|
Khaniyabas
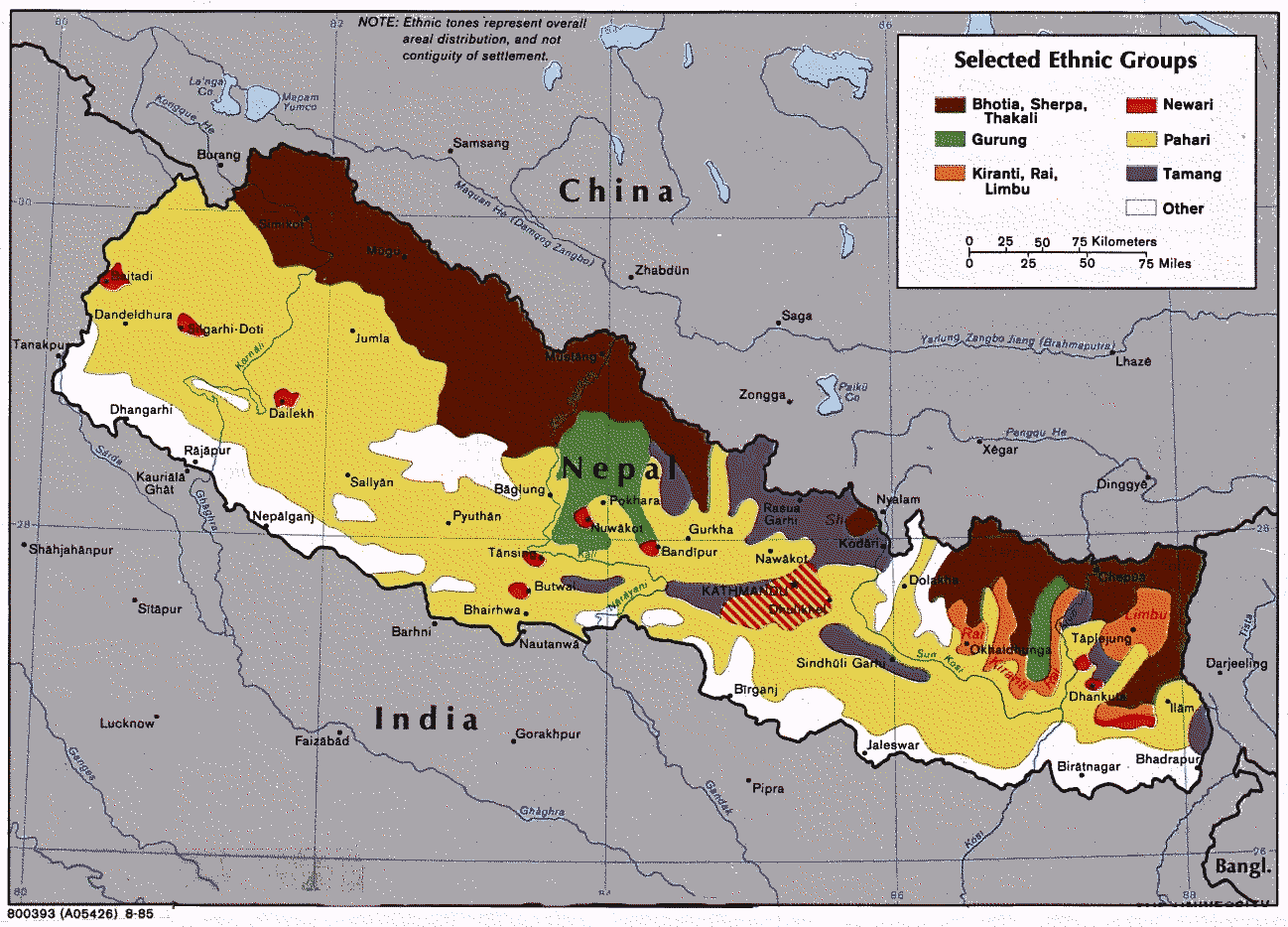
Khaniyabas ( Nepali: खनियाबास; ''khaniyabas'') is a Gaupalika( Nepali: गाउपालिका ; ''gaupalika'') Formerly: village development committee) in Dhading District in the Bagmati Zone of central Nepal. It has a literacy rate of 59.22% . The local body was formed by merging three VDCs namely Jharlang, Darkha and Satyadevi. The population of the rural municipality is 12,749 according to the data collected on 2017 Nepalese local elections. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Khaniyabas Rural Municipality had a population of 12,749. Of these, 86.8% spoke Tamang, 12.2% Nepali, 0.5% Gurung, 0.1% Newar and 0.2% other languages as their first language. In terms of ethnicity/caste, 88.2% were Tamang, 4.2% Kami, 2.8% Magar, 1.1% Hill Brahmin, 0.9% Damai/Dholi, 0.9% Gurung, 0.8% Chhetri, 0.4% Gharti/Bhujel, 0.4% Newar, 0.1% Sarki and 0.3% others. In terms of religion, 51.6% were Buddhist, 37.4% Christian, 10.8% Hindu and 0.2% others. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhading District
Dhading District ( ), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Dhading Besi as its district headquarters, covers an area of , had a population of 338,658 in 2001 and 336,067 in 2011. Geography and climate Dhading District spreads from 27'40" E to 28'17" E and 80'17"N to 84'35"N. The mountain range Ganesh Himal is the predominant mountain range located within Dhading. Some of the peaks are over . The highest point in the district is 7,104-metre Pabil. The and the mountain Manaslu is clearly visible from much of Dhading, although it is located within the bounds of Gorkha. The transnational Prithivi Highway connecting Kathmandu and Pokhara runs through the southern portion of the district, making for easy access to the Kathmandu valley. The road parallels the Trishuli River. The western border with Gorkha is bisected by the Budigandaki River. The district is bounded by *East: Kathmandu, Rasuwa and Nuwakot *West: Gorkh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Municipality
A rural municipality is a classification of municipality, a type of local government, found in several countries. These include: * Rural municipality (Canada), Rural municipalities in Canada, a Lists of municipalities in Canada, type of municipality, municipal status in the Canada, Canadian provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Prince Edward Island. In other provinces, such as Alberta and Nova Scotia, the term refers to municipal districts that are not explicitly urban, rather than being a distinct type of municipality. * Municipalities of Estonia, Rural municipalities in Estonia, also called Parish (administrative division), parishes, of which there are 64 in the country. Municipalities may contain one or several Populated places in Estonia, settlements, and while all urban municipalities contain only one settlement, only 6 rural municipalities do. Of these, five are so-called "borough-parishes", consisting of one borough, while Ruhnu Parish consists of one village. *Gaunpalik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jharlang
Jharlang is a village development committee in Dhading District in the Bagmati Zone of central Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census The 1991 Nepal census was a widespread national census conducted by the Nepal Central Bureau of Statistics. Working with Nepal's Village Development Committees at a district level, they recorded data from all the main towns and villages of each ... it had a population of 3891 and had 653 houses in it. References Populated places in Dhading District {{Dhading-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung People
Gurung (exonym; ) or Tamu (endonym; Gurung language, Gurung: ) are a Tibetan people, Tibetan ethnic group living in the hills and mountains of Gandaki Province of Nepal. Gurungs speak Tamu kyi which is a Sino-Tibetan language derived from the Tibeto-Burman language family. The written form of Gurung is heavily dependent on the Tibetan script and history and details related to their culture and tradition is passed on from one generation to the other usually by word-of-mouth. The Gurungs have historically lived a semi-nomadic lifestyle, herding sheep and yaks in the Himalayan foothills, but many have diversified into other professions while retaining strong ties to their cultural heritage. Etymology The term ''Tamu'' (Gurung language, Gurung: ) is used by the Gurungs to refer to themselves. According to oral traditions, the name Gurung is derived from the Tibetan word "Gru-gu", meaning "to bring down," reflecting their migration from the Tibetan plateau to the southern slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damai
Damai ( ; IAST: ''Damāĩ'') is an occupational caste found among indigenous people comprising 45 subgroups. Their surnames take after the subgroup they belong to. People belonging to this caste are traditionally tailors and musicians capable of using the naumati baja - an ensemble of nine traditional musical instruments. The term Damai is coined from the musical instrument Damaha. The 1854 Nepalese Muluki Ain (Legal Code) categorized Damai as "Lower caste” category. The Government of Nepal abolished the caste-system and criminalized any caste-based discrimination, including "untouchability" in 1963. The country, previously ruled by a Hindu monarchy was a Hindu nation which has now become a secular state. It was declared a republic in 2008, thereby ending it as the Hindu kingdom with its caste-based discriminations and the untouchability roots. According to the 2021 Nepal census, Damai make up 1.94% of Nepal's population (or 565,932 people). Damai are categorized under "H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahun
Bahun (), also known as Hill Brahmins, are a Brahmin varna among the Khas of Nepal. They are a sub-caste of the Kanyakubja Brahmin while their origins are from Kannauj and the Himalayan belt of South Asia. According to the 2011 Nepal census, Bahun is the second most populous group after Chhetri. According to 1854 ''Muluki Ain'', the first Nepalese civil code, Bahuns were regarded as caste among sacred thread bearers ( Tagadhari) and twice-born Hindus. Origin Traditionally, Bahuns were members of the Khas community together Chhetris. Possibly due to political power of the Khasa Malla kingdom, Khas Brahmins and Khas Kshatriyas had high social status in the present-day western Nepal. Bahuns, regarded as upper class Khas group together with Chhetris, were associated mostly with the Gorkha Kingdom and its expansion. There appears to be general agreement in historical records and family genealogy that Hill Brahmins (both Purbia and Kumai Bahuns) migrated from the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magars
The Magars, also spelled Mangar and Mongar, are the largest ethnic group native to Nepal and Northeast India, representing 6.9% of Nepal's total population according to the 2021 Nepal census. They are one of the main Gurkha tribes. The first home of the Magars was to the west of the Gandaki River and, roughly speaking, consisted of that portion of Nepal which lies between and around about Gulmi District, Gulmi, Arghakhanchi District, Arghakhanchi, and Palpa District, Palpa. This part of the country was divided into twelve districts known as ''Bahra Magarat'' (Confederation of Twelve Magar villages), which included the following regions of that period: Argha, Arghakhanchi District, Khanchi, Bhirkot, Dhor, Garhung, Ghiring, Gulmi, Isma, Musikot, Rising, Satungal, Satung, and Pyung. During the medieval period, the whole area from Palpa District, Palpa to Rukum Rolpa was called the Magarat, a place settled and inhabited by Magars. Another confederation of eighteen Magar kingdoms, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kami (caste)
Kami is an Indo-Aryan Nepali speaking group that primarily worked as metalsmiths. Later Nepal abolished its grading system. The tribal designation of Khas is given in some contexts. the Government of Nepal legally abolished the caste-system and criminalized any caste-based discrimination, including " untouchability" (the ostracism of a specific caste) - in the year 1963 A.D. With Nepal's step towards freedom and equality, Nepal, previously ruled by a Hindu monarchy was a Hindu nation which has now become a secular state, and on 28 May 2008, it was declared a republic, ending it as the Hindu kingdom. In spite of being the important occupational caste and ethnic group whose metal carving arts are globally recognized but still struggling to be recognized as it is considered as the serving occupation. The most people of this caste group are in absolute poverty to raise the voice and educate themselves to be in a good position to find the history. So they are compelled to face ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang People
The Tamang people (; Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāṅ'') are an ethnic group living in Nepal, Northeast India and southern Bhutan. In Nepal, they are concentrated in the central hilly and Himalayan regions and constituted over 1.6 million people in the 2021 census. In India, Tamang people live in the state of Sikkim, in the Darjeeling district, Darjeeling and Kalimpong districts of West Bengal and in Assam. In Bhutan, they live foremost in the southern foothills including Tsirang District, Dagana District, Samtse District, Chukha District, Sarpang District and Samdrup Jongkhar District. The Tamang language is the fifth most-spoken language in Nepal. History Research indicates that the Tamang people are a hybrid ethnic group with an estimated 59% genetic contribution from Tibetan and 41% from Nepalese ancestries. The Tamangs have been mentioned in various Nepalese and colonial historical records under a variety of names, such as ''Bhote'', ''Bodh'', ''Lama'', ''Murmi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Language
Newar (; , ) is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. The language is known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhasa, a name that has been historically used for the language. The term "Newari" is also used to refer to the language, although the Indic ''-i'' suffix is considered inappropriate by some Newar speakers. The language served as the official language of Nepal during the Malla dynasty (Nepal), Malla dynasty since the 14th century till the end of dynasty in 1769 during which the language was referred as "Nepal Bhasa", a term which literally means "Nepalese Language". However, the language is not the same as Nepali language, Nepali, an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language and the current official language of Nepal, which only got the name Nepali in the 1930s. Newar literature, Literature in Newar is one of the oldest i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung Language
Gurung (Devanagari: ), also known as Tamu Kyi (, ; Tibetan: ) or Tamu Bhāṣā (, ), is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Gurung people of Nepal. The total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal was 227,918 in 1991 and 325,622 in 2011. The official language of Nepal, Nepali, is an Indo-European language, whereas Gurung is a Sino-Tibetan language. Gurung is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, Bhutan, and by diaspora communities in places such as Singapore and Hong Kong. Geographical distribution Gurung is spoken in the following districts of Nepal and India (''Ethnologue''): * Gandaki Province: Kaski District, Syangja District, Lamjung District, Tanahu District, Gorkha District, Manang District and Mustang District * Dhawalagiri Zone: Parbat district *Sikkim: South Sikkim, West Sikkim, East Sikkim Classification At higher levels, Gurung is a member of the Tibeto-Burman (or Trans-Himalayan) family. Robert Shafer classified Guru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% and 63%. For comparison, the lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western Tamang: 323,000 (2000 WCD). Sub-dialects are as follows. ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |