|
Kim Sung-hoon (biologist)
Dr. Kim Sunghoon is a South Korean biologist. Education *1981 B.S. Seoul National University *1983 M.S. Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology *1991 Ph.D. Brown University, U.S. Work Dr. Sunghoon Kim has been studying novel functions of human aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases(ARSs) and searching for their pathophysiological connections to human diseases(PNAS 105:11043, 2008; Nat Rev Cancer 11:708, 2011). He has identified potent novel tumor suppressors such as AIMP2/p38(Nat Genet 34:330, 2003), AIMP3/p18(Cell, 120:209, 2005). Besides, he has also investigated novel extracellular activities of ARSs and associated factors such as lysyl-tRNA synthetase(KRS)(PNAS 102, 6356, 2005), tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase(WRS)(Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:149, 2004) and AIMP1/p43(PNAS 103:14913, 2006). He also discovered the oncogenic variant of AIMP2, designated AIMP2-DX2, as one of the critical factors that determines the survival of lung cancer patients(Plos Genet 7:e1001351, 2011). More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seoul National University
Seoul National University (SNU; ) is a national public research university located in Seoul, South Korea. Founded in 1946, Seoul National University is largely considered the most prestigious university in South Korea; it is one of the three " SKY" universities, denoting the top three institutions in the country. The university has three campuses: the main campus in Gwanak District and two additional campuses in Daehangno and Pyeongchang County. The university comprises sixteen colleges, one graduate school and nine professional schools. The student body consists of nearly 17,000 undergraduate and 11,000 graduate students. According to data compiled by KEDI, the university spends more on its students per capita than any other universities in the country that enroll at least 10,000 students. Seoul National University holds a memorandum of understanding with over 700 academic institutions in 40 countries, the World Bank and a general academic exchange program with the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown University
Brown University is a private research university in Providence, Rhode Island. Brown is the seventh-oldest institution of higher education in the United States, founded in 1764 as the College in the English Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations. Brown is one of nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Admissions at Brown is among the most selective in the United States. In 2022, the university reported a first year acceptance rate of 5%. It is a member of the Ivy League. Brown was the first college in the United States to codify in its charter that admission and instruction of students was to be equal regardless of their religious affiliation. The university is home to the oldest applied mathematics program in the United States, the oldest engineering program in the Ivy League, and the third-oldest medical program in New England. The university was one of the early doctoral-granting U.S. institutions in the late 19th century, adding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korea Science Award
The Korea Science Award is an award presented to South Koreans and Korean scientists working in domestic universities or research positions. It is currently jointly presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Research achievements are limited to that of a single project conducted in Korea. Potential recipients go through a several stage review which includes consolation with foreign scholars. From 1987, it was biennially awarded to frequently three to four recipients. From 2016, it is given annually to two individuals while two other individuals are presented with the Korea Engineering Award The Korea Engineering Award is an award presented to South Koreans and Korean engineers working in domestic universities or research positions. It is currently jointly presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundat .... The Korea Science Award comes with a presidential commendation and a research grant of 30 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top Scientist And Technologist Award Of Korea
Top Scientist and Technologist Award of Korea () is one of two annual awards given in South Korea by the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies () with the other being a government award for contribution to science and technology promotion. The Top Scientist and Technologist Award of Korea was started in 2003 as the successor to the Science and Technology Award of Korea which was established in 1968. The award is to foster honor and pride and create an environment in which people can focus on research and development by discovering and encouraging scientists and engineers with outstanding achievements who can represent South Korea. While previously given to multiple individuals, from 2003 only person is selected for each cycle. Laureates receive the award and 300 million KRW cash prize. Laureates See also * National Scientist of the Republic of Korea * List of general science and technology awards * Highest Science and Technology Award The Highest Science and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually specialize in a particular branch (e.g., molecular biology, zoology, and evolutionary biology) of biology and have a specific research focus (e.g., studying malaria or cancer). Biologists who are involved in basic research have the aim of advancing knowledge about the natural world. They conduct their research using the scientific method, which is an empirical method for testing hypotheses. Their discoveries may have applications for some specific purpose such as in biotechnology, which has the goal of developing medically useful products for humans. In modern times, most biologists have one or more academic degrees such as a bachelor's degree plus an advanced degree like a master's degree or a doctorate. Like other scientists, biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korea Advanced Institute Of Science And Technology
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) is a national research university located in Daedeok Innopolis, Daejeon, South Korea. KAIST was established by the Korean government in 1971 as the nation's first public, research-oriented science and engineering institution. KAIST is considered to be one of the most prestigious universities in the nation. KAIST has been internationally accredited in business education, and hosting the Secretariat of the Association of Asia-Pacific Business Schools (AAPBS). KAIST has 10,504 full-time students and 1,342 faculty researchers (as of Fall 2019 Semester) and had a total budget of US$765 million in 2013, of which US$459 million was from research contracts. In 2007, KAIST partnered with international institutions and adopted dual degree programs for its students. Its partner institutions include the Technical University of Denmark, Carnegie Mellon University, the Georgia Institute of Technology, the Technical University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
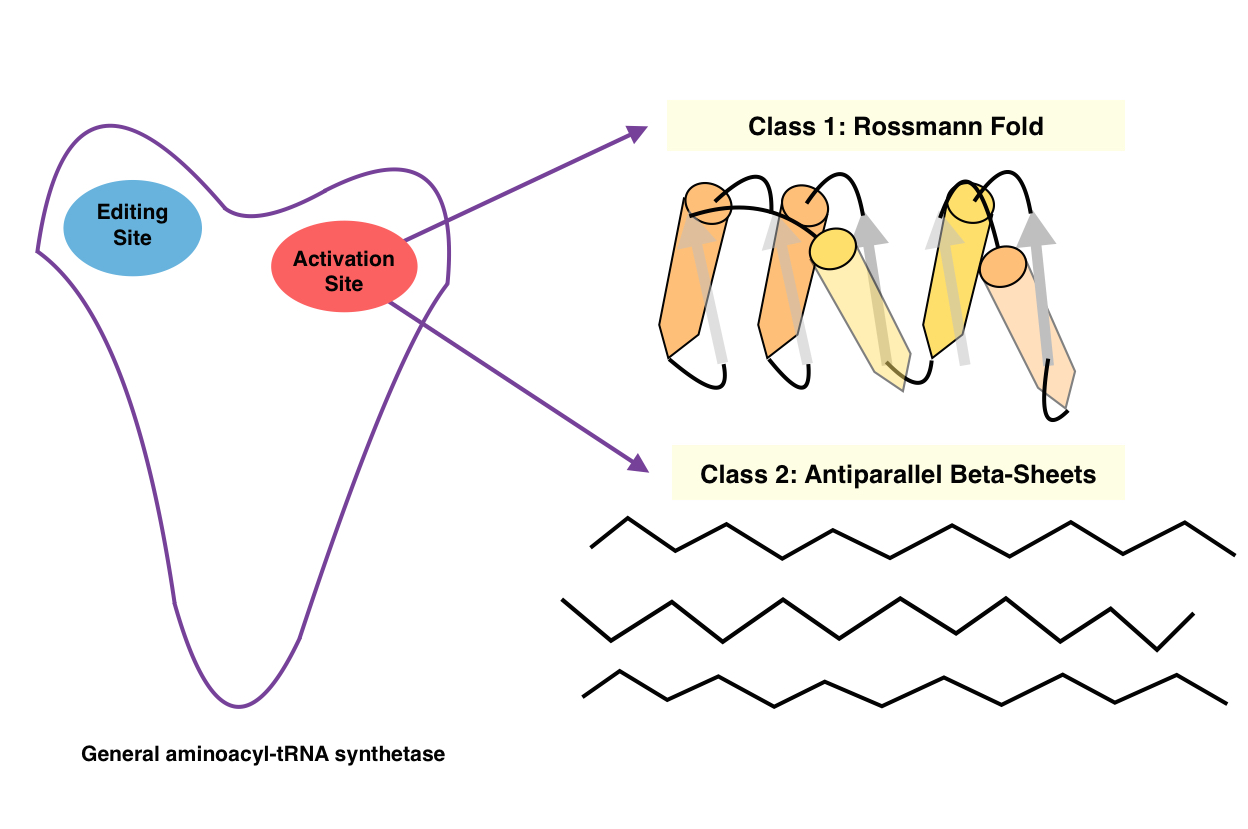
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide, according to the genetic code. Aminoacyl tRNA therefore plays an important role in RNA translation, the expression of genes to create proteins. Mechanism The synthetase first binds ATP and the corresponding amino acid (or its precursor) to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, releasing inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). The adenylate-aaRS complex then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sung Kyun Kwan University
Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU or simply ''Seongdae'', Hangul: 성균관대학교; Hanja: 成均館大學校) is a private comprehensive research university in South Korea. The institution traces its origins to the historic Sungkyunkwan, founded in 1398 and located in central Seoul. SKKU Official Brochure 2013 As the foremost educational institution of the Joseon, Joseon Dynasty, it was governed by the great code of the state administration Gyeongguk Daejeon, the great code [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donghun Award
The Donghun Award is an annual award presented by the Korean Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology awarded to members who made creative research achievements in biochemistry and applied fields. The award was established in accordance with the wishes of Park Ki-Eok and first presented in 1998. Winners are selection by the Constitutional Committee and approval by the board of directors and is notified in April or May with the award ceremony taking place in May. Laureates See also * List of biology awards * William C. Rose Award The William C. Rose Award given by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology recognizes outstanding contributions to biochemical and molecular biological research and a demonstrated commitment to the training of younger scientists ... * Otto Warburg Medal References {{DEFAULTSORT:Donghun Award Awards established in 1998 1998 establishments in South Korea Science and technology awards South Korean awards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Society For Biochemistry And Molecular Biology
The Korean Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (KSBMB; ) is a scholarly association of Korean biochemists and molecular biologists with approximately 15,000 members. It is a member of the Federation of Asia and Oceania Biochemists and Molecular Biologists (FAOBMB), International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST), and Korean Academy of Medical Sciences (KAMS). Naming The Society was originally founded in 1948 under the name the Korean Biochemical Society. In 1995, the name changed to the Korean Society of Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. In 2010, it merged with the Korean Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (founded in 1967) and from then have used the name the Korean Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Journals The society publishes ''Experimental & Molecular Medicine'' (EMM) and ''Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Reports'' (BMB Reports) annually, ''Web ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korean Biologists
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |