|
Kindattu
Kindattu (, ''ki-in-da-tu'', also Kindadu, reigned ca. 2000 BC, middle Chronology) was the 6th king of the Shimashki Dynasty,D. T. Potts (2016). ''The Archaeology of Elam.'' Cambridge University Press. p. 135. in Elam (in present-day southwest Iran), at the time of the third dynasty of Ur in ancient Lower Mesopotamia. He is mentioned in the Shilhak-Inshushinak list of kings who did work on the Inshushinak temple in Susa. Apparently, Kindattu invaded and conquered Ur (2004 BC), and captured Ibbi-Sin, the last of the third dynasty of Ur, and made him a prisoner. The Elamites sacked Ur and settled there, but then were defeated by Ishbi-Erra, the first king of the Isin dynasty in his year 16, and later expelled from Mesopotamia. The destructions are related in the Lament for Ur: The Lament for Sumer and Ur then describes the fate of Ibbi-Sin: An Hymn to Ishbi-Erra, although quite fragmentary, mentions the role played by Kindattu in the destruction of Ur. See also * City Lamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
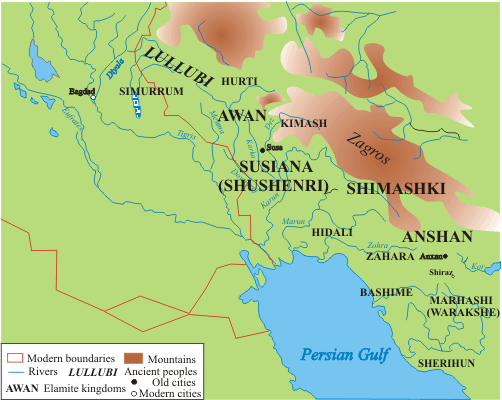
Shimashki Dynasty
The Shimashki or Simashki dynasty (, ''lugal-ene si-mash-giki'' "Kings of the country of Simashgi"), was an early dynasty of the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia, in approximately 2100-1900 BCE. A list of twelve kings of Shimashki is found in the Elamite king-list of Susa, which also contains a list of kings of Awan dynasty. It is uncertain how historically accurate the list is (and whether it reflects a chronological order), although some of its kings can be corroborated by their appearance in the records of neighboring peoples. The Dynasty corresponds to the middle part of the Old Elamite period (dated c.2700 – c. 1600 BC). It was followed by the Sukkalmah Dynasty. Shimashki was likely near today's Masjed Soleyman. Nature of the "Dynasty" Daryaee suggests that, despite the impression from the king-list that the rulers of Shimashki was a dynasty of sequential rulers, it is perhaps better to think of Shimashki as an alliance of various peoples "rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibbi-Sin
Ibbi-Sin ( sux, , ), son of Shu-Sin, was king of Sumer and Akkad and last king of the Ur III dynasty, and reigned c. 2028–2004 BCE (Middle chronology) or possibly c. 1964–1940 BCE (Short chronology). During his reign, the Sumerian empire was attacked repeatedly by Amorites. As faith in Ibbi-Sin's leadership failed, Elam declared its independence and began to raid as well. Ibbi-Sin ordered fortifications built at the important cities of Ur and Nippur, but these efforts were not enough to stop the raids or keep the empire unified. Cities throughout Ibbi-Sin's empire fell away from a king who could not protect them, notably Isin under the Amorite ruler Ishbi-Erra. Ibbi-Sin was, by the end of his kingship, left with only the city of Ur. In 2004 or 1940 BCE, the Elamites, along with "tribesmen from the region of Shimashki in the Zagros Mountains" sacked Ur and took Ibbi-Sin captive; he was taken to the city of Elam where he was imprisoned and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elam
Elam (; Linear Elamite: ''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ; Akkadian: ; he, עֵילָם ''ʿēlām''; peo, 𐎢𐎺𐎩 ''hūja'') was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems from the Sumerian transliteration ''elam(a)'', along with the later Akkadian ''elamtu'', and the Elamite ''haltamti.'' Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East. In classical literature, Elam was also known as Susiana ( ; grc, Σουσιανή ''Sousiānḗ''), a name derived from its capital Susa. Elam was part of the early urbanization of the Near East during the Chalcolithic period (Copper Age). The emergence of written records from around 3000 BC also parallels Sumerian history, where slightly earlier records have been found. In the Old Elamite period (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Dynasty Of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC (middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider to have been a nascent empire. The Third Dynasty of Ur is commonly abbreviated as Ur III by historians studying the period. It is numbered in reference to previous dynasties, such as the First Dynasty of Ur (26-25th century BC), but it seems the once supposed Second Dynasty of Ur was never recorded. The Third Dynasty of Ur was the last Sumerian dynasty which came to preeminent power in Mesopotamia. It began after several centuries of control by Akkadian and Gutian kings. It controlled the cities of Isin, Larsa, and Eshnunna and extended as far north as Upper Mesopotamia. History The Third Dynasty of Ur arose some time after the fall of the Akkad Dynasty. The period between the last powerful king of the Akkad Dynasty, Shar-Kali-Sharri, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishbi-Erra
Ishbi-Erra (Akkadian: d''iš-bi-ir₃-ra'') was the founder of the dynasty of Isin, reigning from ''c.'' 2017 — ''c.'' 1986 BC on the middle chronology or 1953 BC — ''c.'' 1920 BC on the short chronology. Ishbi-Erra was preceded by Ibbi-Sin of the third dynasty of Ur in ancient Lower Mesopotamia, and then succeeded by Šu-ilišu. According to the Weld-Blundell Prism,WB 444, the Weld-Blundell prism, r. 33. Išbi-erra reigned for 33 years and this is corroborated by the number of his extant year-names. While in many ways this dynasty emulated that of the preceding one, its language was Akkadian as the Sumerian language had become moribund in the latter stages of the third dynasty of Ur. Biography At the outset of his career, Ishbi-Erra was an official working for Sumerian King Ibbi-Sin, the last king of the third dynasty of Ur. Ishbi-Erra was described as a man of Mari,Tablet UM 7772. either his origin or the city for which he was assigned. His progress is recorded in let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament For Ur (cropped)
The Lament for Ur, or Lamentation over the city of Ur is a Sumerian lament composed around the time of the fall of Ur to the Elamites and the end of the city's third dynasty (c. 2000 BC). Laments It contains one of five known Mesopotamian "city laments"— dirges for ruined cities in the voice of the city's tutelary goddess. The other city laments are: *The Lament for Sumer and Ur *The Lament for Nippur *The Lament for Eridu *The Lament for Uruk The Book of Lamentations of the Old Testament, which bewails the destruction of Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon in the sixth century B.C., is similar in style and theme to these earlier Mesopotamian laments. Similar laments can be found in the Book of Jeremiah, the Book of Ezekiel and the Book of Psalms, Psalm 137 (). Compilation The first lines of the lament were discovered on the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology catalogue of the Babylonian section, tablet numbers 2204, 2270, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia is a historical region of Mesopotamia. It's located in the alluvial plain of Iraq from the Hamrin Mountains to the Faw Peninsula near the Persian Gulf. In the Middle Ages it was also known as the '' Sawad'' and al-Jazira al-sflia ("Lower Jazira"), which strictly speaking designated only the southern alluvial plain, and ''al-ʻIrāq al-ʻArabi'' ("Arabian Irāq"), as opposed to "Persian Iraq", the Jibal. Lower Mesopotamia was home to Sumer and Babylonia. Regions of Iraq Delimitation The medieval Arab geographers placed the northern border between Iraq and Upper Mesopotamia (the ''Jazirah'') in a line running from Anbar on the Euphrates to Tikrit on the Tigris, although later it was shifted to a line running due west from Tikrit, thus including several towns on the Euphrates past Anbar into Iraq. Geography An alluvial plain begins north of Tikrit Near Hamrin Mountains and extends to the Persian Gulf. Here the Tigris and Euphrates lie above the level of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilhak-Inshushinak
Shilhak-inshushinak (Šilḫak-Inšušinak I) (means powered by inshushinak) was king of Elam from about 1150 to 1120 BC and a king of the Shutrukid Dynasty. When he replaced his older brother, Kutir-nahhunte he became the last great king of Elam. He married the widow of his brother Queen Nahhunte-utu and had 8 children. He waged wars with Babylonia Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state ..., much like his immediate predecessors. He ruled for thirty years and many inscriptions have remained of him. Sources ''Hinz, W. (1964). Das Reich Elam'', Kohl-hammer, Stuttgart. Elamite kings Shuturukid dynasty {{Persia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
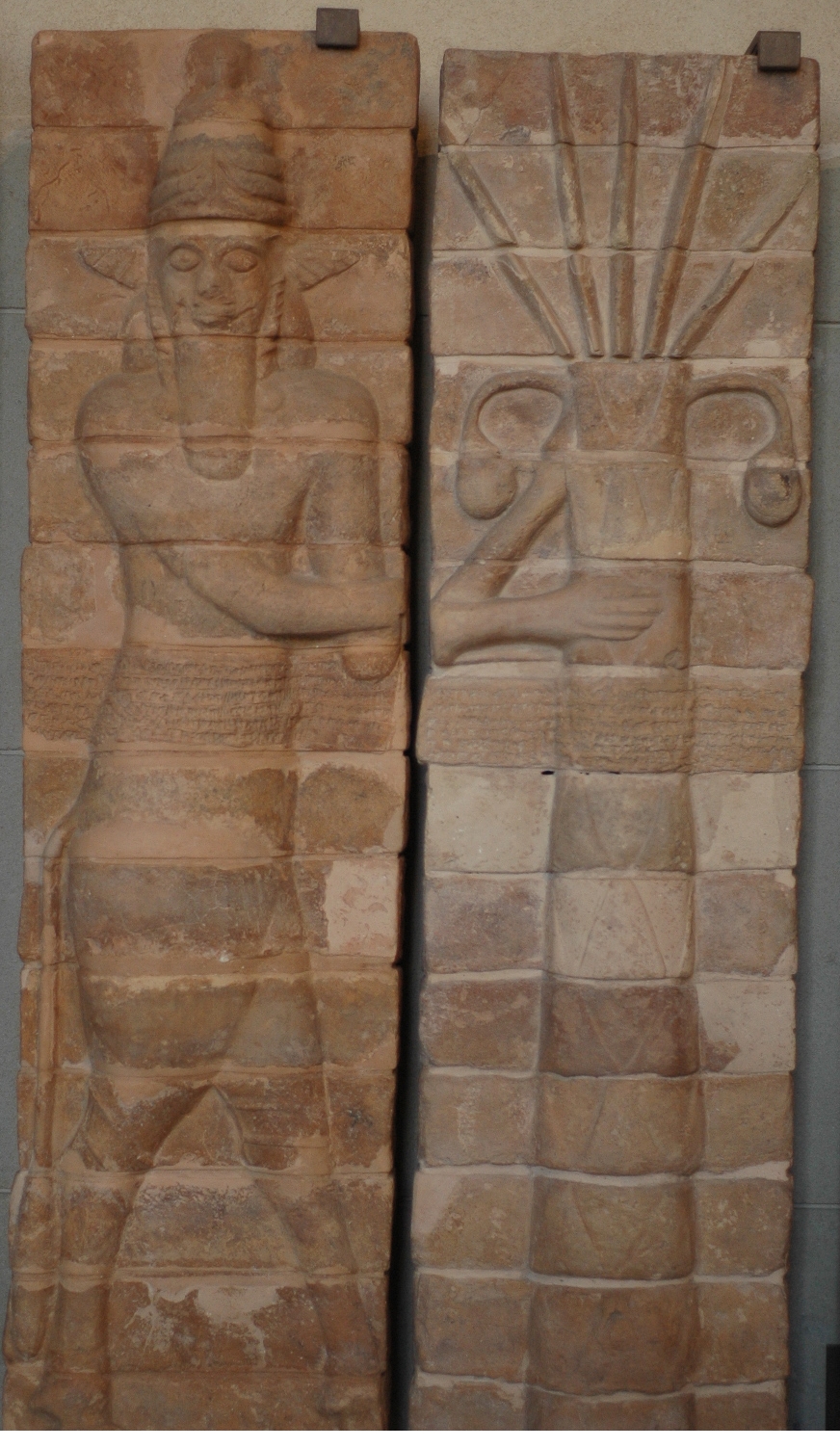
Inshushinak
Inshushinak (Linear Elamite: ''Inšušnak'', Cuneiform: , ''dinšušinakki''; possibly from Sumerian '' en-šušin-a ', "lord of Susa") was one of the major gods of the Elamites and the protector deity of Susa. He was called ''rišar napappair'', "greatest of gods" in some inscriptions. Character and cult Inshushinak is attested for the first time in the treaty of Naram-sin, much like many other Elamite gods. He played an important role as a god connected to royal power in the official ideology of many Elamite dynasties. King Atta-Hushu of the Sukkalmah dynasty called himself "the shepherd of the god Inshushinak." Multiple rulers dedicated new construction projects to Inshushinak using the formula "for his (eg. the king's) life." Shutrukids commonly used the title "(king) whose kingdom Inshushinak loves." He was also a divine witness of contracts, similar to Mesopotamian Shamash. Sometimes he shared this role with both Shamash and the Elamite god Simut in documents from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament For Ur
The Lament for Ur, or Lamentation over the city of Ur is a Sumerian lament composed around the time of the fall of Ur to the Elamites and the end of the city's third dynasty (c. 2000 BC). Laments It contains one of five known Mesopotamian "city laments"—dirges for ruined cities in the voice of the city's tutelary goddess. The other city laments are: *The Lament for Sumer and Ur *The Lament for Nippur *The Lament for Eridu *The Lament for Uruk The Book of Lamentations of the Old Testament, which bewails the destruction of Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon in the sixth century B.C., is similar in style and theme to these earlier Mesopotamian laments. Similar laments can be found in the Book of Jeremiah, the Book of Ezekiel and the Book of Psalms, Psalm 137 (). Compilation The first lines of the lament were discovered on the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology catalogue of the Babylonian section, tablet numbers 2204, 2270, 230 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament For Sumer And Ur
The lament for Sumer and Urim or the lament for Sumer and Ur is a poem and one of five known Mesopotamian "city laments"—dirges for ruined cities in the voice of the city's tutelary goddess. The other city laments are: *The Lament for Ur *The Lament for Nippur *The Lament for Eridu *The Lament for Uruk In 2004 BCE, during the last year of King Ibbi-Sin's reign, Ur fell to an army from the east. The Sumerians decided that such a catastrophic event could only be explained through divine intervention and wrote in the lament that the gods, "An, Enlil, Enki and Ninmah decided r'sfate" The literary works of the Sumerians were widely translated (e.g., by the Hittites, Hurrians and Canaanites). Sumeria historian Samuel Noah Kramer wrote that later Greek as well as Hebrew texts "were profoundly influenced by them." Contemporary scholars have drawn parallels between the lament and passages from the bible (e.g., "the Lord departed from his temple and stood on the mountain east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Lament
A City Lament is a poetic elegy for a lost or fallen city. This literary genre, from around 2000 BCE onwards, was particularly prevalent in the Mesopotamian region of the Ancient Near East. The Bible's Book of Lamentations concerning Jerusalem around 586 BCE, contains some elements of a city lament. Features In the five known Mesopotamian City Laments, the lament is written in voice of the city's tutelary goddess. The destruction of the city, the mass killing of its inhabitants, and the loss of its central temple are vividly described. Special attention is given to the divine sphere, where the gods order the destruction of the city, the city patron gods implore against this, but in vain. The patron gods are exiled to live as deportees in foreign cites, lamenting their devastated shrine. Subsequently they return from exile and renew their former existence. Mesopotamia The Lament for Ur, or Lamentation over the city of Ur is a Sumerian lament composed around the time of the fall o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)