|
Khawaja Ghulam Farid
Khawaja Ghulam Farid (also romanized as Fareed; /1845 – 24 July 1901) was a 19th-century Sufi poet and mystic from Bahawalpur, Punjab, British India belonging to the Chishti Order. Most of his work is in his mother tongue ''Multani'', or what is now known as Saraiki. However, he also contributed to the Punjabi, Urdu, Pashto, Sindhi, Hindi and Persian literature. His writing style is characterized by the integration of themes such as death, passionate worldly and spiritual love, and the grief associated with love. Life He was born into a branch of the Koreja family who claimed descent from Umar (), the second Rashidun caliph through an early migrant to Sindh. The family was established as saints associated with the Suhrawardī Sufi order. Originally from Thatta, Sindh, the family seat later moved to Mithankot in the early 18th century on the invitation of a disciple and subsequently transferred their allegiance to the Chishtī order. Khawaja Farid was born /1845 at Chachran. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chachran
Chachran Sharif (), is a town in Khanpur Katora tehsil of the Rahim Yar Khan district, in the Punjab province of Pakistan. History Chacharan Sharif is a historical town of Rahim Yar Khan district, which is attributed with the name of famous 19th century poet and saint Khawaja Ghulam Farid and it is called Farid city as he was born and lived in this city. This city is situated at the east bank of Indus River and is the last northern town of Rahim Yar Khan district. After it the territory of Rajanpur district begins; Mithankot, another historic town is directly across the river Indus on its west bank. A new Bridge is built on the Indus River useful for connection between two districts, Rahim Yar Khan and Rajanpur. In this way, the bridge facilitates travel for thousands of people of the Rahim Yar Khan and Rajanpur districts. Courts There are no courts in Chachran Sharif itself. However, there is a sub-divisional headquarters for courts in Khanpur Katora tehsil, which comprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diwan (poetry)
A diwan (from Persian language, Persian ; ) is a collection of Poetry, poems by a single author – usually excluding the poet's Mathnawi (poetic form), long poems – in Islamic cultures of West Asia, Central Asia, North Africa, Sicily and South Asia. The vast majority of Diwan poetry was Lyric poetry, lyric in nature: either ghazals (or ''gazel''s, which make up the greatest part of the repertoire of the tradition) or ''kasîde''s. There were, however, other common genres, most particularly the ''mesnevî''—a kind of Courtly romance, verse romance and thus a variety of narrative poetry; the two most notable examples of this form are the ''Layla and Majnun'' (ليلى و مجنون) of Fuzûlî and the ''Hüsn ü Aşk'' (حسن و عشق – 'Beauty and Love') of Şeyh Gâlib. Originating in Persian literature, the idea spread to the Arab, Turkic and Indic worlds, and the term was sometimes used in Europe, albeit not always in the same way. Etymology The English usage of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilla (retreat)
Chilla (, , both literally "forty"), also known as Chilla-nashini, is a spiritual practice of penance and solitude in Sufism known mostly in Indian and Persian traditions. In this ritual a mendicant or ascetic attempts to remain seated in a circle practicing meditation techniques without food for 40 days and nights in imitation of the Arba'een. Etymology The word ''chilla'' is derived from the Persian word ''chehel'' "forty". Chilla-khana Chilla is commonly performed in a solitary cell called a ''chilla-khana''. The place itself is sometimes called Chilla where chilla has been performed. Incidents of Chilla The most famous case of chilla is found in the biographies of the 14th century Sufi poet Hafez of Shiraz. In music A practice similar to chilla is also performed by Hindustani classical music practitioners at an advanced level. It is called chilla katna. See also * Khalwa * Meditation * Sādhanā * Shugendō is a syncretic Esoteric Buddhist religi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholistan Desert
The Cholistan Desert (; ; Saraiki: ), also locally known as Rohi (), is a desert in the southern part of Pakistani Punjab that forms part of the Greater Thar Desert, which extends to Sindh province and the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is one of two large deserts in Punjab, the other being the Thal Desert. The name is derived from the Turkic word ''chol'', meaning "sands," and ''istan'', a Persian suffix meaning "land of." Cholistan was a center for caravan trade, leading to the construction of numerous forts in the medieval period to protect trade routes—of which the Derawar Fort is the best-preserved example. Geography Cholistan covers an area of in the Bahawalpur, Bahawalnagar, and Rahim Yar Khan districts of southern Punjab. The nearest major city is Bahawalpur city, from the edge of the desert. The desert stretches about 480 kilometres in length, with a width varying between 32 and 192 kilometres. It is located between 27°42΄00΄΄ to 29° 45΄00΄΄ north, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its metropolitan population in 2022 was 2.4million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Around 44.5% of the population are Saudis, Saudi citizens and around 55.5% are Muslim world, Muslim foreigners from other countries. Pilgrims more than triple the population number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . With over 10.8 million international visitors in 2023, Mecca was one of the ten List of cities by international visitors, most visited cities in the world. Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by all adult Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey, and of supporting their family during their absence from home. In Islamic terminology, Hajj is a pilgrimage made to the Kaaba, the "House of Allah", in the sacred city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia. It is one of the Five Pillars of Islam, alongside (oath that one believes there is no god but Allah), (prayer), (almsgiving), and (fasting during Ramadan). The Hajj is an annual practice when Muslim brotherhood is on display and their solidarity with fellow Muslim people and submission to God (Allah) is fulfilled. The Hajj is taken by Muslims to cleanse their souls of all worldly sins, which connotes both the outward act of a journey after death and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nawab Of Bahawalpur
State of Bahawalpur was a state in the Punjab region of South Asia that existed as a sovereign polity from 1748 to 1833 and as a princely state, under subsidiary alliance with British India and later Dominion of Pakistan, from 1833 to 1955. It was a part of the Punjab States Agency; and covered an area of with a population of 1,341,209 in 1941. The capital of the state was the town of Bahawalpur. The state was founded in 1748 by Nawab Bahawal Khan Abbasi. On 22 February 1833, Abbasi III entered into a subsidiary alliance with the British, by which Bahawalpur was admitted as a princely state. When British rule ended in 1947 and British Raj was partitioned into India and Pakistan, Bahawalpur joined the Dominion of Pakistan. Bahawalpur remained an autonomous entity until 14 October 1955, when it was merged with the province of West Pakistan. History The Kingdom of Bahawalpur was established by Bahawal Khan, who belonged to the Daudpotra tribe and had migrated from Shikar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadeq Mohammad Khan IV
Sadiq Muhammad Khan IV (; 1861–1899) was the 10th Nawab of Bahawalpur who ruled the Bahawalpur State from 1879 to 1899 under the supervision of the British Raj. He died in 1899 and was succeeded by his eldest son Bahawal Khan V. Biography Sadiq Muhammad Khan Bahadur was born in 1862. He became Nawab of Bahawalpur on 25 March 1866, after the death of his father Mohammad Bahawal Khan IV. As he was still a minor, the British temporarily administered the region. He was invested with full ruling powers at Derawar Fort on 28 November 1879. During his governance, he ordered for construction of many buildings in Bahawalpur including Daulat Khana, Sadiq Garh Palace, Noor Mahal and Gulzar Mahal. In an 1899 account published in the '' Century Magazine'', R.D. Mackenzie portrayed the Nawab as a representative of Indian royalty. According to him, the Nawab chose to reside in a simple, square, flat-roofed palace within his estate, surrounded by buildings in various states of disrepai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
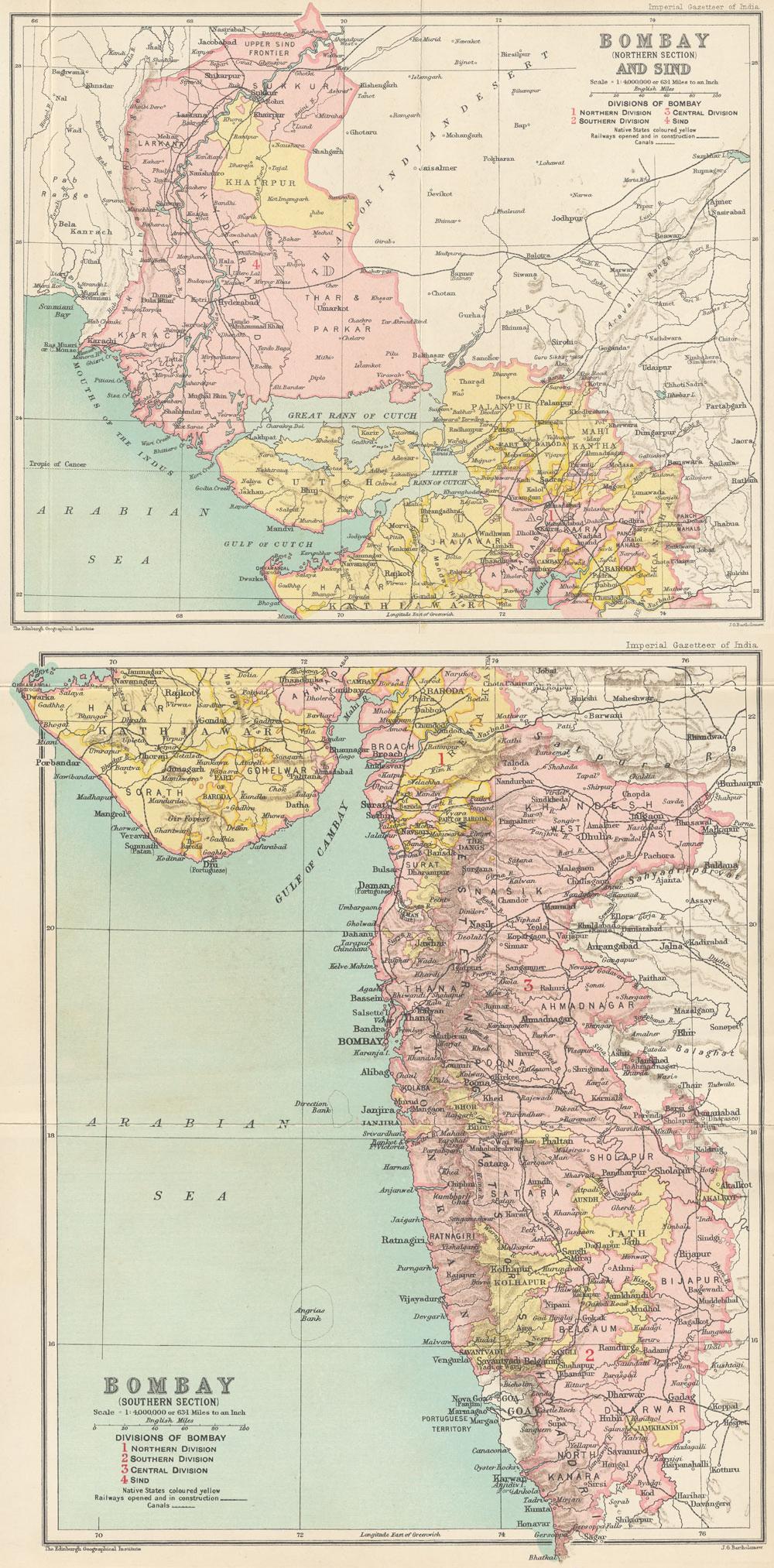
Thatta
Thatta is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh. Thatta was the medieval capital of Sindh, and served as the seat of power for three successive dynasties. Its construction was ordered by Jam Nizamuddin II in 1495. Thatta's historic significance has yielded several monuments in and around the city. Thatta's Makli Necropolis, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is site of one of the world's largest cemeteries and has numerous monumental tombs built between the 14th and 18th centuries designed in a syncretic funerary style characteristic of lower Sindh. The city's 17th century Shah Jahan Mosque is richly embellished with decorative tiles, and is considered to have the most elaborate display of tile work in the South Asia. Etymology ''Thatta'' refers to riverside settlements. Villagers in the rural areas of lower Sindh often refer to the city as ''Thatta Nagar'', or simply ''Nagar''. The name of Thatta, one of the oldest towns, was derived from the Persian term ''Tah-Tah'' which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suhrawardiyya
The Suhrawardi order (, ) is a tariqa, Sufi order founded by Abu al-Najib Suhrawardi, Abu ’l-Nad̲j̲īb Suhrawardī (died 1168). Lacking a centralised structure, it eventually divided into various branches. The order was especially prominent in Indian subcontinent, India. The ideology of the Suhrawardi order was inspired by Junayd of Baghdad (d. 910), a Persian scholar and mystic from Baghdad. Under the Ilkhanate (1256–1335), the Suhrawardi was one of the three leading Sufi orders and was based in western Iran. The order had its own khanqahs (Sufi lodges), which helped them spread their influence throughout Persianate society. The order included prominent members such as the Akbarism, Akbari mystics Abd al-Razzaq Kāshānī (died 1329), Sa'id al-Din Farghani (died 1300), and the Persian poet Saadi Shirazi (died 1292). Today, most orders have dissolved in Middle Eastern countries such as Syria. However, the order is still active in Iraq, where it recruits new members. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the Demographics of Pakistan, second-largest province by population after Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab to the north. It shares an India-Pakistan border, International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert of Sindh, Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the India–Pakistan border, international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |