|
Keijō Shrine
, sometimes Seoul Shrine, was a Shinto shrine in Keijō (Seoul), Korea under Japanese rule, Korea, Empire of Japan. The shrine was established on November 3, 1898,青井哲人「ソウル・南山の神域化-植民都市と神社境内」(明治聖徳記念学会紀要復刊第43号、2006年) and destroyed on November 17, 1945, several months after the end of colonial rule. The shrine was located to the north of the mountain Namsan (Seoul), Namsan. Theological history Initially the shrine only worshipped Amaterasu but it later added the , Ōkuninushi, and Sukunahikona used in Japanese colonial shrines. after it was established that it would not become the Chosen Jingu. Uniquely it referred to Kunitama as Chosen Kunitama suggesting a distinctly Korean flavor, as this shrine attempted to integrate many Korean customs. Many locals identified "Chosen Kunitama" with Dangun. In 1936 the government released a memo saying that Okunitama was in fact a generic title for any Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religions, East Asian religion by Religious studies, scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. With no central authority in control of Shinto, there is much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheism, polytheistic and animism, animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the (神). The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshipped at household shrines, family shrines, and Shinto shrine, ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Financial News
''The Financial News'' () is a South Korean daily newspaper. The newspaper's motto is "First-Class financial paper". Kwon Seong Cheol, an alumnus of Seoul National University Seoul National University (SNU; ) is a public university, public research university in Seoul, South Korea. It is one of the SKY (universities), SKY universities and a part of the Flagship Korean National Universities. The university's main c ..., was appointed president of the paper in 2010. A new president was appointed in March 2021. References External linksThe Financial News Korean-language newspapers Daily newspapers published in South Korea {{SouthKorea-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
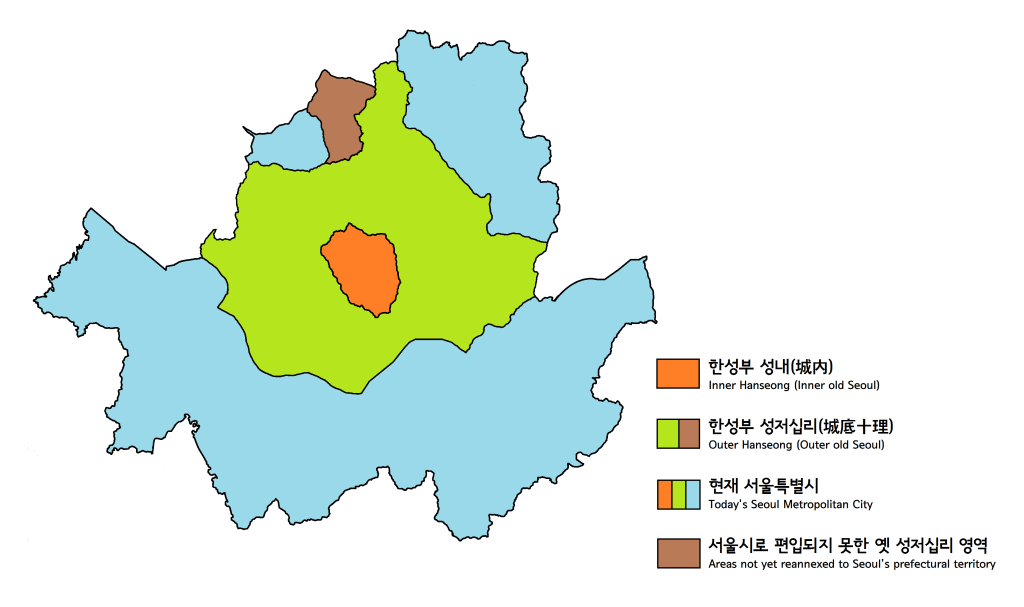
History Of Seoul
The region now corresponding to Seoul, South Korea has been inhabited since the Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of a number of kingdoms since it was established. Prehistoric It is believed that humans were living in the area that is now Seoul along the lower reaches of the Han River during the Paleolithic Age and archaeological research shows that people began to lead settled lives starting in the Neolithic Age. Prehistoric remains that are unearthed in the , located in Gangdong District, date back to about 3,000 to 7,000 years ago. With the introduction of bronze ware from about 700 BC, settlements gradually began to spread from the river basin toward inland areas. Three Kingdoms and Unified Silla period In 18 BC, the kingdom of Baekje founded its capital city, Wiryeseong, which is believed to be inside modern-day Seoul. Baekje subsequently developed from a member state of the Mahan confederacy into one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. There are several city wall re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto Shrines In The Japanese Colonial Empire
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. With no central authority in control of Shinto, there is much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the (神). The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshipped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto Shrines
A Stuart D. B. Picken, 1994. p. xxiii is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more kami, , the deities of the Shinto religion. The Also called the . is where a shrine's patron is or are enshrined.Iwanami Japanese dictionary The may be absent in cases where a shrine stands on or near a sacred mountain, tree, or other object which can be worshipped directly or in cases where a shrine possesses either an altar-like structure, called a himorogi, , or an object believed to be capable of attracting spirits, called a yorishiro, , which can also serve as direct bonds to a . There may be a and other structures as well. Although only one word ("shrine") is used in English, in Japanese, Shinto shrines may carry any one of many different, non-equivalent names like , , , , , , , , , or . Miniature shrines (hokora, ) can occasionally be found on roadsides. Large shrines sometimes have on their precincts miniature shrines, or . Because the and once had differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 1898
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto Shrines In Korea
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. With no central authority in control of Shinto, there is much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the (神). The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshipped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nogi Maresuke
Count , also known as Kiten, Count Nogi GCB (December 25, 1849September 13, 1912), was a Japanese general in the Imperial Japanese Army and a governor-general of Taiwan. He was one of the commanders during the 1894 capture of Port Arthur from China and a prominent figure in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05, as commander of the forces which captured Port Arthur from the Russians. He was a national hero in Imperial Japan as a model of feudal loyalty and self-sacrifice, ultimately to the point of suicide. In the Satsuma Rebellion, he lost a banner of the emperor in battle, for which he tried to atone with suicidal bravery in order to recapture it, until ordered to stop. In the Russo-Japanese War, he captured Port Arthur but he felt that he had lost too many of his soldiers, so requested permission to commit suicide, which the emperor refused. These two events, as well as his desire not to outlive his master, motivated his suicide on the day of the funeral of the Emperor Meiji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaterasu
, often called Amaterasu () for short, also known as and , is the goddess of the sun in Japanese mythology. Often considered the chief deity (''kami'') of the Shinto pantheon, she is also portrayed in Japan's earliest literary texts, the () and the (720 CE), as the ruler (or one of the rulers) of the heavenly realm Takamagahara and as the mythical ancestress of the Imperial House of Japan via her grandson Ninigi. Along with two of her siblings (the moon deity Tsukuyomi and the impetuous storm-god Susanoo) she ranks as one of the "Three Precious Children" (, ), the three most important offspring of the creator god Izanagi. Amaterasu's chief place of worship, the Grand Shrine of Ise in Ise, Mie Prefecture, is one of Shinto's holiest sites and a major pilgrimage center and tourist spot. As with other Shinto ''kami'', she is also enshrined in a number of Shinto shrines throughout Japan. Name The goddess is referred to as ''Amaterasu Ōmikami'' ( / ; historical orthogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |