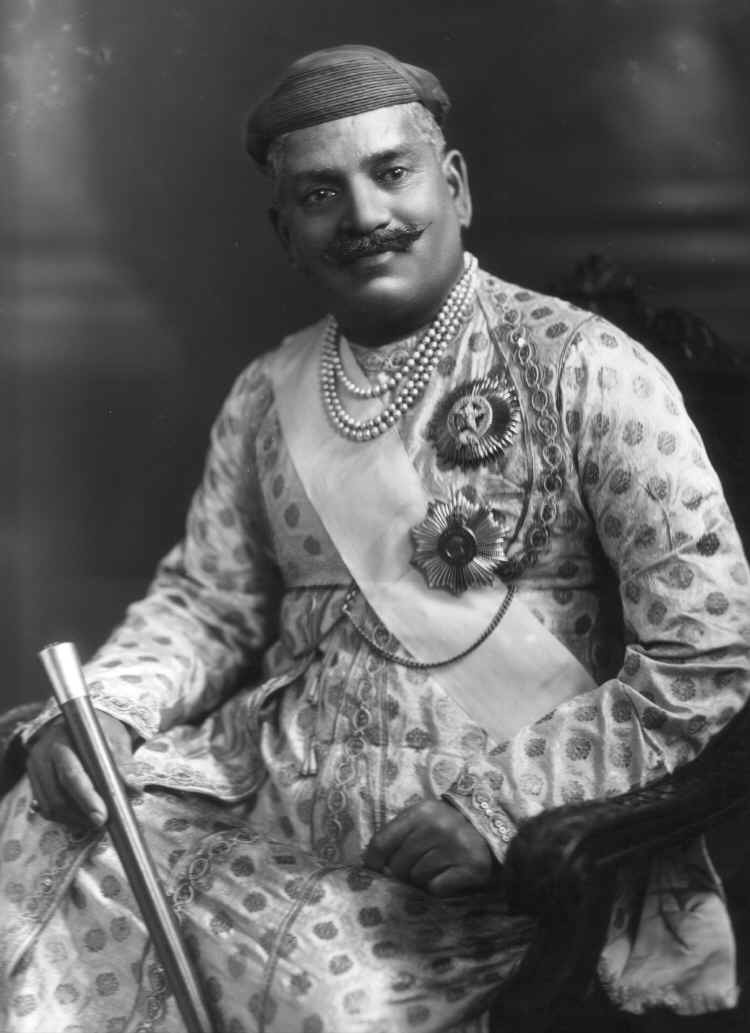
Aundh State was a Maratha princely state in the British Raj, in the Deccan States Agency division of the Bombay Presidency. The Principality of Aundh covered an area of 1298 square kilometers with the population of 88,762 in 1941. The capital of the state was Aundh. History Aundh was a Jagir granted by Chhatrapati Sambhaji to Parshuram Trimbak Pant Pratinidhi, who was a general, administrator and later Pratinidhi of the Maratha Empire during the reign of Chhatrapati Sambhaji and Chhatrapati Rajaram. He played a crucial role in re-capturing Panhala Fort, Ajinkyatara (at Satara), Bhupalgad forts from Mughals during period of 1700–1705. After the fall of Peshwa rule, the British East India company entered separate treaties in 1820 with all the Jagirdars who were nominally subordinate to the Raja of Satara. Aundh became a princely state when Satara state was abolished by the British under the Doctrine of lapse. The last ruler of the Aundh was Raja Shrimant Bhawanrao Shri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large ( Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from thousands of zamindari estates and jagirs. In 1947, princely states covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests ( purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of India
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they are composed of a nested hierarchy of administrative divisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the '' mandals'' of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to ''tehsils'' of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to ''talukas'' of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu). The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas, urban local bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions. Tiers of India The diagram below outlines the six tiers of government: Zones and regions Zones The states of India have been grouped into six zones having an Advisory Council "to develop the habit of cooperative working" among these States. Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. The North East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)