|
Khmer Grammar
This article describes the grammar of the Khmer (Cambodian) language, focusing on the standard dialect. Word formation Khmer is primarily an analytic language, with no inflection. There is some derivation by means of prefixes and infixes, but it is no longer always productive, as those elements are often crystallized in words inherited from Old Khmer. Even in Old Khmer, the same affix could have multiple functions (for example, it could serve as a nominalizer in one word and as a causativizer in another). A common infix has the form or (or with other vowels), inserted after an initial consonant, especially to convert adjectives or verbs into nouns. Compounding is common; in a compound of two nouns, the head generally comes first, often the reverse of the English order: "duck egg" is , literally "egg-duck". Word order Since Khmer is an analytic language, word order is relatively fixed, as changes in word order often affect meaning. Khmer is generally a subject–verb–obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rules, a subject that includes phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, together with phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are, broadly speaking, two different ways to study grammar: traditional grammar and #Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency in a particular language variety involves a speaker internalizing these rules, many or most of which are language acquisition, acquired by observing other speakers, as opposed to intentional study or language teaching, instruction. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more direct instruction. The term ''grammar'' can also describe the linguistic behaviour of groups of speakers and writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or ordinal, is a generalization of ordinal numerals (first, second, th, etc.) aimed to extend enumeration to infinite sets. A finite set can be enumerated by successively labeling each element with the least natural number that has not been previously used. To extend this process to various infinite sets, ordinal numbers are defined more generally using linearly ordered greek letter variables that include the natural numbers and have the property that every set of ordinals has a least or "smallest" element (this is needed for giving a meaning to "the least unused element"). This more general definition allows us to define an ordinal number \omega (omega) to be the least element that is greater than every natural number, along with ordinal numbers , , etc., which are even greater than . A linear order such that every non-empty subset has a least element is called a well-order. The axiom of choice implies that every set can be well-orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khmer Numerals
Khmer numerals ០ ១ ២ ៣ ៤ ៥ ៦ ៧ ៨ ៩ are the Numerical digit, numerals used in the Khmer language. They have been in use since at least the early 7th century. Numerals Having been derived from the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, Hindu numerals, modern Khmer numerals also represent a decimal positional notation system. It is the script with the first extant material evidence of Zero#Zero as a decimal digit, zero as a numerical figure, dating its use back to the seventh century, two centuries before its certain use in India. Old Khmer, or Angkorian Khmer, also possessed separate symbols for the numbers 10, 20, and 100. Each multiple of 20 or 100 would require an additional stroke over the character, so the number 47 was constructed using the 20 symbol with an additional upper stroke, followed by the symbol for number 7. This inconsistency with its decimal, decimal system suggests that spoken #Angkorian numbers, Angkorian Khmer used a vigesimal system. As both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Numerals
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numerals. However the symbols are also used to write numbers in other bases, such as octal, as well as non-numerical information such as trademarks or license plate identifiers. They are also called Western Arabic numerals, Western digits, European digits, Ghubār numerals, or Hindu–Arabic numerals due to positional notation (but not these digits) originating in India. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' uses lowercase ''Arabic numerals'' while using the fully capitalized term ''Arabic Numerals'' for Eastern Arabic numerals. In contemporary society, the terms ''digits'', ''numbers'', and ''numerals'' often implies only these symbols, although it can only be inferred from context. Europeans first learned of Arabic numerals , though their spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khmer Script
Khmer script (, )Huffman, Franklin. 1970. ''Cambodian System of Writing and Beginning Reader''. Yale University Press. . is an abugida (alphasyllabary) script used to write the Khmer language, the official language of Cambodia. It is also used to write Pali in the Buddhist liturgy of Cambodia and Thailand. Khmer is written from left to right. Words within the same sentence or phrase are generally run together with no spaces between them. Consonant clusters within a word are "stacked", with the second (and occasionally third) consonant being written in reduced form under the main consonant. Originally there were 35 consonant characters, but modern Khmer uses only 33. Each character represents a consonant sound together with an inherent vowel, either ''â'' or ''ô''; in many cases, in the absence of another vowel mark, the inherent vowel is to be pronounced after the consonant. There are some independent vowel characters, but vowel sounds are more commonly represented as depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biquinary
Bi-quinary coded decimal is a numeral encoding scheme used in many abacuses and in some early computers, notably the Colossus. The term ''bi-quinary'' indicates that the code comprises both a two-state (''bi'') and a five-state (''quin''ary) component. The encoding resembles that used by many abacuses, with four beads indicating the five values either from 0 through 4 or from 5 through 9 and another bead indicating which of those ranges (which can alternatively be thought of as +5). Several human languages, most notably Fula and Wolof also use biquinary systems. For example, the Fula word for 6, ''jowi e go'o'', literally means ''five lusone''. Roman numerals use a symbolic, rather than positional, bi-quinary base, even though Latin is completely decimal. The Korean finger counting system Chisanbop uses a bi-quinary system, where each finger represents a one and a thumb represents a five, allowing one to count from 0 to 99 with two hands. One advantage of one bi-qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai Language
Thai,In or Central Thai (historically Siamese;Although "Thai" and "Central Thai" have become more common, the older term, "Siamese", is still used by linguists, especially when it is being distinguished from other Tai languages (Diller 2008:6). "Proto-Thai" is, for example, the ancestor of all of Southwestern Tai, not just Siamese (Rischel 1998). ), is a Tai language of the Kra–Dai language family spoken by the Central Thai, Mon, Lao Wiang, Phuan people in Central Thailand and the vast majority of Thai Chinese enclaves throughout the country. It is the sole official language of Thailand. Thai is the most spoken of over 60 languages of Thailand by both number of native and overall speakers. Over half of its vocabulary is derived from or borrowed from Pali, Sanskrit, Mon and Old Khmer. It is a tonal and analytic language. Thai has a complex orthography and system of relational markers. Spoken Thai, depending on standard sociolinguistic factors such as age, gender ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier (linguistics)
A classifier (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a word or affix that accompanies nouns and can be considered to "classify" a noun depending on some characteristics (e.g. humanness, animacy, sex, shape, social status) of its referent. Classifiers in this sense are specifically called noun classifiers because some languages in Papuan languages, Papua as well as the Indigenous languages of the Americas, Americas have verbal classifiers which categorize the referent of its Argument (linguistics), argument. In languages that have classifiers, they are often used when the noun is being counted, that is, when it appears with a numeral (linguistics), numeral. In such languages, a phrase such as "three people" is often required to be expressed as "three ''X'' (of) people", where ''X'' is a classifier appropriate to the noun for "people"; compare to "three blades of grass". Classifiers that appear next to a Numeral (linguistics), numeral or a Quantifier (linguistics), qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
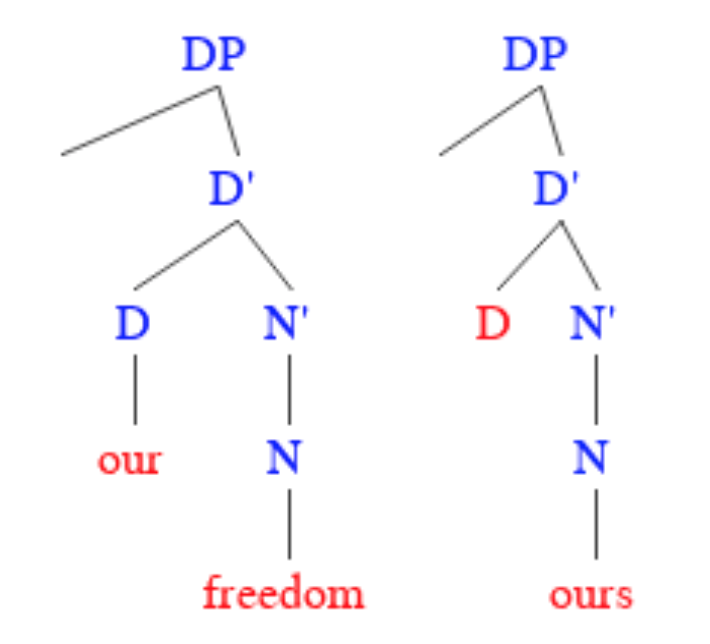
Possessive
A possessive or ktetic form (Glossing abbreviation, abbreviated or ; from ; ) is a word or grammatical construction indicating a relationship of possession (linguistics), possession in a broad sense. This can include strict ownership, or a number of other types of relation to a greater or lesser degree analogous to it. Most European languages feature possessive forms associated with personal pronouns, like the English grammar, English ''my'', ''mine'', ''your'', ''yours'', ''his'' and so on. There are two main ways in which these can be used (and a #Terminology, variety of terminologies for each): * Together with a noun, as in ''my car'', ''your sisters'', ''his boss''. Here the possessive form serves as a ''possessive determiner''. * Without an accompanying noun, as in ''mine is red'', ''I prefer yours'', ''this book is his''. A possessive used in this way is called a ''substantive possessive pronoun'', a possessive pronoun or an ''absolute pronoun''. Some languages, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postnominal
Post-nominal letters, also called post-nominal initials, post-nominal titles, designatory letters, or simply post-nominals, are letters placed after a person's name to indicate that the individual holds a position, an academic degree, accreditation, an office, a military decoration, or honour, or is a member of a religious institute or fraternity. An individual may use several different sets of post-nominal letters, but in some contexts it may be customary to limit the number of sets to one or just a few. The order in which post-nominals are listed after a name is based on rules of precedence and what is appropriate for a given situation. Post-nominal letters are one of the main types of name suffix. In contrast, pre-nominal letters precede the name rather than following it, such as addressing a physician or professor as "Dr. Smith". List Different awards and post-nominal letters are in use in the English-speaking countries. Usage Listing order The order in which post-nomina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |