|
Khoisan Languages
The Khoisan languages ( ; also Khoesan or Khoesaan) are a number of Languages of Africa, African languages once classified together, originally by Joseph Greenberg. Khoisan is defined as those languages that have click languages, click consonants and do not belong to other African language families. For much of the 20th century, they were thought to be Genetic relationship (linguistics), genealogically related to each other, but this is no longer accepted. They are now held to comprise three distinct language family, language families and two language isolates. All but two Khoisan languages are indigenous to southern Africa; these are classified into three language families. The Khoe languages, Khoe family appears to have migrated to southern Africa not long before the Bantu expansion. Ethnically, their speakers are the Khoekhoe and the San people, San (Bushmen). Two languages of eastern Africa, those of the Sandawe people, Sandawe and Hadza people, Hadza, were originally also cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semiarid climate, semiarid sandy savanna in Southern Africa covering including much of Botswana as well as parts of Namibia and South Africa. It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal desert, whose name is of Khoekhoe language, Khoekhoegowab origin and means "vast place". Etymology ''Kalahari'' is derived from the Tswana language, Tswana word ''Kgala'', meaning "the great thirst", or ''Kgalagadi'', meaning "a waterless place"; the Kalahari has vast areas covered by red sand without any permanent surface water. History The Kalahari Desert was not always a dry desert. The fossil flora and fauna from Gcwihaba, Gcwihaba Cave in Botswana indicates that the region was much wetter and cooler at least from 30 to 11 thousand Before Present, especially after 17,500 BP. Geography Drainage of the desert is by dry black valleys, seasonally inundated pans, and the large salt pan (geology), salt pans of the Mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San People
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are the members of any of the indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures of southern Africa, and the oldest surviving cultures of the region. They are thought to have diverged from other humans 100,000 to 200,000 years ago. Their recent ancestral territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, and South Africa. The San speak, or their ancestors spoke, languages of the Khoe, Tuu, and Kxʼa language families, and can be defined as a people only in contrast to neighboring pastoralists such as the Khoekhoe and descendants of more recent waves of immigration such as the Bantu, Europeans, and South Asians. In 2017, Botswana was home to approximately 63,500 San, making it the country with the highest proportion of San people at 2.8%. 71,201 San people were enumerated in Namibia in 2023, making it the country with the second highest proportion of San people at 2.4%. Definition The term "San" comes from the Khoekhoe la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Click Consonant
Click consonants, or clicks, are speech sounds that occur as consonants in many languages of Southern Africa and in three languages of East Africa. Examples familiar to English-speakers are the '' tut-tut'' (British spelling) or '' tsk! tsk!'' (American spelling) used to express disapproval or pity (IPA ), the '' tchick!'' used to spur on a horse (IPA ), and the '' clip-clop!'' sound children make with their tongue to imitate a horse trotting (IPA ). However, these paralinguistic sounds in English are not full click consonants, as they only involve the front of the tongue, without the release of the back of the tongue that is required for clicks to combine with vowels and form syllables. Anatomically, clicks are obstruents articulated with two closures (points of contact) in the mouth, one forward and one at the back. The enclosed pocket of air is rarefied by a sucking action of the tongue (in technical terminology, clicks have a lingual ingressive airstream mechanism). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naro Language
Naro , also Nharo, is a Khoe language spoken in Ghanzi District of Botswana and in eastern Namibia. It is one of the most-spoken of the Tshu–Khwe languages. Naro is a trade language among speakers of different Khoe languages in Ghanzi District. There exists a dictionary. Phonology Naro has the following consonant inventory (in the IPA) as described by Miller (2011), whereas the orthographic symbols were proposed by Visser (2001):Visser originally wrote the palatal clicks with a base of , but switched to to make the language more accessible from English-language typewriters and keyboards. The phonemes and (spelt ⟨kg⟩ and ⟨kgʼ⟩) only contrast for some speakers: ''kgʼám'' ‘mouth’ vs. ''kgʼáù'' ‘male’. The flap /ɾ/ only occurs word-medially except in loan words. The lateral /l/ is only found in loans, and is generally substituted by medially, and by initially. Medial and may be and ; they occur initially only in ''wèé'' ‘all, both’ and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khoekhoe Language
Khoekhoe or Khoikhoi ( ; , ), also known by the ethnic terms Nama ( ; ''Namagowab''), Damara (''ǂNūkhoegowab''), or Nama/Damara and formerly as Hottentot, is the most widespread of the non- Bantu languages of Southern Africa that make heavy use of click consonants and therefore were formerly classified as Khoisan, a grouping now recognized as obsolete. It belongs to the Khoe language family, and is spoken in Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa primarily by three ethnic groups: Namakhoen, ǂNūkhoen, and Haiǁomkhoen. History The Haiǁom, who had spoken a Juu language, later shifted to Khoekhoe. The name for the speakers, '' Khoekhoen'', is from the word ''khoe'' "person", with reduplication and the suffix ''-n'' to indicate the general plural. Georg Friedrich Wreede was the first European to study the language, after arriving in ǁHui!gaeb (later Cape Town) in 1659. Status Khoekhoe is a national language in Namibia. In Namibia and South Africa, state-owned broadcas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Languages
An extinct language or dead language is a language with no living first-language, native speakers. A dormant language is a dead language that still serves as a symbol of ethnic identity to an ethnic group; these languages are often undergoing a process of Language revitalization, revitalisation. Languages that have first-language speakers are known as Modern language, modern or living languages to contrast them with dead languages, especially in educational contexts. Languages have typically become extinct as a result of the process of cultural assimilation leading to language shift, and the gradual abandonment of a native language in favor of a foreign ''lingua franca''. As of the 2000s, a total of roughly 7,000 natively spoken languages existed worldwide. Most of these are minor languages in danger of extinction; one estimate published in 2004 expected that some 90% of the languages spoken at that time will have become extinct by 2050. Language death Normally the transiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moribund Language
An endangered language or moribund language is a language that is at risk of disappearing as its speakers die out or shift to speaking other languages. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers and becomes a " dead language". If no one can speak the language at all, it becomes an "extinct language". A dead language may still be studied through recordings or writings, but it is still dead or extinct unless there are fluent speakers left. Although languages have always become extinct throughout human history, endangered languages are currently dying at an accelerated rate because of globalization, mass migration, cultural replacement, imperialism, neocolonialism and linguicide (language killing). Language shift most commonly occurs when speakers switch to a language associated with social or economic power or one spoken more widely, leading to the gradual decline and eventual death of the endangered language. The process of language shift is often influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The International African Institute
''Africa'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the International African Institute. The journal covers the study of African societies and culture. The journal was established in 1928 and the editors-in-chief are Julie Archambault (Concordia University) and Joost Fontein (University of Johannesburg). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 1.235. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Africa (Journal) African studies journals Academic journals established in 1928 Cambridge University Press academic journals English-language journals 5 times per year j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
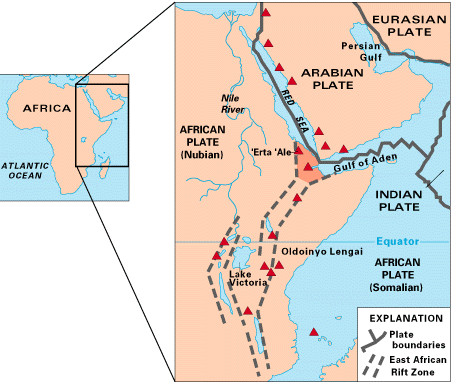
East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor. A narrow zone, the rift is a developing divergent tectonic plate boundary where the African plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali plate and the Nubian plate, at a rate of per year. The rift system consists of three microplates, the Victoria microplate to the north, and the Rovuma and Lwandle microplates to the south. The Victoria microplate is rotating anti-clockwise with respect to the African plate. Its rotation is caused by the configuration of mechanically weaker and stronger lithospheric regions in the EARS. Many of the African Great Lakes lie within the Rift Valley. Extent A series of distinct rift basins, the East A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botswana
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory part of the Kalahari Desert. It is bordered by South Africa to the south and southeast, Namibia to the west and north, Zambia to the north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast. With a population of slightly over 2.4 million people and a comparable land area to France, Botswana is one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most sparsely populated countries in the world. It is essentially the nation-state of the Tswana people, who constitute nearly 80 percent of the population. The Tswana ethnic group are descended mainly from Bantu peoples, Bantu-speaking peoples who Bantu expansion, migrated into southern Africa, including modern Botswana, in several waves before AD 600. In 1885, the British Empire, British colonised the area and declared a protectorate named Bechuanaland. As part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |