|
Kiel Glacier
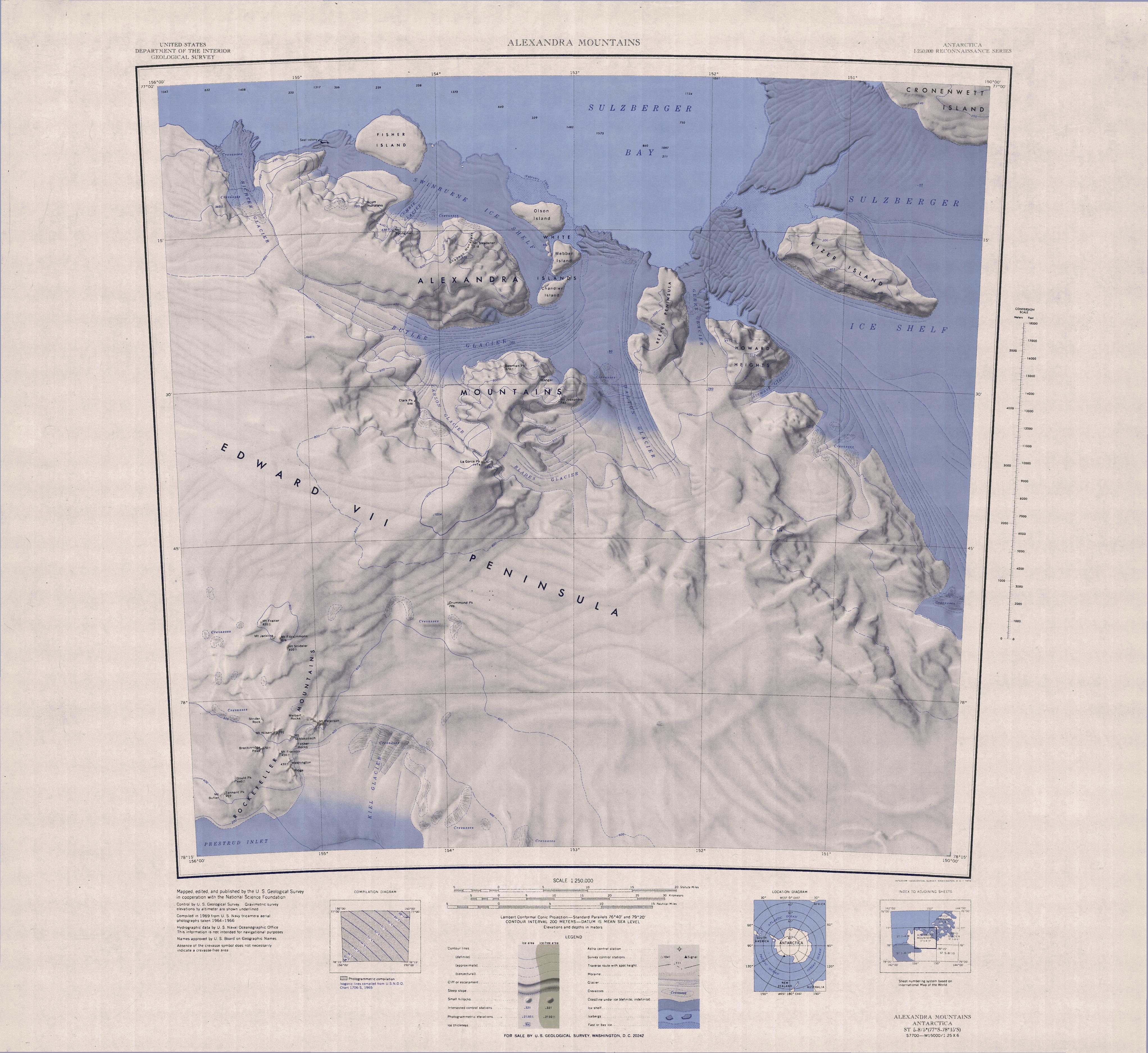
The Rockefeller Mountains () are a group of low-lying, scattered granite peaks and ridges, almost entirely snow-covered, standing south-southwest of the Alexandra Mountains on the Edward VII Peninsula of Antarctica. Location The Rockefeller Mountains are on the south side of the Edward VII Peninsula in Marie Byrd Land, to the south of the Alexandra Mountains. They are north of the Prestrud Inlet and west of the Kiel Glacier. They run from southwest to northeast. Western features, from south to north, include Mount Butler, Tennant Peak, Gould Peak, Breckinridge Peak, Mount Nilsen and Strider Rock- Central features, from south to north, include Washington Ridge, Mount Franklin, Fokker Rocks, Mount Schlossbach, Mount Paterson and Melbert Rocks. Northern features, from south to north, include Mount Shideler, Mount Fitzsimmons, Mount Jackling and Mount Frazier. Drummond Peak is an isolated nunatak to the northeast. Appearance The exposed part of the Rockefeller Mountains covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandra Mountains
The Alexandra Mountains () are a group of low, separated mountains in the north portion of Edward VII Peninsula, just southwest of Sulzberger Bay in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. Discovery and name The Alexandra Mountains were discovered in January–February 1902 by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) during an exploratory cruise of the ''Discovery'' along the Ross Ice Shelf. They were named for Alexandra of Denmark, then Queen of the United Kingdom. Location The Alexandra Mountains are on the north side of the Edward VII Peninsula, to the north of the Rockefeller Mountains. They lie on both sides of the Butler Glacier, which flows from west to east, then turns north to enter Sulzberger Bay. Other glaciers include Cumbie Glacier, flowing from Mount Youngman, Larson Glacier, which feeds Butler Glacier, Dalton Glacier to the west and Blades Glacier to the south. Northern features, from northwest to southeast, include Scott Nunataks, Mount Youngman, Sneddo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward VII Peninsula
King Edward VII Land or King Edward VII Peninsula is a large, ice-covered peninsula which forms the northwestern extremity of Marie Byrd Land in Antarctica. The peninsula projects into the Ross Sea between Sulzberger Bay and the northeast corner of the Ross Ice Shelf, and forms part of the Ross Dependency. Edward VII Peninsula is defined by the Ross Ice Shelf on the southwest, Okuma Bay on the west, and to the east by Sulzberger Bay and the Saunders Coast, all essentially on the Ross Sea / Southern Ocean in Antarctica. The northwest extremity of the peninsula is Cape Colbeck. Edward VII Peninsula is located at . The western coast is Shirase Coast. In the north and east the Swinburne Ice Shelf is located. Edward VII Peninsula was discovered on 30 January 1902 by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) (1901–1904) under Robert Falcon Scott, who named it King Edward VII Land for British monarchy, King Edward VII of the United Kingdom. The coastline was further explored b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Byrd Land
Marie Byrd Land (MBL) is an unclaimed region of Antarctica. With an area of , it is the largest unclaimed territory on Earth. It was named after the wife of American naval officer Richard E. Byrd, who explored the region in the early 20th century. The territory lies in West Antarctica, east of the Ross Ice Shelf and the Ross Sea and south of the Pacific Ocean portion of the Antarctic or Southern Ocean, extending eastward approximately to a line between the head of the Ross Ice Shelf and Eights Coast. It stretches between 158°W and 103°24'W. The inclusion of the area between the Rockefeller Plateau and Eights Coast is based upon Byrd's exploration. Overview Because of its remoteness, even by Antarctic standards, most of Marie Byrd Land (the portion east of 150°W) has not been claimed by any sovereign state. It is by far the largest single unclaimed territory on Earth, with an area of , including Eights Coast, immediately east of Marie Byrd Land. In 1939, United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Gorce Peak
The Alexandra Mountains () are a group of low, separated mountains in the north portion of Edward VII Peninsula, just southwest of Sulzberger Bay in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. Discovery and name The Alexandra Mountains were discovered in January–February 1902 by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) during an exploratory cruise of the ''Discovery'' along the Ross Ice Shelf. They were named for Alexandra of Denmark, then Queen of the United Kingdom. Location The Alexandra Mountains are on the north side of the Edward VII Peninsula, to the north of the Rockefeller Mountains. They lie on both sides of the Butler Glacier, which flows from west to east, then turns north to enter Sulzberger Bay. Other glaciers include Cumbie Glacier, flowing from Mount Youngman, Larson Glacier, which feeds Butler Glacier, Dalton Glacier to the west and Blades Glacier to the south. Northern features, from northwest to southeast, include Scott Nunataks, Mount Youngman, Sneddo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byrd Antarctic Expedition
Richard Evelyn Byrd Jr. (October 25, 1888 – March 11, 1957) was an United States Navy, American naval officer, and pioneering aviator, polar explorer, and organizer of polar logistics. Aircraft flights in which he served as a navigator and expedition leader crossed the Atlantic Ocean, a segment of the Arctic Ocean, and a segment of the Antarctic Plateau. He is also known for discovering Mount Sidley, the largest dormant volcano in Antarctica. Byrd claimed to be the first to reach both the North Pole, North and South Poles by air. However, there is some controversy as to whether Byrd was actually the first person to reach the North Pole. It is generally believed that the distance Byrd claimed to fly was longer than the possible fuel range of his airplane. He was a List of Medal of Honor recipients during peacetime, recipient of the Medal of Honor, the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration, and the Navy Cross, the second highest honor for valor given by the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John D
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurence McKinley Gould
Laurence McKinley Gould (August 22, 1896 – June 21, 1995) was an American geologist, educator, and polar explorer. He made expeditions to both the Arctic and Antarctic, and was chief scientist on Richard Evelyn Byrd's first Antarctic expedition, which Gould described in his 1931 book ''Cold: the Record of an Antarctic Sledge Journey.'' He served as president of Carleton College from 1945 to 1962, and president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 1964. His namesakes include the research vessel ''Laurence M. Gould'' as well as Antarctic features including Gould Bay, Gould Coast, and Mount Gould. Biography Gould was born in Lacota, Michigan on August 22, 1896. After completing high school in South Haven, Michigan in 1914, he went to Boca Raton, Florida and taught grades 1 to 8 in a one-room school for two years, while saving money for college. He enrolled at the University of Michigan in 1916, but interrupted his education the following year to enlis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Storm
A winter storm (also known as snow storm) is an event in which wind coincides with varieties of precipitation that only occur at freezing temperatures, such as snow, mixed snow and rain, or freezing rain. In temperate continental and subarctic climates, these storms are not necessarily restricted to the winter season, but may occur in the late autumn and early spring as well. A snowstorm with strong winds and low visibility is called a blizzard. Formation Winter storms are formed when moist air rises up into the atmosphere, creating low pressure near the ground and clouds up in the air. The air can also be pushed upwards by hills or large mountains. The upward motion is called lift. The moisture is collected by the wind from large bodies of water, such as a big lake or the ocean. If temperature is below freezing, , near the ground and up in the clouds, precipitation will fall as snow, ice, rain and snow mixed (sleet), ice pellets or even graupel (soft hail). Since cold ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
With Byrd At The South Pole
''With Byrd at the South Pole'' (1930) is a sound part-talkie documentary film about Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd and his 1st quest to the South Pole beginning at the Little America-Exploration Base. In addition to sequences with audible dialogue or talking sequences, the film features a synchronized musical score and sound effects along with English intertitles. The dialogue sequences consist mainly of narration that is read aloud by Floyd Gibbons. The film won at the 3rd Academy Awards for Best Cinematography. The film was the first documentary to win any Oscar and the only one to win cinematography. Cast *Richard E. Byrd...Himself (Expedition Commander) (as Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd) * Claire Alexander...Supply Officer *Bernt Balchen...Aviation Pilot * George H. Black...Seaman and Tractor Man * Quin A. Blackburn...Topographer * Kennard F. Bubier...Aviation Mechanic * Christopher Braathen...Seaman, Ski Man * Jacob Bursey...Seaman, Dog Driver * Arnold H. Clark... Firem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Breckinridge
Henry Skillman Breckinridge (May 25, 1886 – May 2, 1960) was an American lawyer and politician who was a member of the prominent Breckinridge family and served as the United States Assistant Secretary of War from 1913 to 1916. During the Lindbergh kidnapping trial he served as Charles Lindbergh's attorney. Breckinridge opposed the New Deal from the right. As an opponent of President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the 1936 Democratic primaries he polled less than 3 percent of the vote. Early life Breckinridge was born in Chicago, on May 25, 1886, to Louise Ludlow Dudley and Joseph Cabell Breckinridge Sr.Brown, Alexander The Cabells and Their Kin: A Memorial Volume of History, Biography, and Genealogy' (1895). Among his many siblings was older brother was Joseph Cabell Breckinridge Jr., an officer in the United States Navy in the Spanish–American War who died while serving on the torpedo boat USS ''Cushing''. Another older brother, Scott Dudley Breckinridge, was a physician an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George J
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |