|
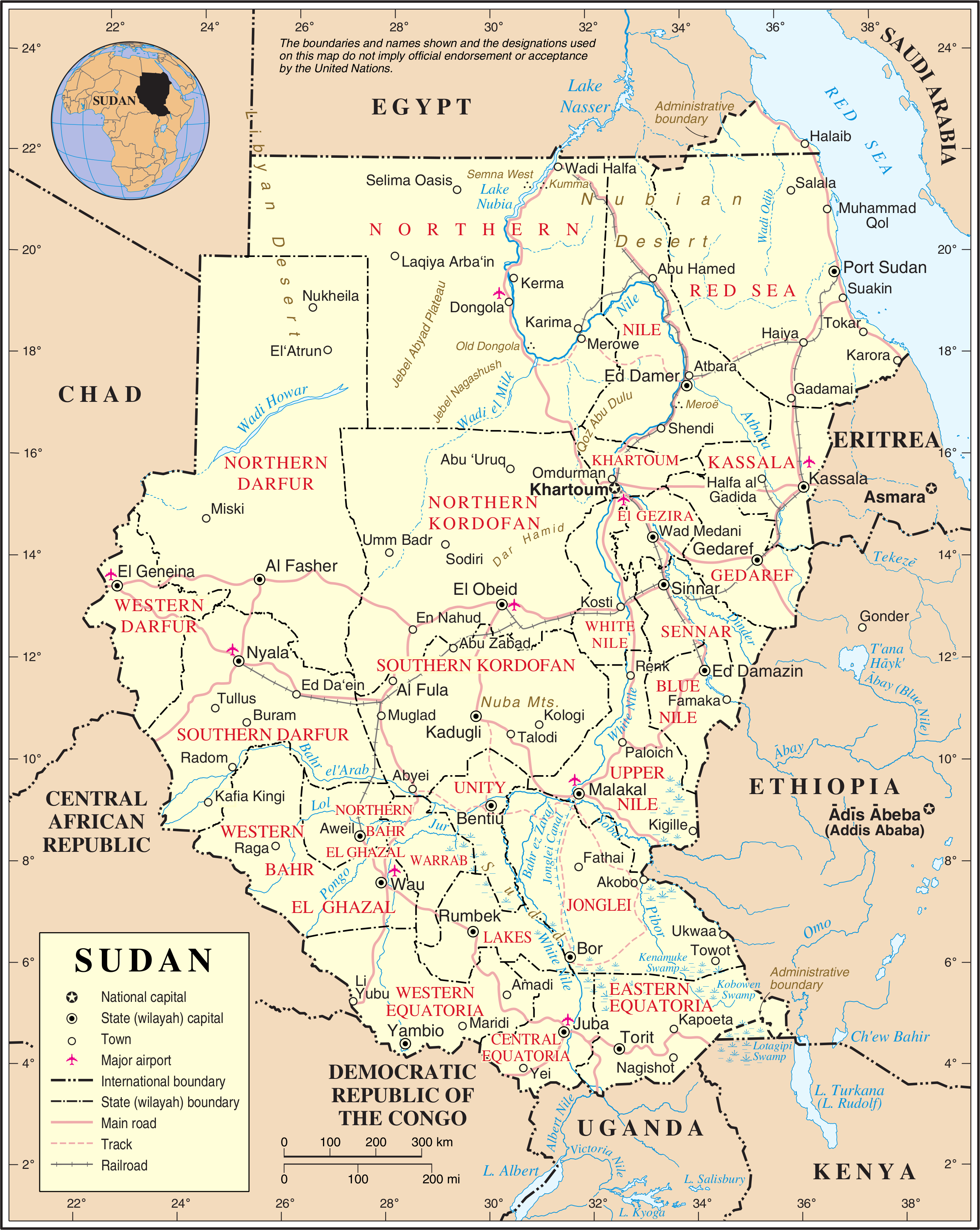
Kharga
The Kharga Oasis ( , ) ; , "Oasis of Hib", "Oasis of Psoi") is the southernmost of Egypt's five western oases. It is located in the Western Desert, about 200 km (125 miles) to the west of the Nile valley. "Kharga" or "El Kharga" is also the name of a major town located in the oasis, the capital of New Valley Governorate. The oasis, which was known as the 'Southern Oasis' to the Ancient Egyptians, the 'outer' (''he Exotero'') to the Greeks and Oasis Magna to the Romans, is the largest of the oases in the Libyan desert of Egypt. It is in a depression about 160 km (100 miles) long and from 20 km (12 miles) to 80 km (50 miles) wide. Its population is 67,700 (2012). Overview Kharga is the most modernised of Egypt's western oases. The main town is highly functional with all modern facilities, and virtually nothing left of old architecture. There is extensive thorny date palm, acacia, buffalo thorn, and jujube growth in the oasis surrounding the modern to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Valley Governorate
New Valley (or El Wadi El Gedid ( , )) is a governorate of Egypt. It is in the southwestern part of the country, in the south of Egypt Western Desert (part of the Sahara Desert), between the Nile, northern Sudan, and southeastern Libya. Comprising roughly half of Egypt's area, this governorate is the country's largest and most sparsely populated, and one of the largest country subdivisions in the world. The capital is Kharga. New Valley Governorate is named after the New Valley Project, which aims to irrigate parts of the Western Desert. Municipal divisions The governorate is divided into municipal divisions with a total estimated population, as of January 2024, a270,854 In the case of New Valley governorate, there is one kism with urban and rural parts, and four marakiz. In an effort to decentralize the administration of Kharga, it was divided into four sections effective 19 June 2018. Population According to population estimates, in 2015 the majority of residents i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darb El Arba'īn
Darb El Arba'īn () (also called the Forty Days Road, for the number of days the journey was said to take in antiquity) is the easternmost of the great north–south Trans-Saharan trade routes. The Darb El Arba'īn route was used to move trade goods, livestock (camels, donkeys, cattle, horses) and History of slavery, slaves via a chain of oases from the interior of Africa to portage on the Nile River and thence to the rest of the world. The journey from what is now North Darfur, Sudan to what is now Asyut Governorate, Egypt is approximately and usually took closer to 60 days due to the need to rest and water the herd. Traveling by the desert route was more direct, less expensive and safer than the Nile route. The desert between the Nile River#Yellow Nile, Yellow Nile Wadi Howar, riverbed in north Sudan and the Geography of Egypt#Natural region, limestone plateau of Middle Egypt receives average annual precipitation of less than 5 mm a year "and a frequency of 30 to 40 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Desert (Egypt)
In Egypt, the Western Desert is an area of the Sahara that lies west of the river Nile, up to the Egypt–Libya border, Libyan border, and south from the Mediterranean Sea to the Egypt–Sudan border, border with Sudan. It is named in contrast to the Eastern Desert which extends east from the Nile to the Red Sea. The Western Desert is mostly Reg (landform), rocky desert, though an area of Erg (landform), sandy desert, known as the Great Sand Sea, lies to the west against the Libyan border. The desert covers an area of which is two-thirds of the land area of the country. Its highest elevation is in the Gilf Kebir plateau to the far south-west of the country, on the Egypt-Sudan-Libya border. The Western Desert is barren and uninhabited save for a chain of oases which extend in an arc from Siwa Oasis, Siwa, in the north-west, to Kharga in the south. It has been the scene of conflict in modern times, particularly during the Second World War. Administratively the Western Desert is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Hibis
The Temple of Hibis is the largest and best preserved ancient Egyptian temple in the Kharga Oasis, as well as the only structure in Egypt dating to the Saite-Persian period (664–404 BCE) which has come down to modern times in relatively good condition. Located about 2 km north of Kharga, it was devoted to a syncretism of two local forms of the deity Amun: "Amun of Hibis" and "Amun- Ra of Karnak who dwells in Hibis". It is alternatively believed to be dedicated to Amun and Osiris, its sanctuary contains depictions of hundreds of Egyptian deities. History The temple of Hibis was once surrounded by the city of Hibis (Egyptian: ''Hebet'', meaning "the plough"), which nowadays lies under the crops. Construction of the temple started during the 26th Dynasty, most likely under Pharaoh Psamtik II, or possibly even earlier, during the 25th Dynasty. Archaeological evidences suggest that an older temple, dating back to the New Kingdom, was already present in the same place. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
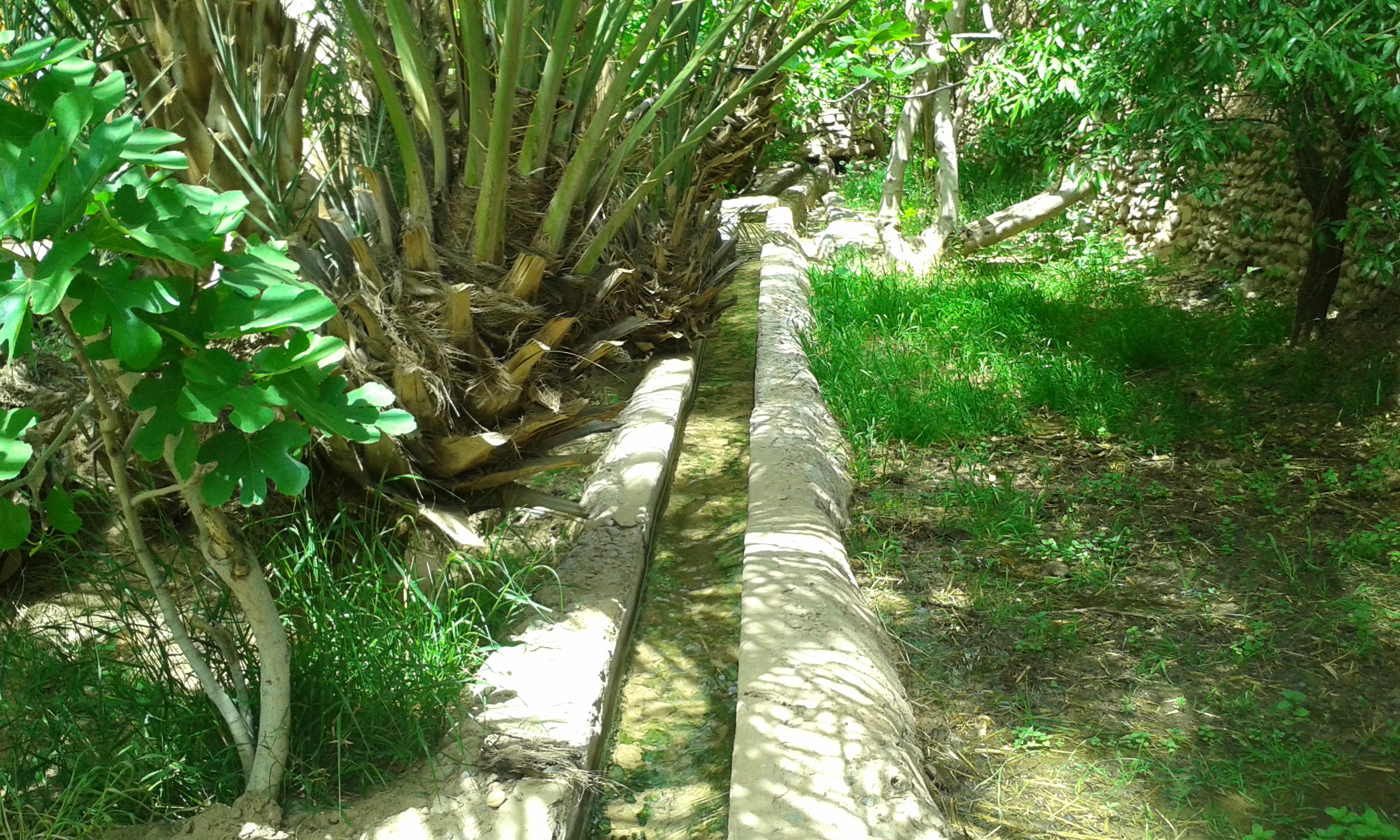
Qanat
A qanāt () or kārīz () is a water supply system that was developed in ancient Iran for the purpose of transporting usable water to the surface from an aquifer or a well through an underground aqueduct. Originating approximately 3,000 years ago, its function is essentially the same across the Middle East and North Africa, but it is known by a variety of regional names beyond today's Iran, including: kārēz in Afghanistan and Pakistan; foggāra in Algeria; khettāra in Morocco; falaj in Oman and the United Arab Emirates; and ʿuyūn in Saudi Arabia. In addition to those in Iran, the largest extant and functional qanats are located in Afghanistan, Algeria, China (i.e., the Turpan water system), Oman, and Pakistan. Proving crucial to water supply in areas with hot and dry climates, a qanat enables water to be transported over long distances by largely eliminating the risk of much of it evaporating on the journey. The system also has the advantage of being fairly resistant to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentBattesti, Vincent (2005) Jardins au désert: Évolution des pratiques et savoirs oasiens: Jérid tunisien. Paris: IRD éditions. . that sustains plant life and provides habitat for animals. Surface water may be present, or water may only be accessible from wells or underground channels created by humans. In geography, an oasis may be a current or past rest stop on a transportation route, or less-than-verdant location that nonetheless provides access to underground water through deep wells created and maintained by humans. Although they depend on a natural condition, such as the presence of water that may be stored in reservoirs and us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asyut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut''. ( ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at , while the ancient city is located at . The city is home to one of the largest Coptic Christian communities in the country. History Names and etymology The name of the city is derived from Egyptian language, early Egyptian (late Egyptian, Səyáwt) which became Coptic language, Coptic , meaning "''Guardian''" of the northern approach of Upper Egypt. In Graeco-Roman Ægyptus, Egypt, it was called Lycopolis or Lykopolis (, ""), ('wolf city') Lycon, or Lyco. Ancient Asyut Ancient Asyut was the capital of the Thirteenth Nome (Egypt), Nome of Upper Egypt (''Lycopolites Nome'') around 3100 BC. It was located on the western bank of the Nile. The two most prominent Egyptian pantheon, gods of ancient Egyptian Asyut were Anubis and Wepwawet, both funerary deities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northern coast of Egypt, the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to Egypt–Israel barrier, the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to Egypt–Sudan border, the south, and Libya to Egypt–Libya border, the west; the Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital, list of cities and towns in Egypt, largest city, and leading cultural center, while Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important hub of industry and tourism. With over 109 million inhabitants, Egypt is the List of African countries by population, third-most populous country in Africa and List of countries and dependencies by population, 15th-most populated in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selima Oasis
Selima Oasis is an oasis in the Sudan located west of the Third Cataract of the Nile and the ancient site of Amara West. It lies along the Darb al-Arbaʿīn (Forty Days' Road), a desert track linking Kordofan with Egypt. Just to the north of Selima, the track splits into a northern route going to Kharga Oasis and a northwestern route going to Dunqul Oasis.Richard Lobban, ''Historical Dictionary of Ancient and Medieval Nubia'' (Scarecrow Press, 2004), p. 347. Geography Selima lies at the base of an escarpment of Jurassic and Cretaceous rock. Around 8300 BC, a freshwater lake formed over the site with depths of . The surrounding vegetation was savannah at the time. The remains of lacustrine fauna and of Palaeolithic artefacts have been recovered from the site. Around 4300, it transitioned to a saltwater ''sabkha'' and by 2700 it had dried up. Today it lies over the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System.Friederike Jesse, Coralie Gradel and Franck Derrien"Archaeology at Selima Oasis, Northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorates Of Egypt
Egypt is administratively organized under a dual system that may consist of either two or three tiers, with further subdivisions occasionally resulting in an additional layer. It follows a centralized system of local government, officially termed local administration, as it functions as a part of the executive branch of the government. Overview Egyptian law delineates the units of local governance as governorates, centers, cities, districts, and villages, each possessing legal personality. The legal framework establishes a dual system of local administration that alternates between a two-tier and a three-tier structure, depending on the characteristics of the governorate. At the top of the hierarchy are 27 governorates (singular: ', plural: '). Each governorate has a capital, typically its largest city, and is headed by a governor, appointed by the President of Egypt, serving at the president’s discretion. Governors hold the civilian rank of minister and report directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libyan Desert
The Libyan Desert (not to be confused with the Libyan Sahara) is a geographical region filling the northeastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval maps, its use predates today's Sahara, and parts of the Libyan Desert include the Sahara's most arid and least populated regions; this is chiefly what sets the Libyan Desert apart from the greater Sahara. The consequent absence of grazing, and near absence of waterholes or wells needed to sustain camel caravans, prevented Trans-Saharan trade between Kharga (the Darb al Arbein) close to the Nile, and Murzuk in the Libyan Fezzan. This obscurity saw the region overlooked by early European explorers, and it was not until the early 20th century and the advent of the motor car before the Libyan Desert started to be fully explored. Nomenclature The term ''Libyan Desert'' began to appear widely on European maps in the last decades of the 19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Fashir
Al-Fashir or El Fasher () is the capital city of North Darfur, Sudan. It is a city in the Darfur region of southwestern Sudan, northeast of Nyala, Sudan. "Al-Fashir" (description) ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2007, webpage: A historical Caravan (travellers), caravan post, Al-Fashir is located at an elevation of about . The city serves as an agricultural marketing point for the cereals and fruits grown in the surrounding region. Al-Fashir is linked by road with both Geneina and Umm Keddada. Al-Fashir had 264,734 residents , an increase from 2001, when the population was estimated to be 178,500. UN Habitat reported a population of 500,000 for al-Fashir in 2009, attributing the increase to refugees and economic migrants. Al Fashir University was created in 1990 by decree of President Omar Hassan Ahmed Bashir, and was officially opened in February 1991 in premises west of El Fasher Airport and south of the El Fashir School. History Late in the 18th century, Sultan Abd-er-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |