|
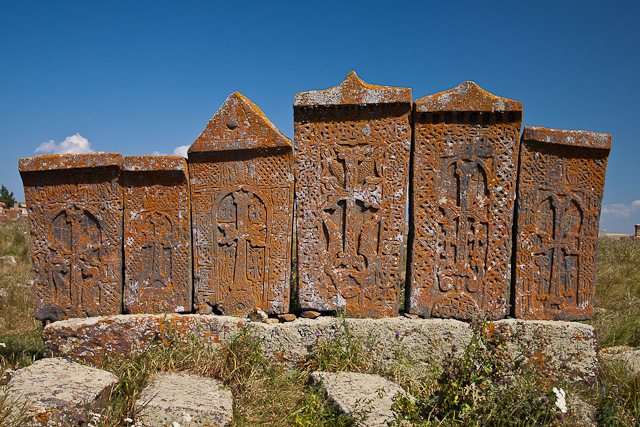
Khachkars
A ''khachkar'' (also spelled as ''khatchkar'') or Armenian cross-stone (, , խաչ ''xačʿ'' "cross" + քար ''kʿar'' "stone") is a carved, memorial stele bearing a cross, and often with additional motifs such as rosettes, interlaces, and botanical motifs. ''Khachkars'' are characteristic of medieval Christian Armenian art.The Grove Encyclopedia of Medieval Art and Architecture. — Oxford University Press, 2012. — Vol. 2. — P. 222.''"'Khatck'ar' rmen.:'cross-stone'Typical Armenian stone monument, comprising an upright slab (h. c. 1—3 m) carved with a cross design, usually set on a plinth or rectangular base. "'' Since 2010, khachkars, their symbolism and craftsmanship are inscribed in the UNESCO list of Intangible Cultural Heritage. Description The most common ''khachkar'' feature is a cross surmounting a rosette or a solar disc. The remainder of the stone face is typically filled with elaborate patterns of leaves, grapes, pomegranates, and bands of interlace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Cemetery In Julfa
The Armenian cemetery in Julfa (, ''Jughayi gerezmanatun'') was a cemetery near the town of Julfa, Azerbaijan (city), Julfa (known as Jugha in Armenian), in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan that originally housed around 10,000 funerary monuments. The tombstones consisted mainly of thousands of ''khachkars—''uniquely decorated cross-stones characteristic of medieval Christian Armenian art. The cemetery was still standing in the late 1990s, when the government of Azerbaijan began a the monuments. Several appeals were filed by both Armenian and international organizations, condemning the Azerbaijani government and calling on it to desist from such activity. In 2006, Azerbaijan barred European Parliament members from investigating the claims, charging them with a "biased and hysterical approach" to the issue and stating that it would only accept a delegation if it visited Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh, Armenian-occupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noraduz Cemetery
Noratus cemetery (), also spelled Noraduz, is a medieval cemetery with many early khachkars (carved memorial stones) located in the village of Noratus in the Gegharkunik Province of Armenia, near Gavar and Lake Sevan, 90 km north of Yerevan. The cemetery has the largest cluster of khachkars in Armenia. It is currently the largest surviving cemetery with khachkars following the destruction of the khachkars in Old Julfa, Nakhichevan by the government of Azerbaijan. Khachkars The oldest khachkars in the cemetery date back to the late 10th century. During the revival of the khachkar tradition in the 16-17th centuries many khachkars were built under the yoke of the Safavid Empire when oriental influences seeped into Armenian art. Three master carvers from this period carved khachkars in Noraduz, the most notable of whom was Kiram Kazmogh (1551–1610), his contemporaries were Arakel and Meliset. The cemetery is spread over a seven hectare field containing almost a thousan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
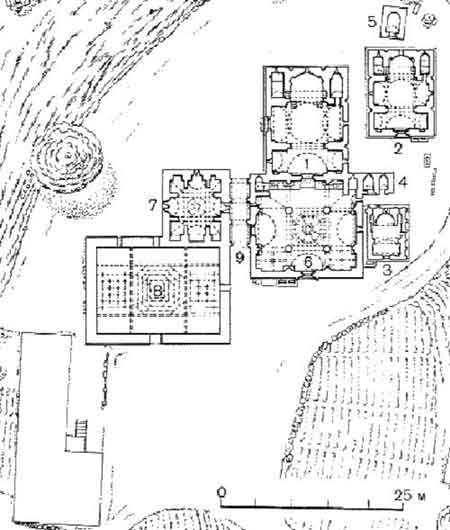
Geghard
Geghard (, meaning "spear") is a medieval monastery in the Kotayk province of Armenia, being partially carved out of the adjacent mountain, surrounded by cliffs. It is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site with enhanced protection status. While the main chapel was built in 1215, the monastery complex was founded in the 4th century by Gregory the Illuminator at the site of a sacred spring inside a cave. The monastery had thus been originally named Ayrivank (Այրիվանք), meaning "the Monastery of the Cave". The name commonly used for the monastery today, Geghard, or more fully Geghardavank (Գեղարդավանք), meaning "the Monastery of the Spear", originates from the spear which had wounded Jesus at the Crucifixion, allegedly brought to Armenia by Apostle Jude, called here Thaddeus, and stored amongst many other relics. Now it is displayed in the Echmiadzin treasury. The spectacular towering cliffs surrounding the monastery are part of the Azat River gorge, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
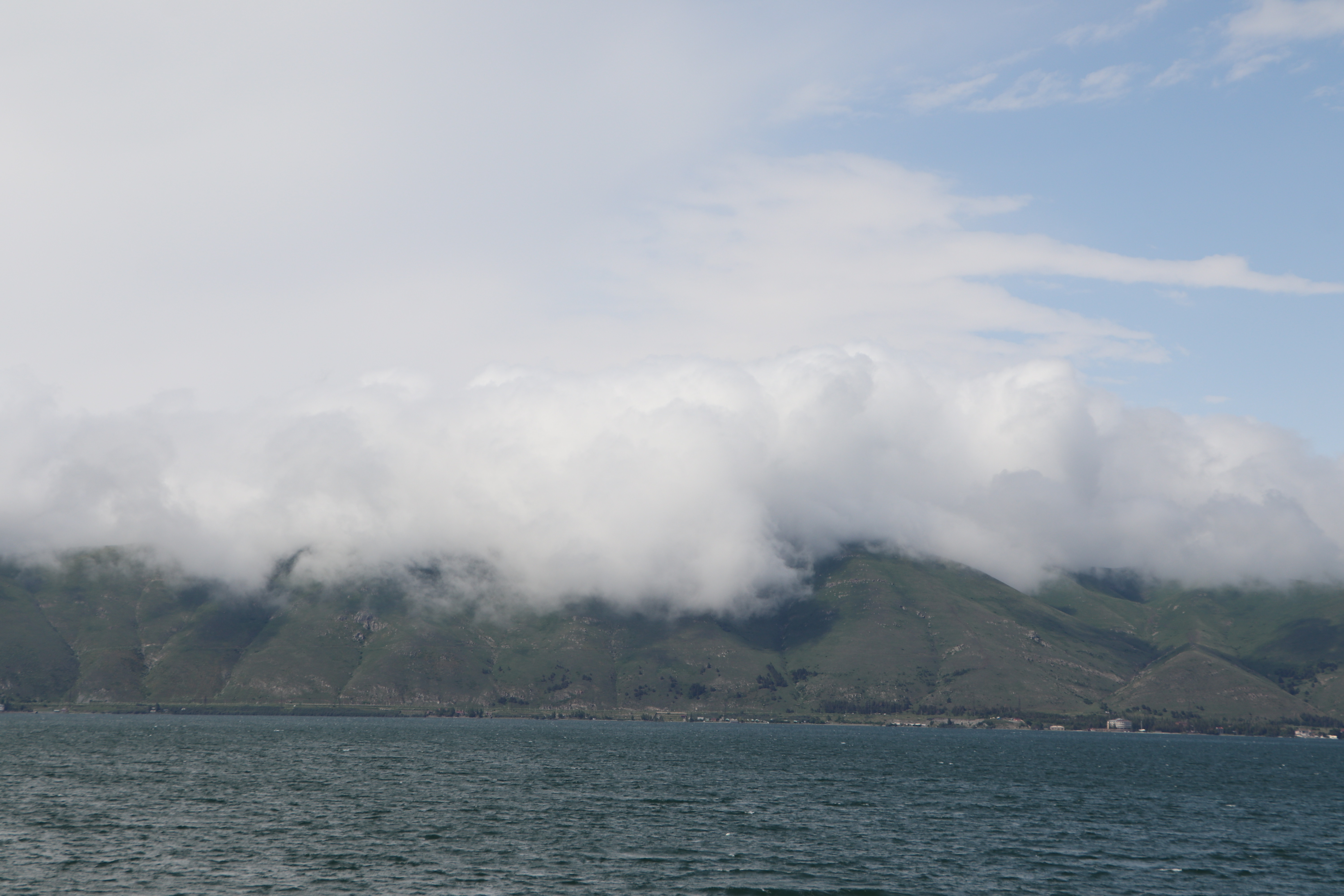
Lake Sevan
Lake Sevan () is the largest body of water in both Armenia and the Caucasus region. It is one of the largest freshwater Alpine lake, high-altitude (alpine) lakes in Eurasia. The lake is situated in Gegharkunik Province, at an altitude of above sea level. The total surface area of its basin is about , which makes up of Armenia's territory. The lake itself is , and the volume is . It is fed by 28 rivers and streams. Only 10% of the incoming water is drained by the Hrazdan River, while the remaining 90% evaporates. Sevan has significant economic, cultural, and recreational value. Its sole major island (now a peninsula) is home to a Sevanavank, medieval monastery. The lake provides some 90% of the fish and 80% of the crayfish catch of Armenia. Sevan was heavily exploited for irrigation of the Ararat plain and hydroelectric power generation during the Soviet period. Consequently, its water level decreased by around and its volume reduced by more than 40%. Later, two Water tunne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Art
Armenian art is the unique form of art developed over the last five millennia in which the Armenian people lived on the Armenian Highland. Armenian architecture and miniature painting have dominated Armenian art and have shown consistent development over the centuries. Other forms of Armenian art include sculpture, fresco, mosaic, ceramic, metalwork, engraving, and textiles, especially Armenian carpets. Prehistoric Armenia was home to the Urartu culture in the Iron Age, notable for its early metal sculptures, often of animals. The region was, as later, often contested by the large empires holding the nearby regions of Persia, Mesopotamia and Anatolia. The Armenians adopted Christianity very early, and developed their own version of Eastern Christian art, with much use of icons, Armenian miniatures in books, and the very original architecture Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists
UNESCO established its Lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage with the aim of ensuring better protection of important intangible cultural heritages worldwide and the awareness of their significance.Compare: This list is published by the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, the members of which are elected by State Parties meeting in a General Assembly. Through a compendium of the different oral and intangible treasures of humankind worldwide, the programme aims to draw attention to the importance of safeguarding intangible heritage, which UNESCO has identified as an essential component and as a repository of cultural diversity and of creative expression. The list was established in 2008 when the 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage took effect. , the programme compiles three lists. The longer Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity comprises cultural "practices and expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan (civilization), Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaan#Canaanites, Canaanite and Aramaeans, Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echmiadzin
Vagharshapat ( ) is the 5th-largest city in Armenia and the most populous municipal community of Armavir Province, located about west of the capital Yerevan, and north of the closed Turkish-Armenian border. It is commonly known as Ejmiatsin (also spelled Echmiadzin or Etchmiadzin, , ), which was its official name between 1945 and 1995. It is still commonly used colloquially and in official bureaucracy, a case of dual naming. The city is best known as the location of Etchmiadzin Cathedral and Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin, the center of the Armenian Apostolic Church. It is thus unofficially known in Western sources as a "holy city" and in Armenia as the country's "spiritual capital". It was one of the major cities and a capital of the ancient Kingdom of Greater Armenia. Reduced to a small town by the early 20th century, it experienced large expansion during the Soviet period becoming, effectively, a suburb of Yerevan. Its population stands just over 37,000 based on 2016 esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goshavank
Goshavank (; meaning "Monastery of Gosh"; previously known as Nor Getik) is a 12–13th-century Armenian monastery located in the village of Gosh, Armenia, Gosh in the Tavush Province of Armenia. The monastery which has remained in relatively good condition also houses one of the world's finest examples of a khachkar. History Goshavank was erected in the place of an older monastery once known as ''Nor Getik'', which had been destroyed by an earthquake in 1188. Mkhitar Gosh, a statesman, scientist and author of numerous fables and parables as well as The Lawcode (Datastanagirk') of Mkhitar Gosh, the first criminal code, took part in the rebuilding of the monastery. At Goshavank, Mkhitar Gosh founded a school. One of its alumni, an Armenian scientist by the name of Kirakos Gandzaketsi wrote ''The History of Armenia''. The architect Mkhitar the Carpenter and his disciple Hovhannes also took an active part in the building of the monastery. The complex was later renamed Goshavan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |