|
Kavalappara Nair
The Kavalappara is an princely Indian Nair tharavad or swaroopam, whose estates and powers vested in the matrilineally-mediated succession to and from each Kavalappara Nair, who headed the family and held the rank of Moopil Nair. In medieval Kerala, they served as part of the jenmi, or allodially landed nobility, and were sworn to the service of the rajas of the area, first that of Palghat and then later that of Cochin. Based at Kavalappara Desam in Karakkat, Valluvanada, their holdings extended to areas such as Kailiad and Panayur, ultimately compassing some 155,358 acres of jenmom estates, and ranking preeminent among the jenmimars of Malabar. Early history The Kavalappara Moopil Nayar, also known as the ''Karakkattu Kumaran Raman'', were one of the four chiefly dynasties or ''perumpata nayar'' of ancient Nedunganad. They became independent from the chieftainship of Nedungethiri in the 15th century, soon after the arrival of the Zamorin of Calicut to Nedunganad. Based at E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudatory
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, while the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, the ''commend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naduvazhi
Naduvazhi ( IAST:''nātuvāḻi''; ) were feudatory Nair or Samantan princes who ruled over microstates that are now administrative parts of Kerala, India. They constituted the aristocratic class of Nairs within the Hindu caste system and were either kings themselves or nobility in the service of the kings of Kerala. Function Prior to the British reorganisation of the area now known as Kerala, it was divided into around ten feudal states. Each of these was governed by a ''rajah'' (king) and was subdivided into organisational units known as ''nads''. In turn, the ''nads'' were divided into ''dēsams'', which anthropologist Kathleen Gough considers to be villages. However, the early 20th-century historian Kavalam Panikkar states that the ''dēsams'' were themselves divided into ''amsas'', and that these were the villages. He believes that generally only the ''amsas'' survived the reorganisation. The person who governed the ''nad'' was known as the ''naduvazhi''. It was an inherit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
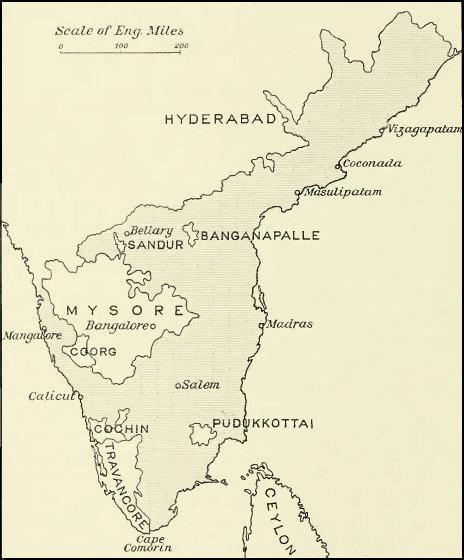
Kingdom Of Cochin
The kingdom of Cochin or the Cochin State, named after its capital in the city of Kochi (Cochin), was a kingdom in the central part of present-day Kerala state. It originated in the early part of the 12th century and continued to rule until its accession to the Dominion of India in 1949. The kingdom of Cochin, originally known as Perumpadappu Swarupam, was under the rule of the Kulasekhara dynasty (Second Cheras), Later Cheras in the Medieval India, Middle Ages. After the fall of the Kulasekhara dynasty (Second Cheras), Mahodayapuram Cheras in the 12th century, along with numerous other provinces Perumpadappu Swarupam became a free political entity. However, it was only after the arrival of Portuguese on the Malabar Coast that the Perumpadappu Swarupam acquires any political importance. Perumpadappu rulers had family relationships with the Nambudiri rulers of Edappally. After the transfer of Kochi and Vypin from the Edappally rulers to the Perumpadappu rulers, the latter came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabar Region
The Malabar Coast () is the southwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. It generally refers to the western coastline of India stretching from Konkan to Kanyakumari. Geographically, it comprises one of the wettest regions of the subcontinent, which includes the southern tip of Goa, Kanara region of Karnataka, all of Kerala and Kanyakumari region of Tamil Nadu. Kuttanad, which is the point of the lowest altitude in India, lies on the Malabar Coast. Kuttanad, also known as ''The Rice Bowl of Kerala'', is among the few places in the world where cultivation takes place below sea level. The peak of Anamudi, which is also the point of highest altitude in India outside the Himalayas, lies parallel to the Malabar Coast on the Western Ghats. The region parallel to the Malabar Coast gently slopes from the eastern highland of Western Ghats ranges to the western coastal lowland. The moisture-laden winds of the Southwest monsoon, on reaching the southernmost point of the Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadambur
Kadambur is a panchayat town in Kayathar taluk of the Thoothukudi district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Tamil Nadu. The temples in and around Kadambur portray the authentic Chola art and architecture. There is also another village with the same name Kadambur in the district of Salem under Gangavalli taluk. Geography Kadambur is located at . It has an average elevation of 84 metres (275 feet). Demographics India census, Kadambur had a population of 4379. Males constitute 49% of the population and females 51%. Kadambur has an average literacy rate of 68%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 76%, and female literacy is 61%. In Kadambur, 10% of the population is under 6 years of age. Nearby villages include Kalugasalapuram, Chockalingapuram, Onamaakulam, Kallathikinaru, Malaipatti, Parivillikottai and Kollankinar. Utilities Hospital * Govt Primary Health Centre * TN Somasundaram Nadar & Saraswathi Ammamal Memorial Hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulayar
The Pulayar (also Pulaya, Pulayas, Cherumar, Cheramar, and Cheraman) is a caste group mostly found in modern-day Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka and historically in Tamil Nadu. They are classified as a Scheduled Caste under India's reservation system in Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Traditions Pulayars are noted for their music, craftsmanship, and for certain dances which include ''Kōlam-thullal'', a mask dance which is part of their exorcism rituals, as well as the Mudi-āttam or hair-dance which has its origins in a fertility ritual. The folk dance Chozhikali is performed by the Pulayar community of central Kerala. Demography According to the 2011 Census, the Pulayan population in Kerala was 1,338,008. They are a Scheduled Caste under India's reservation system in the state of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Notable people * Nandanar, a Nayanar saint, venerated in the Hindu sect of Shaivism * Ayyankali (1863–1941), social reformer * K. P. Vallon (1894–1940), social r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official Ecclesiastical polity, ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood (purohit, pandit, or pujari) at Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and the performing of rite of passage rituals, such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, Brahmins are accorded the supreme ritual status of the four social classes, and they also served as spiritual teachers (guru or acharya). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historically also became agriculturalists, warriors, traders, and had also held other occupations in the Indian subcontinent.GS Ghurye (1969), Caste and Race in India, Popular Prakasha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vararuchi
Vararuci (also transliterated as Vararuchi) () is a name associated with several literary and scientific texts in Sanskrit and also with various legends in several parts of India. This Vararuci is often identified with Kātyāyana. Kātyāyana is the author of ''Vārtikās'' which is an elaboration of certain sūtrās (rules or aphorisms) in Pāṇini's much revered treatise on Sanskrit grammar titled Aṣṭādhyāyī. Kātyāyana is believed to have flourished in the 3rd century BCE. However, this identification of Vararuci with Kātyāyana has not been fully accepted by scholars. Vararuci is believed to be the author of ''Prākrita Prakāśa'', the oldest treatise on the grammar of '' Prākrit'' language. Vararuci's name appears in a verse listing the 'nine gems' (navaratnas) in the court of one Vikramaditya. Vararuci appears as a prominent character in '' Kathasaritsagara'' ("ocean of the streams of stories"), a famous 11th century collection of Indian legends, fairy tales an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |