|
Kiltonanlea
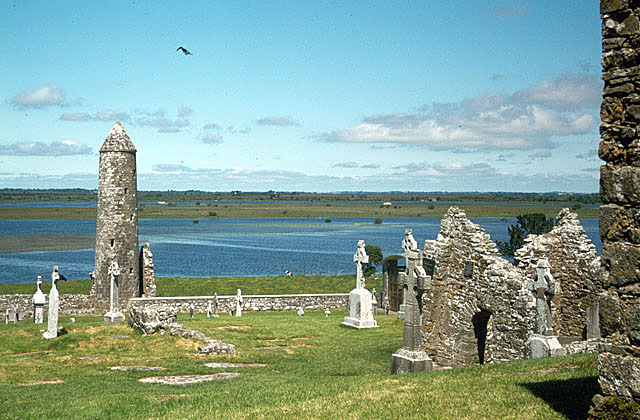
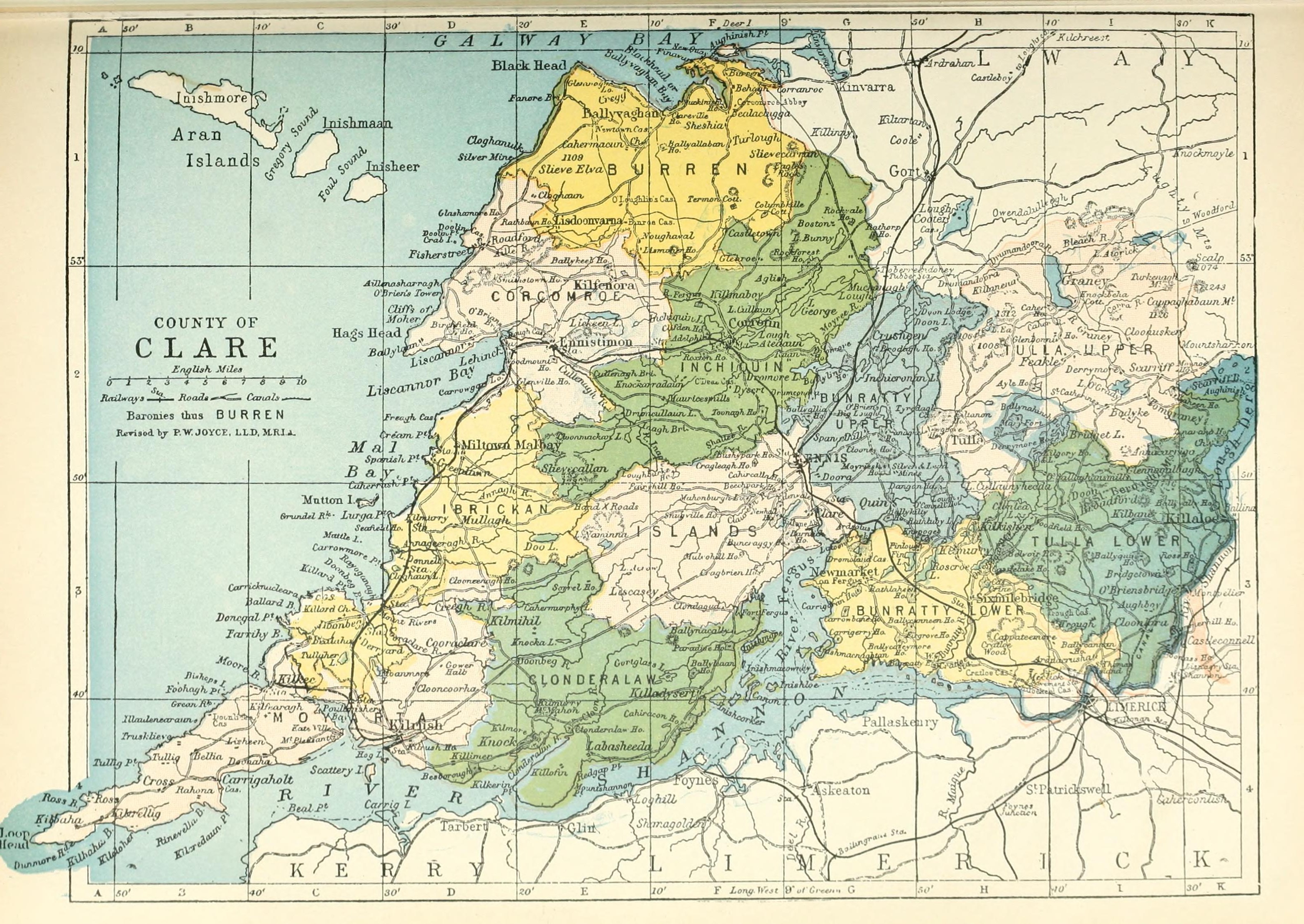
Kiltenanlea or Kiltonanlea () is a civil parish in County Clare, Ireland. Name The name in Irish is , meaning 'of Saint Senán, the hoary'. Saint Senán is considered to be the brother of Saint Mochuille in local tradition, and is thought to be different from Saint Senán of Iniscathy. However Saint Senán's festival is held on 8 March in Kiltenanlea, the same day that the festival of Saint Senán of Iniscathy is celebrated according to the Martyrology of Donegal. Location The parish is in the barony of Tulla Lower, SSW of Killaloe on the road to Limerick. It is bounded to the east by the River Shannon. As of 1837 it held 6,595 statute acres, as applotted under the tithe act, most of which was cultivated, but including some bog. The parish contains the village of Cloonlara. It extends about , and covers . As of 1841 the parish had a population of 4,016 in 629 houses. The Roman Catholic chapels of Kiltonanlea and Killokennedy were united in one parish. A canal about long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulla Lower
Tulla Lower (or Tullagh Lower) is a barony in County Clare, Ireland. This ancient geographical division of land is in turn divided into eight civil parishes. Legal context Baronies were created after the Norman invasion of Ireland as divisions of counties and were used the administration of justice and the raising of revenue. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they have been administratively obsolete since 1898. However, they continue to be used in land registration and in specification, such as in planning permissions. In many cases, a barony corresponds to an earlier Gaelic túath which had submitted to the Crown. Location Tulla Lower lies in the south-east of County Clare. As late as 1831, it was united with Tulla Upper as a single barony. The barony is bounded to the east by Lough Derg and the River Shannon which separates it from the counties of Tipperary and Tipperary. Within the county of Clare, it is bounded by the baronies of Bunratty Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloonlara
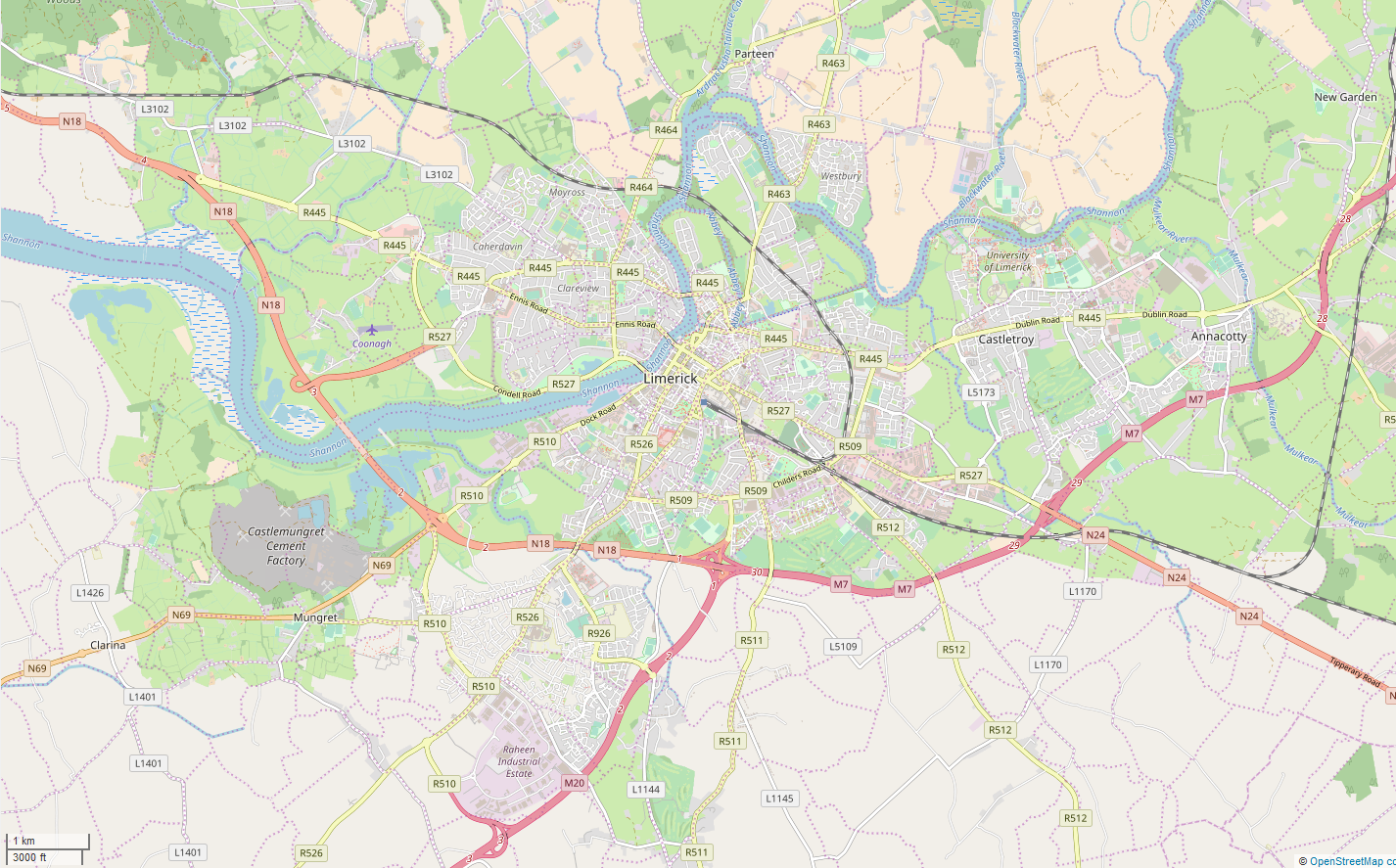
Clonlara, officially Cloonlara (), is a village in County Clare, Ireland, and a Roman Catholic parish of the same name. Village and amenities Clonlara is in the east of County Clare in the civil parish of Kiltonanlea or Doonass, barony of Tulla Lower. It lies between the River Shannon to the east and the Clare hills to the west and north. Clonlara village is on the road between Killaloe and Limerick, 8 km north-east of the centre of Limerick city. In 1841 there were 219 people in 31 houses. The village lies beside the head-race canal that deliver water to power the Ardnacrusha power plant a few kilometres to the southwest. Clonlara has an equestrian centre and a Gaelic Athletic Association club, Clonlara GAA. Religion The village is part of Clonlara (Doonas and Truagh) parish of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Killaloe, and the Church of Ireland parish of Kiltenanlea. The parish has two churches: Mary, the Mother of God (Truagh) and St Senan's (Clonlara), both Roman Cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In Ireland
Civil parishes () are units of territory in the island of Ireland that have their origins in old Gaelic territorial divisions. They were adopted by the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Ireland and then by the Elizabethan Kingdom of Ireland, and were formalised as land divisions at the time of the Plantations of Ireland. They no longer correspond to the boundaries of Roman Catholic or Church of Ireland parishes, which are generally larger. Their use as administrative units was gradually replaced by Poor_law_union#Ireland, Poor Law Divisions in the 19th century, although they were not formally abolished. Today they are still sometimes used for legal purposes, such as to locate property in deeds of property registered between 1833 and 1946. Origins The Irish parish was based on the Gaelic territorial unit called a ''túath'' or ''Trícha cét''. Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman barons retained the ''tuath'', later renamed a parish or manor, as a un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martyrology Of Donegal
A martyrology is a catalogue or list of martyrs and other saints and beati arranged in the calendar order of their anniversaries or feasts. Local martyrologies record exclusively the custom of a particular Church. Local lists were enriched by names borrowed from neighbouring churches. Consolidation occurred, by the combination of several local martyrologies, with or without borrowings from literary sources. This is the now accepted meaning in the Latin Church. In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the nearest equivalent to the martyrology are the Synaxaria and the longer Menaia, both sometimes known as Menologia. Simple martyrologies only enumerate names. Historical martyrologies, also sometimes called passionaries, also include stories or biographical details. Oldest examples The martyrology, or ''ferial'', of the Roman Church in the middle of the fourth century still exists. It comprises two distinct lists, the '' Depositio martyrum'' and the '' Depositio episcoporum'', lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigit Of Kildare
Saint Brigid of Kildare or Saint Brigid of Ireland (; Classical Irish: ''Brighid''; ; ) is the patroness saint (or 'mother saint') of Ireland, and one of its three national saints along with Patrick and Columba. According to medieval Irish hagiographies, she was an abbess who founded the important abbey of Kildare (''Cill Dara''), as well as several other convents of nuns. There are few documented historical facts about her, and her hagiographies are mainly anecdotes and miracle tales, some of which are rooted in pagan folklore.Farmer, David. ''The Oxford Dictionary of Saints'' (Fifth Edition, Revised). Oxford University Press, 2011. pp.66–67, 467–470. They say Brigid was the daughter of an Irish clan chief and an enslaved Christian woman, and was fostered in a druid's household before becoming a consecrated virgin. She is patroness of many things, including poetry, learning, healing, protection, blacksmithing, livestock, and dairy production. In her honour, a perpetua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killokennedy
Killokennedy () is a civil parish in County Clare, Ireland. Location Killokennedy lies in the barony of Tulla Lower, County Clare, about west of Killaloe. It is on the road from Killaloe to Ennis. In 1837, as applotted under the tithe act, it contained . Much of this is mountain pasture, and there is some bog. The Cragnamurragh and Glennagalliagh mountains rise to and in altitude. The parish is about covering in total. History As of 1841 there were 3811 inhabitants in 596 houses. The Catholic chapel of Killokennedy was united to the chapel of Kiltenanlea. Part of Killokennedy was amalgamated with Kilseily to form what is now the parish of Broadford in the Diocese of Killaloe. Townlands Townland A townland (; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a traditional small land division used in Ireland and in the Western Isles of Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of medieval Gaelic origin, predating the Norman invasion, and mo ...s are Aharinaghbeg, Ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( or archaic ') is the major river on the island of Ireland, and at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of Ireland. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying into the Atlantic Ocean through the long Shannon Estuary. Limerick city stands at the point where the river water meets the sea water of the estuary. The Shannon is tidal east of Limerick as far as the base of the Ardnacrusha dam. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south (Leinster and most of Munster; County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. With a population of 102,287 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, Limerick is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, third-most populous urban area in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland. It was founded by Scandinavian settlers in 812, during the Viking Age. The city straddles the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, Limerick, King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey River, Limerick, Abbey Rivers. Limerick is at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the Local gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killaloe, County Clare
Killaloe ( ; ) is a small town in east County Clare, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It lies on the River Shannon on the western bank of Lough Derg (Shannon), Lough Derg and is connected by Killaloe Bridge to the "twin town" of Ballina, County Tipperary, Ballina on the eastern bank of the lake. The Killaloe Electoral Area is one of six such areas in County Clare and returns four members to Clare County Council. Killaloe is at the center of the Killaloe, County Clare (Civil parish), Killaloe Civil parish. History The town owes its origin to a sixth-century monastic settlement founded by Saint Molua, or Lua, on an island in the Shannon 1 km downstream from the present Killaloe Bridge which later moved onto the mainland. In the tenth century it was a base for Brian Boru as it controlled the strategic crossing of the Shannon above Limerick, where the Viking#Ireland, Vikings were in control. Brian Boru had his palace, Kincora (Ceann Coradh), on the high ground where the curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Ireland
Ireland ( ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland, with a population of about 5.4 million. Its capital city, capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island, with a population of over 1.5 million. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, which is Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a Unitary state, unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the , consists of a lower house, ; an upper house, ; and an elected President of Ireland, president () who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the (prime minister, ), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Summer Time
Western European Summer Time (WEST, UTC+01:00) is a summer daylight saving time scheme, 1 hour ahead of Greenwich Mean Time and Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in: * the Canary Islands * Portugal (including Madeira but not the Azores) * the Faroe Islands The following countries also use the same time zone for their daylight saving time but use a different title: *United Kingdom, which uses British Summer Time (BST) *Ireland, which uses Irish Standard Time (IST) ( (ACÉ)). Also sometimes erroneously referred to as "Irish Summer Time" (). The scheme runs from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October each year. At both the start and end of the schemes, clock changes take place at 01:00 UTC+00:00. During the winter, Western European Time (WET, GMT+0 or UTC+00:00) is used. The start and end dates of the scheme are asymmetrical in terms of daylight hours: the vernal time of year with a similar amount of daylight to late October is mid-February, well before th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |