|
Kenneth Kaunda
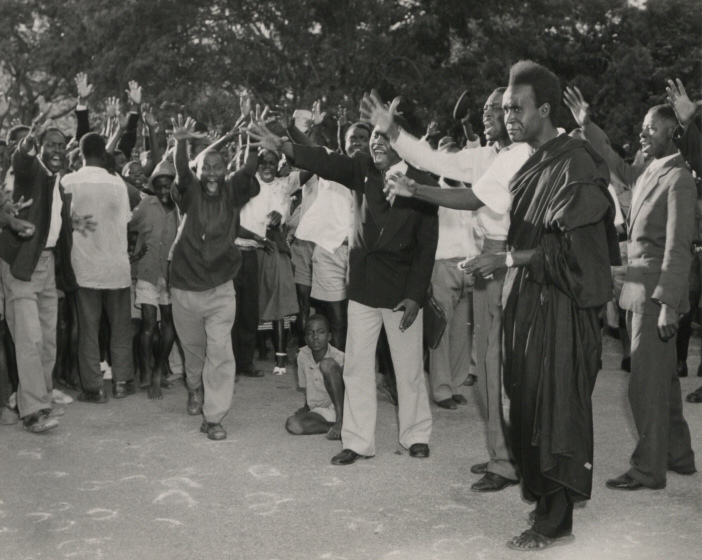
Kenneth Kaunda (28 April 1924 – 17 June 2021), also known as KK, was a Zambian politician who served as the first president of Zambia from 1964 to 1991. He was at the forefront of the struggle for independence from Northern Rhodesia, British rule. Dissatisfied with Harry Nkumbula's leadership of the Zambian African National Congress, Northern Rhodesian African National Congress, he broke away and founded the Zambian African National Congress (1958–1959), Zambian African National Congress, later becoming the head of the socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP). Kaunda was the first president of independent Zambia. In 1973, following tribal and inter-party violence, all political parties except UNIP were banned through an amendment of the constitution after the signing of the Choma Declaration. At the same time, Kaunda oversaw the acquisition of majority stakes in key foreign-owned companies. The 1973 oil crisis and a slump in export revenues put Zambia in a state o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Northern Rhodesia
The prime minister of Zambia was the head of government of Zambia. From 1973 to 1975, Mainza Chona was the first person to hold the position following independence from the United Kingdom (Kenneth Kaunda was the only prime minister of Northern Rhodesia in 1964, before it became independent as Zambia). The position of the prime minister of Zambia was abolished in 1991, in the last months of Kaunda's presidential term. Since then, the President of Zambia serves as both the head of state and the head of government. History Northern Rhodesia When the country was founded as the British colony of Northern Rhodesia separate from British South Africa Company rule in the Rhodesias, the elected Legislative Council was created. At the time, the office of prime minister did not exist, with all executive power being vested in the governor of Northern Rhodesia. However, the leader of the largest elected party on the council was considered as the "unofficial" prime minister. When Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statelessness
In international law, a stateless person is someone who is "not considered as a national by any state under the operation of its law". Some stateless people are also refugees. However, not all refugees are stateless, and many people who are stateless have never crossed an international border. At the end of 2022, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees published an estimation of 4.4 million people worldwide as either stateless or of undetermined nationality, 90,800 (+2%) more than at the end of 2021. However, the data itself is not complete because UNHCR does not have data from many countries, such as from at least 22 countries where mass statelessness exists. The data also does not include de facto stateless people who have no legal identification to prove their nationality or legal existence. According to the World Bank, at least 850 million fit that category. Given that the legal concept of nationality prevails in practice, completely undocumented people fit the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Scotland
The Church of Scotland (CoS; ; ) is a Presbyterian denomination of Christianity that holds the status of the national church in Scotland. It is one of the country's largest, having 245,000 members in 2024 and 259,200 members in 2023. While membership in the church has declined significantly in recent decades (in 1982 it had nearly 920,000 members), the government Scottish Household Survey found that 20% of the Scottish population, or over one million people, identified the Church of Scotland as their religious identity in 2019. In the 2022 census, 20.4% of the Scottish population, or 1,108,796 adherents, identified the Church of Scotland as their religious identity. The Church of Scotland's governing system is Presbyterian polity, presbyterian in its approach, therefore, no one individual or group within the church has more or less influence over church matters. There is no one person who acts as the head of faith, as the church believes that role is the "Lord God's". As a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movement For Multi-Party Democracy
The Movement for Multi-party Democracy (MMD) also known as New Hope MMD is a political party in Zambia. Originally formed to oust the previous government, MMD controlled an absolute majority in parliament between 1991 and 2001, when its past leader, Frederick Chiluba was President of Zambia. Its election into power in 1991 ended the 27-year rule of President Kenneth Kaunda and his United National Independence Party (UNIP). It remained the dominant party within Zambian politics until the general elections of September 2011. History Formation and government Growing opposition to UNIP's monopoly on power, due in part to economic problems and corruption, led to the formation of the MMD in July 1990, led by Frederick Chiluba, the head of the country's trade unions. During that same year, pushed by internal and international pressure, Kaunda agreed to a referendum on the one-party state, but in the face of continued opposition, dropped the referendum and signed a constitutional amen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1991 Zambian General Election
General elections were held in Zambia on 31 October 1991 to elect a President and National Assembly. They were the first multi-party elections since 1968, and only the second multi-party elections since independence in 1964. The United National Independence Party (UNIP), which had led the country since independence (from 1973 to 1990 as the sole legal party), was comprehensively beaten by the Movement for Multi-Party Democracy (MMD). Kenneth Kaunda, who had been president since independence, was defeated in a landslide by MMD challenger Frederick Chiluba in the presidential elections, whilst the MMD won 125 of the 150 elected seats in the expanded National Assembly. Voter turnout was 45%. Background In 1973 Kaunda had declared UNIP the only legally permitted party in Zambia. From then until 1990, the government and UNIP were effectively one. Every five years, Kaunda was automatically elected to a five-year term as president by virtue of being leader of UNIP. Voters also chose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-party System
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional representation compared to those using winner-take-all elections, a result known as Duverger's law. In these countries, usually no single party has a parliamentary majority by itself ( hung parliaments). Instead, multiple political parties must negotiate to form a coalition with a majority of the vote, in order to make substantial changes. Comparisons with other party systems Unlike a one-party system (or a dominant-party system), a multi-party system encourages the general constituency to form multiple distinct, officially recognized groups, generally called political parties. Each party competes for votes from the enfranchised constituents (those allowed to vote). A multi-party system prevents the leadership of a single party fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
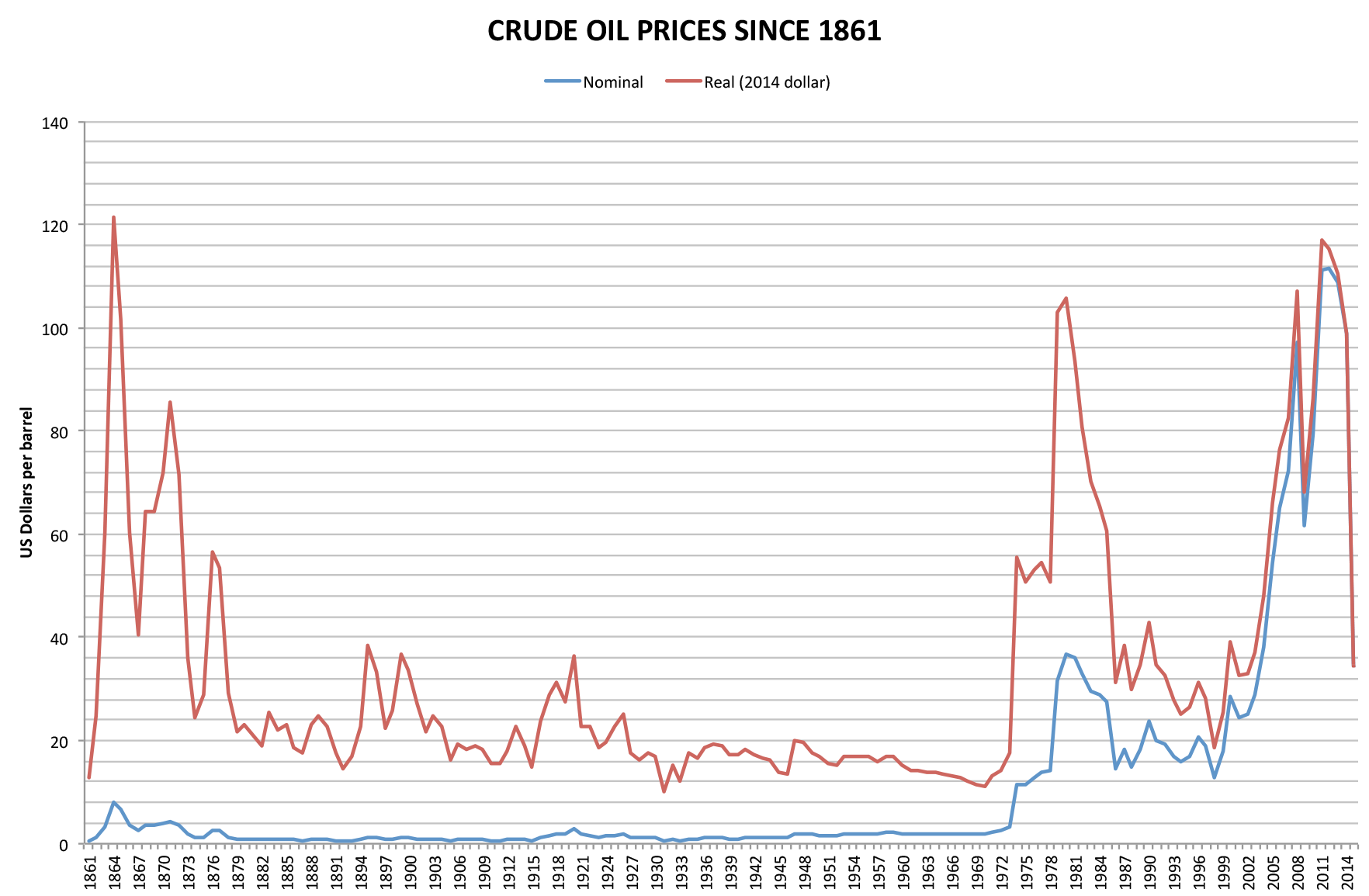
1973 Oil Crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Estado Novo (Portugal), Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US to nearly US globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United National Independence Party
The United National Independence Party (UNIP) is a political party in Zambia. It governed the country from 1964 to 1991 under the socialist President (government title), presidency of Kenneth Kaunda, and was the sole legal party in the country between 1973 and 1990. On 4 April 2021, Trevor Mwamba, Bishop Trevor Mwamba was elected President of UNIP. History UNIP was founded in October 1959 by Mainza Chona as a successor of the Zambian African National Congress (1958–1959), Zambian African National Congress (ZANC), banned earlier that year. UNIP was initially led Chona as the ZANC leader, Kaunda, had been imprisoned. Kaunda later assumed power as leader of UNIP after he was released from prison in 1960. In the general elections, UNIP won 14 seats, in second position, the first being taken by United Federal Party (UFP). Although Zambian African National Congress, Northern Rhodesian African National Congress leader Harry Nkumbula had made a secret electoral pact with the UFP, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambian African National Congress (1958–1959)
The Zambian African National Congress (ZANC) was a political party in Northern Rhodesia dedicated to promoting the rights of black people. History The ZANC was formed in October 1958, Andrew Sardanis (2011) ''Africa: Another Side of the Coin: Northern Rhodesia's Final Years and Zambia's Nationhood'', p62 following a split from the Northern Rhodesian African National Congress led by Harry Nkumbula, which Kaunda regarded as being too moderate.Anthony Appiah & Henry Louis Gates (2010) ''Encyclopedia of Africa, Volume 2'', Oxford University Press, p636 However, it was banned in March the following year and Kaunda imprisoned. upon his release Kaunda joined United National Independence Party in 1960. In 1964, after Northern Rhodesia achieved independence as Zambia Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambian African National Congress
The Northern Rhodesia Congress was a political party in Zambia. History In 1940, as the Northern Rhodesia Congress (NRC), also known as the Northern Rhodesia African Congress (NRAC), was formed. Godwin Lewanika, a Barotseland native from an aristocratic background, became the first president. "Northern Rhodesia Congress", Britannica.com, 2011, web: EB-NRC It was the first African political party in the country. NRC had its roots in the Federation of Welfare Societies, active between 1940 and 1946. In 1951 the party adopted the name Northern Rhodesian African National Congress (NRANC) under the presidency of Harry Nkumbula, and was linked to the African National Congress in South Africa. In 1953 Kenneth Kaunda became the general secretary of the organization. The NRANC was the leading force of Northern Rhodesian nationalism in the 1950s. It opposed federation, and boycotted shops where the Colour Bar was implemented. In 1955 Nkumbula was imprisoned for possessing banned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Nkumbula
Harry Mwaanga Nkumbula (15 January 1916 – 8 October 1983)Harry Mwaanga Nkumbula's bio from daughter's narrative '' Zambia Daily Mail'', 23 December 2016 Greenwood Publishing Group, Jacqueline Audrey Kalley, Elna Schoeman, Lydia Eve Andor, page 687 was a |
President Of Zambia
The president of the Republic of Zambia is the head of state and head of government of Zambia and is the highest executive authority in the country. The president is elected by popular vote for a five-year term and is responsible for the administration of the government, overseeing the implementation of national policies, and representing Zambia in international affairs. The office was established at Zambia's independence in 1964. The current president is Hakainde Hichilema, who assumed office on August 24, 2021, following the 2021 Zambian general election, 2021 presidential election where his party, the United Party for National Development, won a majority. The president's role includes appointing the Cabinet of Zambia, Cabinet, serving as Commander-in-Chief of the Zambian Defence Force, and ensuring the enforcement of laws. The office was first held by Kenneth Kaunda following Zambia Independence Act 1964, independence in 1964. Since 1991, when Kaunda left the presidency, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |