|
Kelloe
Kelloe is a village and civil parish in County Durham, England. The population of the civil parish as taken at the 2011 Census was 1,502. It is situated to the south-east of Durham. History The village takes its name from the family of Kelloe or Kellaw: Richard Kellaw was Bishop of Durham in 1311. The Lordship of the Manor of Kelloe was bought by the Tempests of Broughton Hall, North Yorkshire, and bequeathed by Sir Henry Vane-Tempest to his daughter, Lady Frances Vane, who married the third Marquess of Londonderry. The current holder of the Lordship of Kelloe is Mr Barrington Edward Kerr Gilmour of Northumberland. New villages were formed in the area with the expansion of the mining industry: the population of Kelloe parish—which included the townships (later to become separate parishes) of Cassop, Coxhoe, Quarrington, Thornley and Wingate—had increased from 663 to more than 11,000 by 1848. The population of Kelloe township remained low, with only 156 inhabitants. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stan Seymour
George Stanley Seymour Sr (16 May 1895 – 24 December 1978) was an English footballer. Regarded as one of the all-time greats to play for Newcastle United, he would come to be known as "Mr. Newcastle United", due to becoming manager (on three occasions), vice-chairman and director of the club. As a player, despite his small physique, he was famous for his runs from the left wing. Career Early career Seymour was born in Kelloe. After originally being rejected by Newcastle United as a teenager (the local pit worker was told to "come back when you grow up"), he played some non-league football for Shildon Athletic and Coxhoe before joining Bradford City in 1911 for a short spell, making only one competitive appearance. He then joined Scottish side Greenock Morton. He developed as a player at Morton, becoming popular with the locals who called him "the little Englishman". Unlike in England, a fairly normal league season was played throughout the First World War in Scotland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Barrett Browning
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (née Moulton-Barrett; 6 March 1806 – 29 June 1861) was an English poet of the Victorian era, popular in Britain and the United States during her lifetime and frequently anthologised after her death. Her work received renewed attention following the feminist scholarship of the 1970s and 1980s, and greater recognition of women writers in English. Born in County Durham, the eldest of 12 children, Elizabeth Barrett wrote poetry from the age of eleven. Her mother's collection of her poems forms one of the largest extant literature, extant collections of juvenilia by any English writer. At 15, she became ill, suffering intense head and spinal pain for the rest of her life. Later in life, she also developed lung problems, possibly tuberculosis. She took laudanum for the pain from an early age, which is likely to have contributed to her frail health. In the 1840s, Elizabeth was introduced to literary society through her distant cousin and patron John Kenyon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarrington Hill
Quarrington Hill is a village in County Durham, in England. It is situated a short distance to the north of Kelloe. Having been part of the extensive parish of Kelloe, it merged with the village of Cassop during the 19th century to form the parish of Cassop-cum-Quarrington, it is now in the parish of Coxhoe. As in most of County Durham, the chief trade here was coal mining and Cassop Colliery was where the miners worked. The inhabitants of Quarrington Hill also shared the church of St. Pauls (built in 1868), with Cassop Cassop (formerly New Cassop) is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Cassop-cum-Quarrington, in the County Durham (district), County Durham district, in the ceremonial county of County Durham, Durham, England. It has a populat .... The stones that were used in its construction were allegedly transported by William Smith, Innkeeper of the Half Moon Inn, Quarrington Hill, as he was the only villager to own such a cart to make this possible. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassop
Cassop (formerly New Cassop) is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Cassop-cum-Quarrington, in the County Durham (district), County Durham district, in the ceremonial county of County Durham, Durham, England. It has a population of about 500 and is located near the city of Durham, England, Durham. A former mining village, mining is no longer the main occupation of Cassop's inhabitants due to extensive mine closure over the last 30 years. Cassop Primary School is believed to have been the first in the UK to generate some of its own electricity with its own wind turbine which was erected in February 1999. History Cassop was formerly a Township (England), township and chapelry in the parish of Kelloe, from 1866 Cassop was a civil parish in its own right, on 24 March 1887 the parish was abolished and merged with Quarrington, County Durham, Quarrington to form "Cassop cum Quarrington". In 1881 the parish had a population of 596. Religious sites The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimdon Grange
Trimdon Grange is a village in County Durham, in England. It is situated ten miles to the west of Hartlepool, and a short distance to the north of Trimdon. Colliery disaster At 14:40 on 16 February 1882 the Trimdon Grange Coal mining, colliery suffered a major explosion causing the deaths of 69 men and boys. The coroner (TW Snagge) reported to both houses of Parliament: * The mine was a dusty mine and watering should have been daily but it was done "not in all places, but where it was absolutely necessary." * The mine was not "more than ordinarily gassy", but there is some evidence that the identified points of leakage might have been points of accumulation from leaks elsewhere. * The lamps in use were Davy lamp, Davy pattern and naked lights called "midgies" in some areas. The coroner found no evidence that the midgies were connected with the explosion. * Good order and discipline prevailed in Trimdon Grange Colliery. * The air pressure had been exceptionally low, the lowest i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Durham (district)
County Durham is a unitary authority area in the ceremonial county of County Durham, England. It is governed by Durham County Council. The district has an area of , and contains 135 civil parishes. It forms part of the larger ceremonial county of Durham, together with boroughs of Darlington, Hartlepool, and the part of Stockton-on-Tees north of the River Tees. History Between 1974 and 1 April 2009, County Durham was governed as a two-tier non-metropolitan county, with a county council and district councils. The original eight districts were Chester-le-Street, Darlington, Derwentside, Durham (city), Easington, Sedgefield, Teesdale, and Wear Valley. In 1997 Darlington was removed from the non-metropolitan county and became a separate unitary authority. In 2009 the remaining districts were abolished and replaced by a single district covering the non-metropolitan county, with Durham County Council as the sole local authority. Geography The district has multiple hamlets and vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durham Cathedral
Durham Cathedral, formally the , is a Church of England cathedral in the city of Durham, England. The cathedral is the seat of the bishop of Durham and is the Mother Church#Cathedral, mother church of the diocese of Durham. It also contains the shrines of the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon saints Cuthbert and Bede. There are daily Church of England services at the cathedral, and it received 727,367 visitors in 2019. It is a grade I listed building and forms part of the Durham Castle and Cathedral World Heritage Site. The cathedral is the successor to the Anglo-Saxon Lindisfarne Priory, which was established but abandoned in 875 in the face of Viking Age, Viking raids. The monks settled at Chester-le-Street from 882 until 995, when they moved to Durham. The cathedral remained a monastery until it was Dissolution of the monasteries, dissolved in 1541, since when it has been governed by a Dean of Durham, dean and Chapter (religion), chapter. The cathedral precinct formed part of Durham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
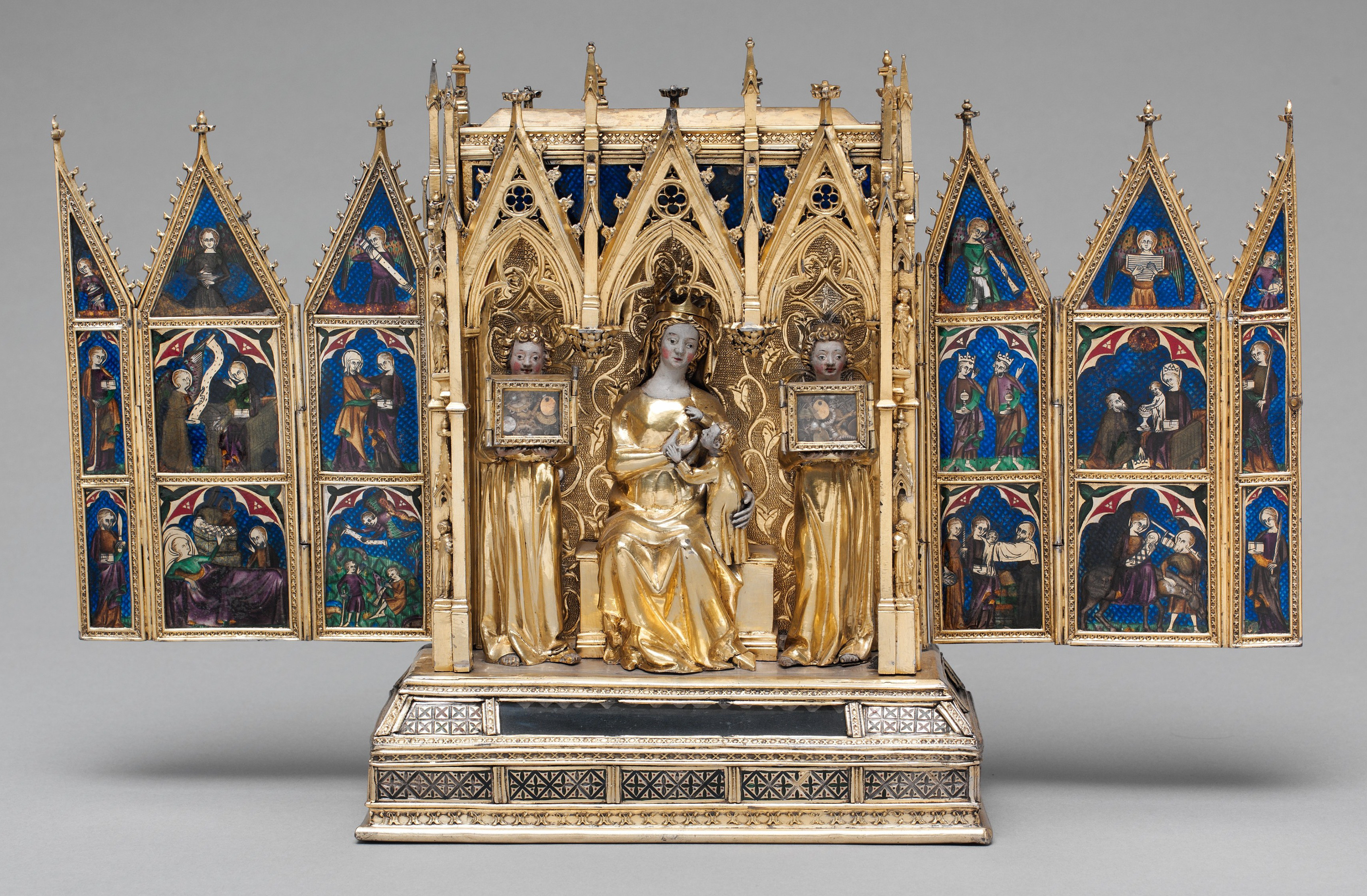
Reliquary
A reliquary (also referred to as a ''shrine'', ''Chasse (casket), chasse'', or ''phylactery'') is a container for relics. A portable reliquary, or the room in which one is stored, may also be called a ''feretory''. Relics may be the purported or actual physical remains of saints, and may comprise bones, pieces of clothing, or some object associated with saints or with other religious figures. The authenticity of any given relic is often a matter of debate; for that reason, some churches require documentation of a relic's provenance. Relics have long been important to Buddhism, Buddhists, Christianity , Christians, Hinduism , Hindus, and to followers of many other religions. These cultures often display reliquaries in shrines, churches, or temples to which the faithful make pilgrimages to gain blessings. The term is sometimes used in a looser sense to mean a container for the remains of any important figure, even non-religious ones. In particular, the kings of France often spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena (empress)
Flavia Julia Helena (; , ''Helénē''; – 330), also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an '' Augusta'' of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the lower classes'' Anonymus Valesianus'1.2 "Origo Constantini Imperatoris". traditionally in the city of Drepanon, Bithynia, in Asia Minor, which was renamed Helenopolis. Helena ranks as an important figure in the history of Christianity. In her final years, she made a religious tour of Syria Palaestina and Jerusalem, during which ancient tradition claims that she discovered the True Cross. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Anglican Communion, and the Lutheran Church revere her as a saint. Early life Though Helena's birthplace is not known with certainty, Helenopolis, then Drepanon, in Bithynia, following Procopius, is the one supported by most secondary sources, and by far the most likely candidate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
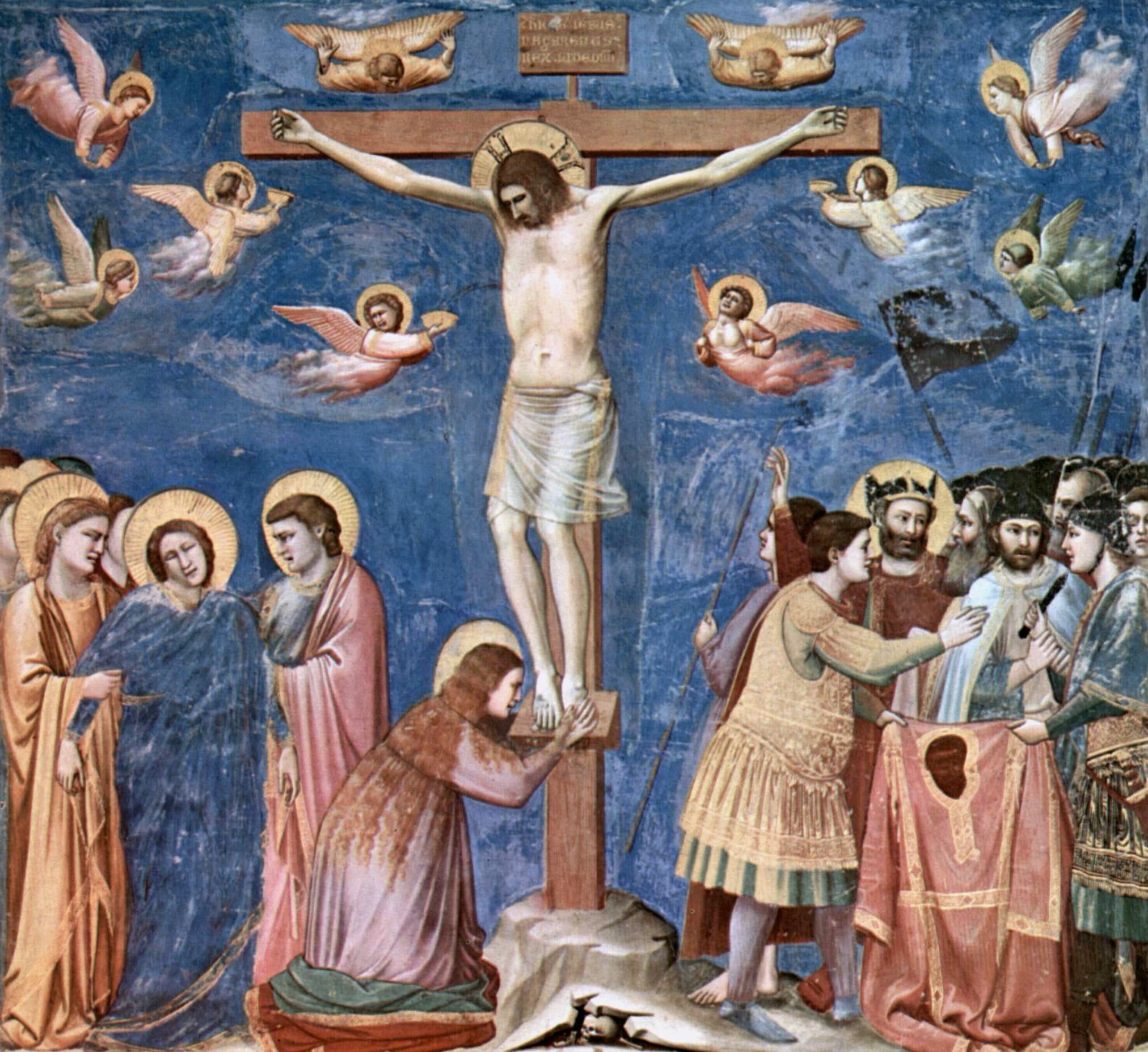
True Cross
According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real instrument of Jesus' crucifixion, cross on which Jesus of Nazareth was Crucifixion of Jesus, crucified. It is related by numerous historical accounts and Christian mythology, legends that Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helen, the mother of Roman emperor Constantine the Great, recovered the True Cross at the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, when she travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328. The late fourth-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus wrote that while Helen was there, she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, Penitent thief, Dismas and Impenitent thief, Gestas, who were executed with him. To one cross was affixed the Titulus (inscription), titulus bearing Jesus' name, but according to Rufinus, Helen was unsure of its legitimacy until a miracle revealed that it was the True Cross. This event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |