|
Kepler-22b
Kepler-22b (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation ''KOI-087.01'') is an exoplanet orbiting within the Circumstellar habitable zone, habitable zone of the Solar analog, Sun-like star Kepler-22. It is located about from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus (constellation), Cygnus. It was discovered by NASA's Kepler (spacecraft), Kepler Space Telescope in December 2011 and was the first known Transit method, transiting planet to orbit within the habitable zone of a Sun-like star, where liquid water could exist on the planet's surface. Kepler-22 is too dim to be seen with the naked eye. Kepler-22b's radius is roughly twice that of Earth. Its mass and surface composition are unknown. However, an Structure of the Earth, Earth-like composition for the planet is believed to be unlikely; it is more likely to be an ocean planet or have a Volatile (astrogeology), volatile-rich composition with a liquid or gaseous outer shell. The only parameters of the planet's orbit tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-22
Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia, Extrasolar PlanetsEncyclopaedia Kepler-22 is a Sun-like star in the northern constellation of Cygnus (constellation), Cygnus, the swan, that is orbited by at least 1 Kepler-22b, planet found to be unequivocally within the star's habitable zone. It is located at the celestial coordinates: Right Ascension , Declination . With an apparent visual magnitude of 11.7, this star is too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It can be viewed with a telescope having an aperture of at least . The estimated distance to Kepler-22 is . __TOC__ Stellar characteristics Kepler-22 is slightly smaller and cooler than the Sun, with a lower abundance of elements having more mass than helium. It has a spectral type of G5V, while the luminosity class remains undetermined. This star is radiating 79% of the Sun's luminosity from its stellar atmosphere, outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 5,518 K, giving it the yellow-hued glow of a G-type star. A p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitable Zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the habitable zone (HZ), or more precisely the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure.J. F. Kasting, D. P. Whitmire, R. T. Reynolds, Icarus 101, 108 (1993). The bounds of the HZ are based on Earth's position in the Solar System and the amount of radiant energy it receives from the Sun. Due to the importance of liquid water to Earth's biosphere, the nature of the HZ and the objects within it may be instrumental in determining the scope and distribution of planets capable of supporting Earth-like extraterrestrial life and extraterrestrial intelligence, intelligence. As such, it is considered by many to be a major factor of planetary habitability, and the most likely place to find extraterrestrial liquid water and biosignatures elsewhere in the universe. The habitable zone is also called the Goldilocks zone, a metaphor, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler Telescope
The Kepler space telescope is a defunct space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. The principal investigator was William J. Borucki. After nine and a half years of operation, the telescope's reaction control system fuel was depleted, and NASA announced its retirement on October 30, 2018. Designed to survey a portion of Earth's region of the Milky Way to discover Earth-size exoplanets in or near habitable zones and to estimate how many of the billions of stars in the Milky Way have such planets, Kepler's sole scientific instrument is a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of approximately 150,000 main sequence stars in a fixed field of view. These data were transmitted to Earth, then analyzed to detect periodic dimming caused by exoplanets that cross in front of their host star. Only planets whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler (spacecraft)
The Kepler space telescope is a defunct space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized Exoplanet, planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. The principal investigator was William J. Borucki. After nine and a half years of operation, the telescope's reaction control system fuel was depleted, and NASA announced its retirement on October 30, 2018. Designed to survey a portion of Earth's region of the Milky Way to discover Terrestrial planet, Earth-size exoplanets in or near habitable zones and to estimate how many of the billions of stars in the Milky Way have such planets, Kepler's sole scientific instrument is a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of approximately 150,000 main sequence stars in a fixed field of view. These data were transmitted to Earth, then transit method, analyzed to detect periodic dimming caused by exoplanets that Astronomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Planet
An ocean world, ocean planet or water world is a type of planet or natural satellite that contains a substantial amount of water in the form of oceans, as part of its hydrosphere, either beneath the planetary surface, surface, as subsurface oceans, or on the surface, potentially submerging all dry land. The term ''ocean world'' is also used sometimes for astronomical bodies with an ocean composed of a different fluid or thalassogen, such as lava (the case of Io (moon), Io), ammonia (in a eutectic mixture with water, as is likely the case of Titan (moon), Titan's inner ocean) or hydrocarbons (like on Titan's surface, which could be the most abundant kind of exosea). The study of extraterrestrial oceans is referred to as planetary oceanography. Earth is the only astronomical object known to presently have bodies of liquid water on its surface, although subsurface oceans are suspected to exist on Jupiter's moons Europa (moon), Europa and Ganymede (moon), Ganymede and Saturn's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit (astronomy)
In astronomy, a transit (or astronomical transit) is the passage of a astronomical object, celestial body directly between a larger body and the observer. As viewed from a particular vantage point, the transiting body appears to move across the face of the larger body, eclipse, covering a small portion of it. The word "transit" refers to cases where the nearer object apparent size, appears smaller than the more distant object. Cases where the nearer object appears larger and completely hides the more distant object are known as occultation, ''occultations''. However, the probability of seeing a transiting planet is low because it is dependent on the alignment of the three objects in a nearly perfectly straight line. Many parameters of a planet and its parent star can be determined based on the transit. In the Solar System One type of transit involves the motion of a planet between a Earth, terrestrial observer and the Sun. This can happen only with inferior and superior pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or come from an external source, such as its host star. In the case of Earth, the Sun emits shortwave radiation (sunlight) that passes through greenhouse gases to heat the Earth's surface. In response, the Earth's surface emits outgoing longwave radiation, longwave radiation that is mostly Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed by greenhouse gases. The absorption of longwave radiation prevents it from reaching space, reducing the rate at which the Earth can cool off. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's average surface temperature would be as cold as . This is of course much less than the 20th century average of about . In addition to naturally present greenhouse gases, burning of fossil fuels has greenhouse gas emissions, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
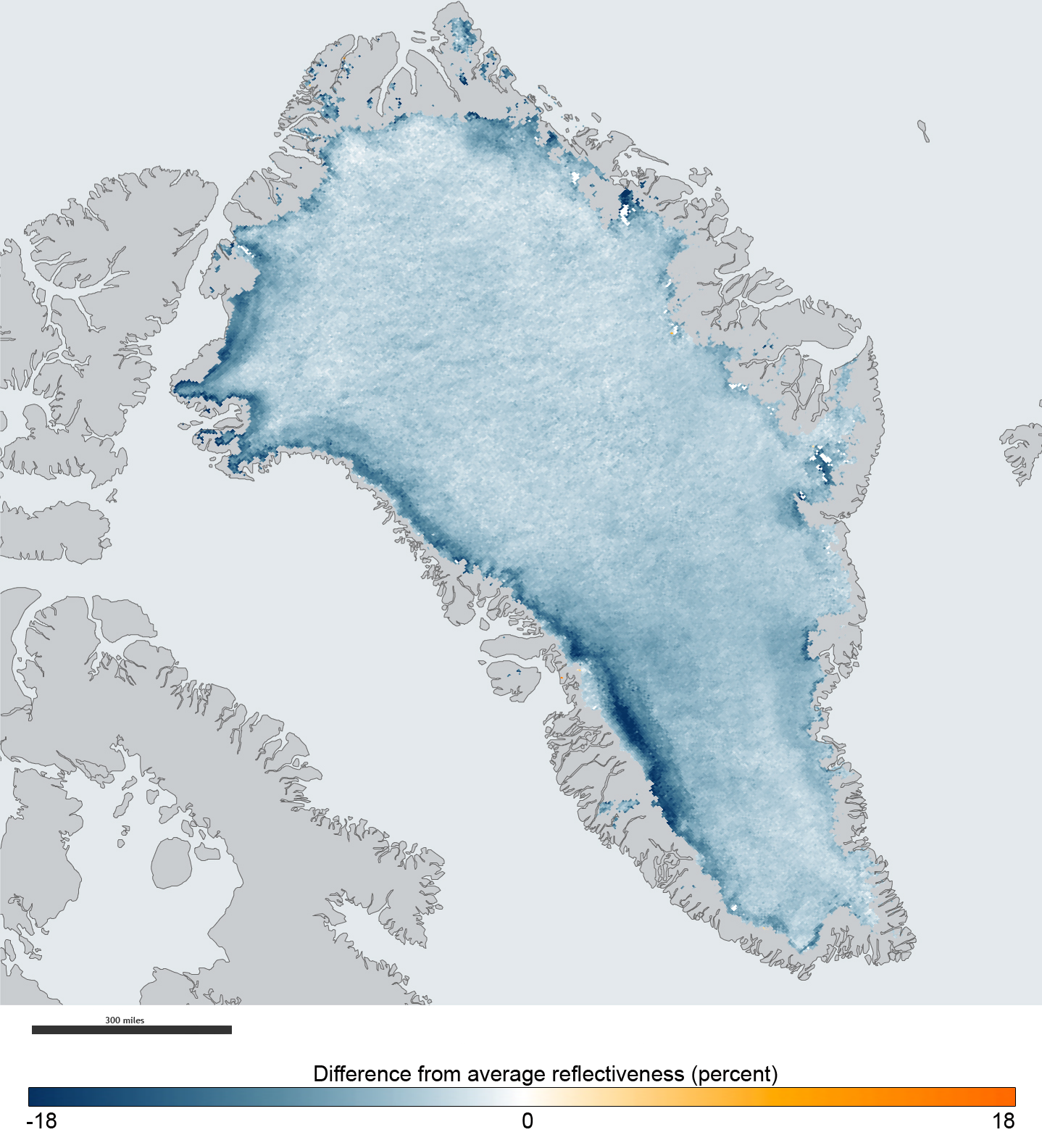
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is the line segment or distance from its center to any of its Vertex (geometry), vertices. The name comes from the Latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the spoke of a chariot wheel.Definition of Radius at dictionary.reference.com. Accessed on 2009-08-08. The typical abbreviation and mathematical symbol for radius is ''R'' or ''r''. By extension, the diameter ''D'' is defined as twice the radius:Definition of radius at mathwords.com. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |