|
King Lobengula
Lobengula Khumalo (c. 1845 – presumed January 1894) was the second and last official king of the Northern Ndebele people (historically called Matabele in English). Both names in the Ndebele language mean "the men of the long shields", a reference to the Ndebele warriors' use of the Nguni shield. Background The Matabele were descendants of a faction of the Zulu people who fled north during the reign of Shaka following the '' mfecane'' ("the crushing") or ''difaqane'' ("the scattering"). Shaka's general, Mzilikazi led his followers away from Zulu territory after a falling-out. In the late 1830s, they settled in what is now called Matabeleland in western Zimbabwe, but they claimed sovereignty over a much wider area. Members of the tribe had a privileged position against outsiders whose lives were subject to the will of the king. In return for their privileges, however, the Ndebele people both men and women had to submit to a strict discipline and status within the hierarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
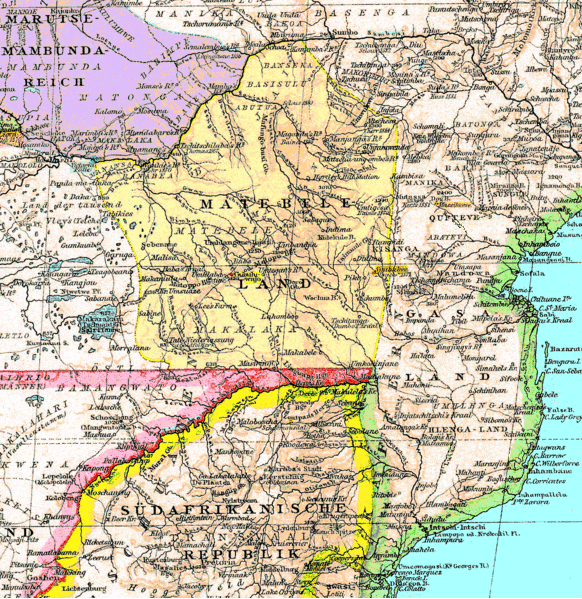
Matabeleland
Matabeleland is a region located in southwestern Zimbabwe that is divided into three provinces: Matabeleland North, Bulawayo, and Matabeleland South. These provinces are in the west and south-west of Zimbabwe, between the Limpopo and Zambezi rivers and are further separated from Midlands by the Shangani River in central Zimbabwe. The region is named after its inhabitants, the Ndebele people who were called "Amatabele"(people with long spears - Mzilikazi 's group of people who were escaping the Mfecani wars). Other ethnic groups who inhabit parts of Matabeleland include the Tonga, Bakalanga, Venda, Nambya, Khoisan, Xhosa, Sotho, Tswana, and Tsonga. The population of Matabeleland is just over 20% of the Zimbabwe's total. The capital and largest city is Bulawayo, other notable towns are Plumtree, Victoria Falls, Beitbridge, Lupane, Esigodini, Hwange and Gwanda. The land is fertile but semi arid. This area has coal and gold deposits. Industries include gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulawayo
Bulawayo (, ; Ndebele: ''Bulawayo'') is the second largest city in Zimbabwe, and the largest city in the country's Matabeleland region. The city's population is disputed; the 2022 census listed it at 665,940, while the Bulawayo City Council claimed it to be about 1.2 million. Bulawayo covers an area of about in the western part of the country, along the Matsheumhlope River. Along with the capital Harare, Bulawayo is one of two cities in Zimbabwe that is also a province. Bulawayo was founded by a group led by Gundwane Ndiweni around 1840 as the kraal of Mzilikazi, the Ndebele king and was known as Gibixhegu. His son, Lobengula, succeeded him in the 1860s, and changed the name to kobulawayo and ruled from Bulawayo until 1893, when the settlement was captured by British South Africa Company soldiers during the First Matabele War. That year, the first white settlers arrived and rebuilt the town. The town was besieged by Ndebele warriors during the Second Matabele War. Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudd Concession
The Rudd Concession, a written concession for exclusive mining rights in Matabeleland, Mashonaland and other adjoining territories in what is today Zimbabwe, was granted by King Lobengula of Matabeleland to Charles Rudd, James Rochfort Maguire and Francis Thompson, three agents acting on behalf of the South African-based politician and businessman Cecil Rhodes, on 30 October 1888. Despite Lobengula's retrospective attempts to disavow it, it proved the foundation for the royal charter granted by the United Kingdom to Rhodes's British South Africa Company in October 1889, and thereafter for the Pioneer Column's occupation of Mashonaland in 1890, which marked the beginning of white settlement, administration and development in the country that eventually became Rhodesia, named after Rhodes, in 1895. Rhodes's pursuit of the exclusive mining rights in Matabeleland, Mashonaland and the surrounding areas was motivated by his wish to annex them into the British Empire as part of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Beit
Alfred Beit (15 February 1853 – 16 July 1906) was a Anglo-German gold and diamond magnate in South Africa, and a major donor and profiteer of infrastructure development on the African continent. He also donated much money to university education and research in several countries, and was the "silent partner" who structured the capital flight from post-Boer War South Africa to Rhodesia, and the Rhodes Scholarship, named after his employee, Cecil Rhodes. Beit's assets were structured around the so-called Corner House Group, which through its holdings in various companies controlled 37 per cent of the gold produced at the Witwatersrand's goldfields in Johannesburg in 1913.See chapter 12 in Rönnbäck & Broberg (2019) Capital and Colonialism. The Return on British Investments in Africa 1869-1969 (Palgrave Studies in Economic History) Life and career Born and brought up in[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India. Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 after her father's three elder brothers died without surviving legitimate issue. Victoria, a constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this area, but the United Kingdom incorporated it into the British Empire in 1806. The name of the group is derived from "boer", which means "farmer" in Dutch and Afrikaans. In addition, the term also applied to those who left the Cape Colony during the 19th century to colonise in the Orange Free State, Transvaal (together known as the Boer Republics), and to a lesser extent Natal. They emigrated from the Cape to live beyond the reach of the British colonial administration, with their reasons for doing so primarily being the new Anglophone common law system being introduced into the Cape and the British abolition of slavery in 1833. The term '' Afrikaners'' or ''Afrikaans people'' is generally used in modern-day South Africa for the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leander Starr Jameson
Sir Leander Starr Jameson, 1st Baronet, (9 February 1853 – 26 November 1917), was a British colonial politician, who was best known for his involvement in the ill-fated Jameson Raid. Early life and family He was born on 9 February 1853, of the Jameson family of Edinburgh, the son of Robert William Jameson (1805–1868), a Writer to the Signet, and Christian Pringle, daughter of Major-General Pringle of Symington House. Robert William and Christian Jameson had twelve children, of whom Leander Starr was the youngest, born at Stranraer, Wigtownshire (now part of Dumfries and Galloway), in the south-west of Scotland, a great-nephew of Professor Robert Jameson, Regius Professor of Natural History at the University of Edinburgh. Fort's biography of Jameson notes that Starr's "chief Gamaliel, however, was a Professor Grant, a man of advanced age, who had been a pupil of his great-uncle, the Professor of Natural History at Edinburgh." Leander Starr Jameson's somewhat unusual n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
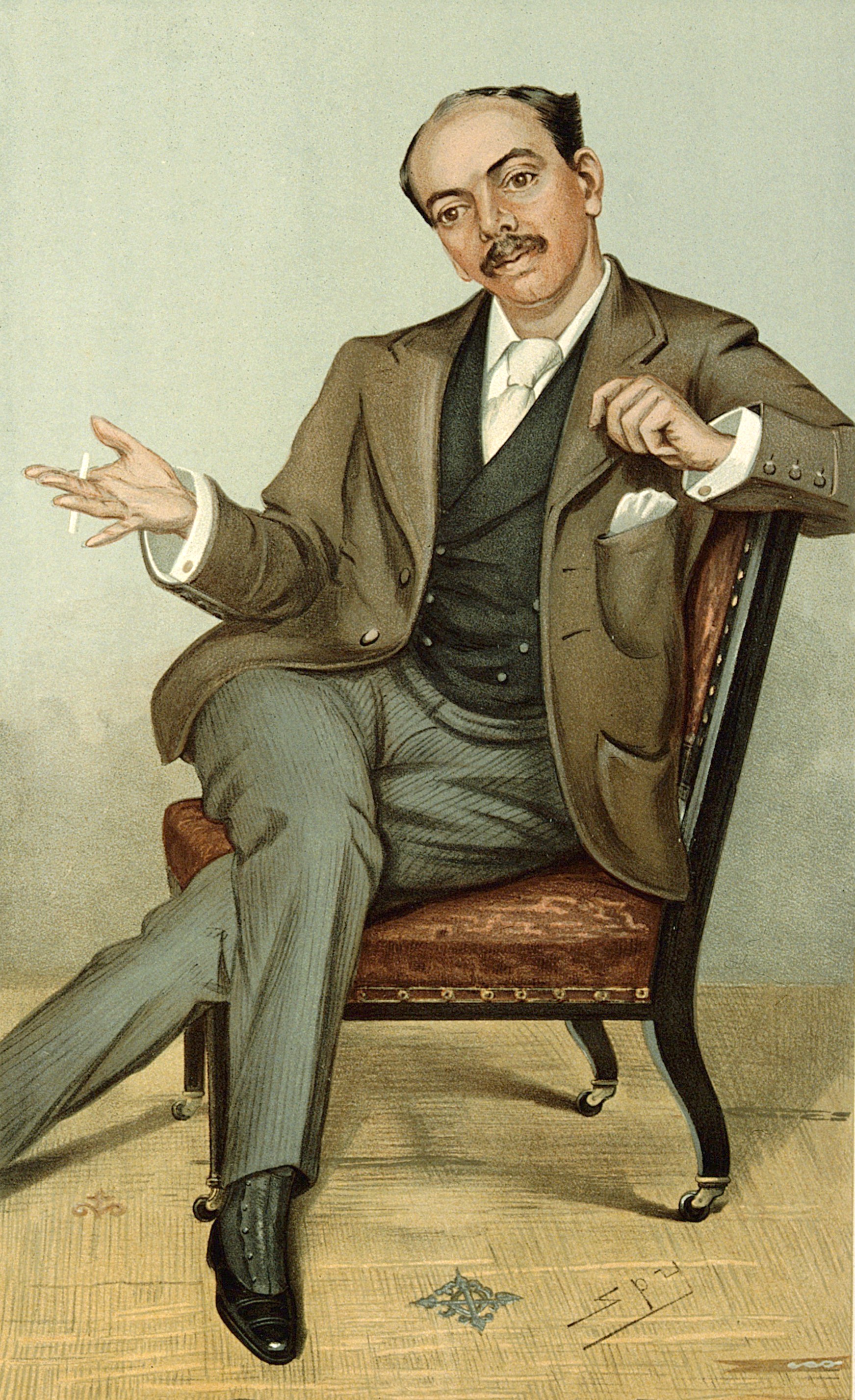
Rochfort Maguire
Rochfort Maguire (18 June 1815 – 29 June 1867) was an Irish Royal Navy officer who served as captain of from 1852 to 1853 during the Franklin search expedition. Career Royal Navy Maguire joined the Royal Navy in 1830. He came to notice when he was wounded in action in 1840 at Sidon whilst serving on HMS ''Wasp'' under Sir Charles Napier.Rochfort Maguire Spink.com. accessed August 2009 He was mentioned in despatches and as a result he was promoted to lieutenant on in the Mediterranean. Search for Franklin Maguire was assigned to the Franklin search expedition in 1848. They sailed out of on a mission to find the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Rudd
Charles Dunell Rudd (22 October 1844 – 15 November 1916) was the main business associate of Cecil Rhodes. Early life He was born at Hamworth Hall, Northamptonshire, the son of Henry Rudd (1809–1884), who had a shipbuilding business in London, and his first wife Mary Stanbridge. Rudd studied at Harrow School (1857–1862) and then entered Trinity College, Cambridge in 1863, where he excelled in playing rackets. He left for Cape Colony in 1865 before completing his degree, according to himself under medical advice. There he hunted with the likes of John Dunn and endeavored in various business enterprises. In the early 1870s, he worked for his brother Thomas' (1831–1902) Port Elizabeth-based trading firm. Partnership with Cecil Rhodes In 1872/3 Rudd and Rhodes became friends and partners, working diamond claims in Kimberley, dealing in diamonds and operating pumping and ice-making machinery, amongst many other odds and ends. Between 1873 and 1881, while Rhodes intermi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tati Concessions Land
The Tati Concession was a land and mining concession created in the western borderlands of the Matabele Kingdom. The concession was originally granted by the Matabele King, Lobengula, son of Mzilikazi, to Sir John Swinburne in exchange for gold and arms. It was administered by the territory known as the Bechuanaland Protectorate after 1893, but was formally annexed to it by Proclamation Number 2 of 1911 by the High Commissioner of Bechuanaland. It was locally administered by a Justice of the Peace. The chief town of this region is Francistown, now one of Botswana's major settlements. Chronology :* 1864: Gold is discovered by Europeans in Tati River area ( Tati Goldfields), then part of the Matabele kingdom. :* 1870: Concession granted to Sir John Swinburne's London and Limpopo Mining Company. :* 1880 The concession was revoked for failure to pay the annual fee, and the concession was granted instead to the Northern Light Mining Company, a syndicate formed by Danial Francis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shashe River
The Shashe River (or Shashi River) is a major left-bank tributary of the Limpopo River in Zimbabwe. It rises northwest of Francistown, Botswana and flows into the Limpopo River where Botswana, Zimbabwe and South Africa meet. The confluence is at the site of the . Hydrology The Shashe River is a highly river, with flow generally restricted to a few days of the year. The river contributes 12.2% of the mean annual |