|
Kelabit Highlands
The Kelabit Highlands are a mountain range located in the northernmost part of Sarawak, Malaysia in the Miri Division. It hosts the Bario village. The highest mountains in this range are Mount Murud at , Bukit Batu Buli at , and Bukit Batu Lawi at . The current population of the Kelabit people is about 6,800. Maligan Highlands, another highland nearby located within the Limbang Division, hosts the Ba'kelalan village. Geography The rocks of the Kelabit Highlands comprise mudstones, sandstones, and limestones ranging in age from the Oligocene to Miocene periods. In terms of plate tectonics, the region was a basin formed by warping at a subduction zone where the continental crust was forced upwards. The estimated rate of uplift is 20 mm per century for the last two million years. Bario showed a lowering in temperatures during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). Villages Bario The area hosts 13 villages. Seven of these are in the Bario area while the others are around the outskirts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny. Mountain ranges are formed by a variety of geological processes, but most of the significant ones on Earth are the result of plate tectonics. Mountain ranges are also found on many planetary mass objects in the Solar System and are likely a feature of most terrestrial planets. Mountain ranges are usually segmented by highlands or mountain passes and valleys. Individual mountains within the same mountain range do not necessarily have the same geologic structure or petrology. They may be a mix of different orogenic expressions and terranes, for example thrust sheets, uplifted blocks, fold mountains, and volcanic landforms resulting in a variety of rock types. Major ranges Most geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
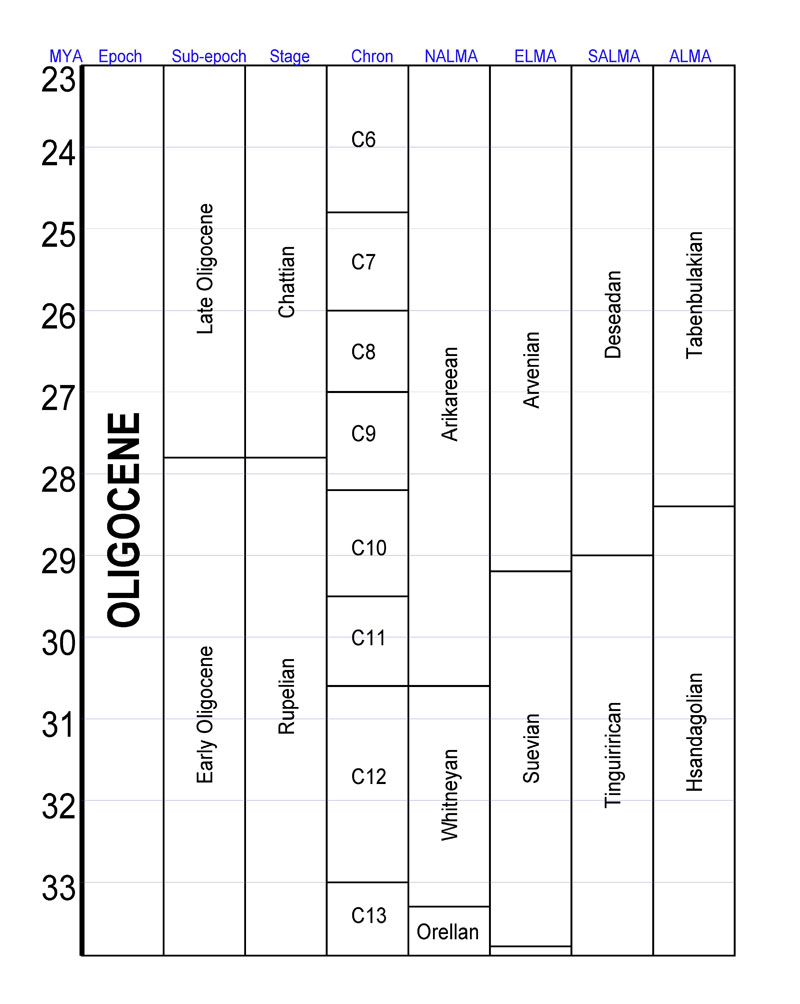
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Areas Of Sarawak
Importance is a property of entities that matter or make a difference. For example, World War II was an important event and Albert Einstein was an important person because of how they affected the world. There are disagreements in the academic literature about what type of difference is required. According to the causal impact view, something is important if it has a big causal impact on the world. This view is rejected by various theorists, who insist that an additional aspect is required: that the impact in question makes a value difference. This is often understood in terms of how the important thing affects the well-being of people. So in this view, World War II was important, not just because it brought about many wide-ranging changes but because these changes had severe negative impacts on the well-being of the people involved. The difference in question is usually understood counterfactually as the contrast between how the world is and how the world would have been witho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Sarawak
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Malaysia
The geography of Malaysia includes both the physical and the human geography of Malaysia, a Southeast Asian country made up of two major landmasses separated by water—Peninsular Malaysia to the west and East Malaysia to the east—and numerous smaller islands that surround those landmasses. Peninsular Malaysia is on the southernmost part of the Malay Peninsula, south of Thailand, north of Singapore and east of the Indonesian island of Sumatra; East Malaysia comprises most of the northern part of Borneo, and shares land borders with Brunei to the north and Indonesian Borneo to the south. Climate Located near the equator, Malaysia's climate is categorised as equatorial, being hot and humid throughout the year. The average rainfall is a year and the average temperature is . The climates of Peninsular Malaysia and the East Malaysia differ, as the climate on the peninsula is directly affected by wind from the mainland, as opposed to the more maritime weather of East Malaysia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Seridan
Long Seridan is a Kelabit settlement in the Miri division of Sarawak, Malaysia. It lies approximately east-north-east of the state capital Kuching. Long Seridan Airport has a STOL runway, originally built by Gurkha engineers in 1963. There are several homestays where tourists can stay and enjoy the local jungle trekking, fishing and visiting Penan The Penan are a nomadic indigenous people living in Sarawak and Brunei, although there is only one small community in Brunei; among those in Brunei half have been converted to Islam, even if only superficially. Penan are one of the last such p ... settlements. Neighbouring settlements include: * Buyo southeast * Long Napir north * Rumah Unar north * Rumah Sigarsei north * Kubaan southeast * Pa Tik southeast * Rumah Danau north * Rumah Ambau northwest * Rumah Haling northwest * Rumah Sungai Medalam northwest References {{Sarawak Populated places in Sarawak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Lellang
Long Lellang (also known as Long Lelang) is a small village in the Kelabit highlands of Sarawak, Malaysia. It lies approximately east-north-east of the state capital Kuching. The village is predominantly populated by the Kelabit tribe, though a number of Penan people also live there. All the surrounding villages near Long Lellang are Penan villages. The village has shops and a church, and over 100 students are enrolled at the village school, SRK Long Lellang. The population of Long Lellang is about 100 families. Long Lellang Airport is a STOL airfield, providing access to this remote village. An aerial view of the village as it was before the new airstrip and terminal building were constructed is viewable on the Aviation Forum. Neighbouring settlements include: * Long Datih southwest *Aro Kangan Aro Kangan is a settlement in the remote mountainous interior of Sarawak, Malaysia. It lies approximately east-north-east of the state capital Kuching. To reach Aro Kangan from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pa Umor
Pa Umor is a settlement in the Marudi division of Sarawak, Malaysia. It lies approximately east-north-east of the state's capital, Kuching. The village lies about an hour’s walk east of Bario, and is only a few kilometres from the Indonesian border. There is a salt spring close to Pa Umor, significant because, without a local source of salt, inhabitants would have to travel to the coast for it. In 2007 the village population was made up of about forty Kelabit families. Neighbouring settlements include: *Bario Bario is a community of 13 to 16 villages located on the Kelabit Highlands in Miri Division, Sarawak, Malaysia, lying at an altitude of 1000 m (3280 ft) above sea level. It is located close to the Sarawak-Kalimantan border, 178 k ... west * Pa Lungan north * Pa Main south * Pa Mada south * Pa Bangar south * Long Semirang west * Long Rapung north * Long Danau south * Pa Dali south * Ramudu Hulu south References Villages in Sarawak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing a major expansion of deserts, along with a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via cosmogenic nuclide, terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets in the southern hemisphere commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage has been estimated to have occurred sometime between 26,500 years ago and 20,000 years ago. After this, deglaciation caused an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
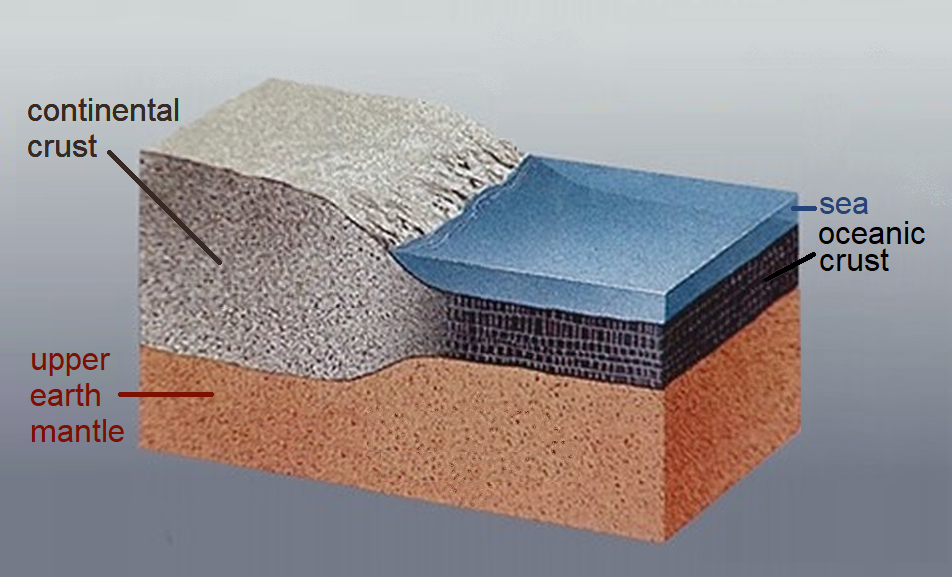
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. Most continental crust is dry land above sea level. However, 94% of the Zealandia continental crust region is submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean, with New Zealand constituting 93% of the above-water portion. Thickness and density The continental crust consists of various layers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |