|
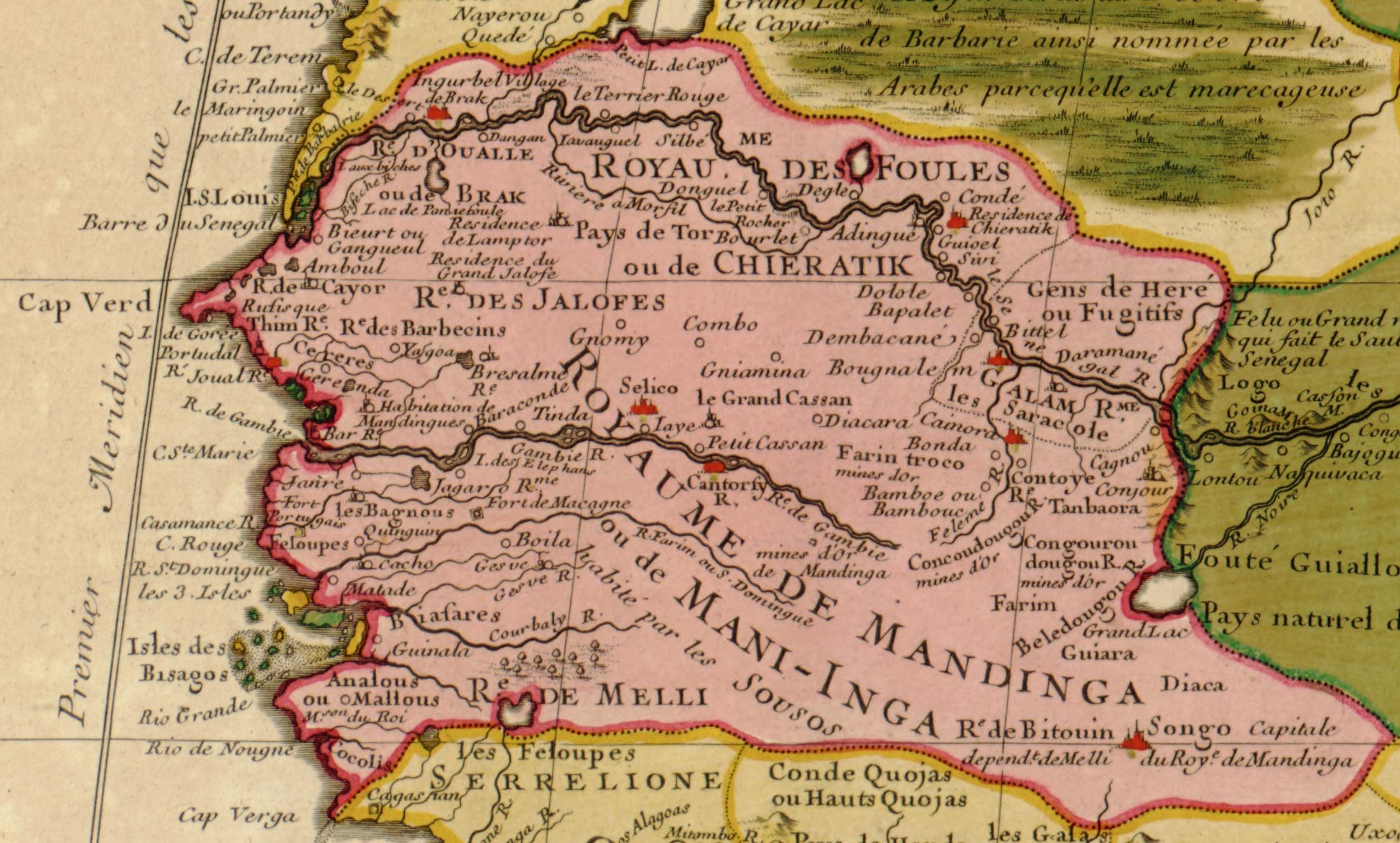
Kayor
Cayor ( wo, Kajoor; ar, كاجور) was the largest and most powerful kingdom (1549–1879) that split off from the Jolof Empire in what is now Senegal. Cayor was located in northern and central Senegal, southeast of Walo, west of the kingdom of Jolof, and north of Baol and the Kingdom of Sine. History In 1549, the damel (''dammeel'' in Wolof, often translated into European languages as "king") Dece Fu Njogu became independent from Jolof and set Cayor's capital at Mboul. The French, under governor Louis Faidherbe, annexed Cayor in 1868; Cayor re-established independence in 1871. France invaded again and annexed Cayor again in 1879, when it ceased to be a sovereign state. The kingdom was extinguished in its entirety October 6, 1886. In addition to Cayor, the damels also ruled over the Lebou area of Cap-Vert (where modern Dakar is), and they became the " Teignes" (rulers) of the neighboring kingdom of Baol. Traditionally the damel himself was not purely hereditary, but w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lat Jor
Lat Jor Ngoné Latir Diop ( wo, Lat Joor Ngoone Latiir Joop; french: Lat Dior Ngoné Latyr Diop; 1842–1886), son of Sahewer Sohna Mbay (''Sakhéwère Sokhna Mbaye'') and the Linguère royal Ngoné Latir Fal (''Ngoné Latyr Fall''), Ngoné Latyr Fall was from the Wolof Dynasty of Paleen Dedd which ruled the two kingdoms of Cayor and BaoLat Joor was a nineteenth-century damel (king) of Cayor, a Wolof state that is today in south-central Sénégal. Lat Jor belonged to the '' Geej'' or ''Guedj'' Wolof maternal dynasty that had ruled Baol and Cayor for two centuries. The matriarch of that matriclan was the Wolof Lingeer Ngoné Dièye, a Princess from Tubé Dieye in Gandiol. Gandiol is a Wolof region in the north of Senegal that borders MauritaniLat Jor was a direct maternal descendant of Lingeer Ngoné Dièye of Tubé Dieye. Religion Lat Jior was born a Muslim in the Muslim family of Sakhewar FatmHis grandfather Sakhewar Fatma Converted to Islam from the Wolof Islamic scholar of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Senegal
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era. Paleolithic The earliest evidence of human life is found in the valley of the Falémé in the south-east. The presence of man in the Lower Paleolithic is attested by the discovery of stone tools characteristic of Acheulean such as hand axes reported by Théodore Monod at the tip of Fann in the peninsula of Cap-Vert in 1938, or cleavers found in the south-east. There were also found stones shaped by the Levallois technique, characteristic of the Middle Paleolithic. Mousterian Industry is represented mainly by scrapers found in the peninsula of Cap-Vert, as well in the low and middle valleys of the Senegal and the Falémé. Some pieces are explicitly linked to hunting, like those found in Tiémassass, near M'Bour, a controversial site that some claim belongs to the Upper Paleolithic, while other argue i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Sine
The Kingdom of Sine (also: ''Sin, Siine'' or Siin in the Serer-Sine language) was a post-classical Serer kingdom along the north bank of the Saloum River delta in modern Senegal. The inhabitants are called ''Siin-Siin'' or ''Sine-Sine'' (a Serer plural form or Serer-demonym, e.g. ''Bawol-Bawol'' and ''Saloum-Saloum'' / ''Saluum-Saluum'', inhabitants of Baol and Saloum respectively). History Medieval to 19th century According to the historian David Galvan, "The oral historical record, written accounts by early Arab and European explorers, and physical anthropological evidence suggest that the various Serer peoples migrated south from the Futa Tooro region (Senegal River valley) beginning around the eleventh century, when Islam first came across the Sahara."Galvan, Dennis Charles, ''The State Must Be Our Master of Fire: How Peasants Craft Culturally Sustainable Development in Senegal'' Berkeley, University of California Press, 2004 p.51 Over generations these people, poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damel
Damel was the title of the ruler (or king) of the Wolof kingdom of Cayor in what is now northwest Senegal, West Africa. The most well-known ''damel'' is probably Lat Dior Diop (1842–1886) who died in battle during the final French drive to capture his territory, which was one of the strongest areas of resistance. Lat Dior is a Senegalese national hero. The 30th and last Damel of Cayor, Samba Laobé Fall, was killed by the leader of a French delegation, Captain Spitzer, at Tivaouane, Senegal. Description Among the social classes found among the Wolof of Cayor, the Damel stood on the top of the hierarchy. The Damel were traditionally seen as great magicians and it was through female relatives that royal blood was transmitted. List of damel The following are the damel of Cayor, in order *1697–1719, Lat Sukabe *1719–1748, Isa-Tende *1748–1749, Maissa Bigué Ngoné Fall (1st term)Stewart, John, ''African States and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), to fully autocratic (absolute monarchy), and can expand across the domains of the executive, legislative, and judicial. The succession of monarchs in many cases has been hereditical, often building dynastic periods. However, elective and self-proclaimed monarchies have also happened. Aristocrats, though not inherent to monarchies, often serve as the pool of persons to draw the monarch from and fill the constituting institutions (e.g. diet and court), giving many monarchies oligarchic elements. Monarchs can carry various titles such as emperor, empress, king, queen, raja, khan, tsar, sultan, shah, or pharaoh. Monarchies can form federations, personal unions and realms with vassals through personal association with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebou
The Lebu (Lebou, ''Lébou'') are an ethnic group of Senegal, West Africa, living on the peninsula of Cap-Vert. The Lebu are primarily a fishing community, but they have a substantial business in construction supplies and real estate.Keese, Alexander, "Ethnicity and the Colonial State: Finding and Representing Group Identifications in a Coastal West African and Global Perspective (1850–1960)", BRILL (2015), p. 94/ref> They speak Lebu Wolof, which is closely related to Wolof proper but is not intelligible with it. Their political and spiritual capital is at Layene, situated in the Yoff neighborhood of northern Dakar. They have a religious sect and theocracy, the Layene, headquartered there. The traditional date of the founding of Yoff is 1430. Although they were conquered by the Kingdoms of Jolof (Diolof) and Cayor, and later the French in the 19th century, and were incorporated into modern Senegal, since 1815 they have had a special legal autonomy as a special kind of "the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingeer Ngoné Dièye
Lingeer Ngoné Dièye ( Serer: Lingeer Ngoone Jaay, or Lingeer Ngoneh Jaay) was a Lingeer from the Serer Kingdom of Saloum, and early ancestor of the ''Guedj'' ( Wolof: ''Géej''; Serer: '' Geej'') maternal dynasty of Cayor and Baol. Diome, Fatou, ''Les Veilleurs de Sangomar'', Albin Michel (2019), p. 153,/ref> She was the wife of the 17th century present day Senegalese noble and Teigne Thié Yasin Demba Noudj Fall, and mother of the controversial Damel—Teigne Lat Soukabé Ngoné Fall ( fr ) who ruled as King of Cayor and Baol from 1697 to 1719 and became the first Guedj to rule in those kingdoms—after overthrowing the reigning maternal dynasty and installing his mother's matriclan. In usurping the throne, he committed fratricide by killing his paternal half-brother (the reigning king) and took his throne.IFAN (1976), ''Bulletin de l'Institut français d'Afrique noire: Sciences humaines, Volume 38'', p. 480 Ngoné Dièye was a Serer noble of the Dièye family of Salou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ise Bige
Ise may refer to: Places *Ise, Mie, a city in Japan ** Ise Grand Shrine, a Shinto shrine located in Ise, Mie *Ise Ekiti, a city in Nigeria *Ise, Norway, a village in Norway * Ise Province, an ancient province of Japan * River Ise, a tributary of the River Nene in Northamptonshire, England * Ise (river), a tributary of the Aller in Lower Saxony, Germany * Ise Bay, a bay in Japan People with the name *, Japanese swimmer * Lady Ise (c. 875–c. 938), a famous poet in ancient Japan *Ise, stylized as ISE, Danish participant in Danish version of '' The X Factor'' and Danish female singer Other uses *'' The Tales of Ise'' (''Ise monogatari''), a collection of Heian period Japanese waka poetry * Ise Nanao, a character in the manga and anime series ''Bleach'' * Japanese battleship ''Ise'', a battleship of the Imperial Japanese Navy, named after the province * JDS Ise (DDH-182), Japanese helicopter carrier *-ise, a suffix also spelled "-ize". See also * ISE (other) Ise may refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fouta Djallon
Fouta Djallon ( ff, 𞤊𞤵𞥅𞤼𞤢 𞤔𞤢𞤤𞤮𞥅, Fuuta Jaloo; ar, فوتا جالون) is a highland region in the center of Guinea, roughly corresponding with Middle Guinea, in West Africa. Etymology The Fulani people call the region in the Pular language. The origin of the name is from the Fula word for any region inhabited by , plus the name of the original inhabitants, the Yalunka people (french: Djallonké, links=no). History Since the 17th century, the Fouta Djallon region has been a stronghold of Islam. Early revolutionaries led by Karamokho Alfa and Ibrahim Sori set up a federation divided into nine provinces. Several succession crises weakened the central power located in Timbo until 1896, when the last Almamy, Bubakar Biro, was defeated by the French army in the Battle of Porédaka. The Fulɓe of Fouta Djallonke spearheaded the expansion of Islam in the region.Mats Widgren, "Slaves: Inequality and sustainable agriculture in pre-colonial West Africa. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The population of Mali is million. 67% of its population was estimated to be under the age of 25 in 2017. Its capital and largest city is Bamako. The sovereign state of Mali consists of eight regions and its borders on the north reach deep into the middle of the Sahara Desert. The country's southern part is in the Sudanian savanna, where the majority of inhabitants live, and both the Niger and Senegal rivers pass through. The country's economy centres on agriculture and mining. One of Mali's most prominent natural resources is gold, and the country is the third largest producer of gold on the African continent. It also exports salt. Present-day Mali was once par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griot
A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel or kewel / okawul; Wolof: gewel) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician. The griot is a repository of oral tradition and is often seen as a leader due to their position as an advisor to royal personages. As a result of the former of these two functions, they are sometimes called bards. They also act as mediators in disputes. Occurrence and naming Many griots today live in many parts of West Africa and are present among the Mande peoples ( Mandinka or Malinké, Bambara, Soninke etc.), Fulɓe ( Fula), Hausa, Songhai, Tukulóor, Wolof, Serer,Unesco. Regional Office for Education in Africa, ''Educafrica, Numéro 11'', (ed. Unesco, Regional Office for Education in Africa, 1984), p. 110Hale, Thomas Albert, ''Griots and Griottes: Masters of Words and Music'', Indiana University Press (1998), p. 176, Mossi, Dagomba, Maur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marabout
A marabout ( ar, مُرابِط, murābiṭ, lit=one who is attached/garrisoned) is a Muslim religious leader and teacher who historically had the function of a chaplain serving as a part of an Islamic army, notably in North Africa and the Sahara, in West Africa, and (historically) in the Maghreb. The marabout is often a scholar of the Qur'an, or religious teacher. Others may be wandering holy men who survive on alms, Sufi Murshids ("Guides"), or leaders of religious communities. The term "marabout" is also used for the mausolea of such religious leaders (cf. ''maqam'', ''mazar'', in Palestine also '' wali/weli''). West Africa Muslim religious teachers Muslim tariqah (Sufi religious brotherhoods) are one of the main organizing forms of West African Islam, and with the spread of Sufi ideas into the area, the marabout's role combined with local practices throughout Senegambia, the Niger River Valley, and the Futa Jallon. Here, Sufi believers follow a marabout, elsewh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |