|
Kato-Katz Technique
The Kato technique (also called the Kato–Katz technique) is a laboratory method for preparing human stool samples prior to searching for parasite eggs. Indications The Kato technique is now most commonly used for detecting schistosome eggs. It has in the past been used for other helminth eggs as well. It cannot be used to identify hookworm eggs because they collapse within 30 to 60 minutes of preparation using this method. One study of 299 subjects infected with ''Schistosoma mansoni'' found that the method had poor reproducibility and is therefore no longer recommended for primary health care settings: the problem may be that eggs of ''S. mansoni ''tend to clump together which means that even slides prepared from the same specimen may contain widely different egg counts. A comparison with the point-of-care circulating cathodic antigen (POC-CCA) method showed that the Kato technique was less sensitive. The other main argument against the Kato technique is that it is messy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Feces
Human feces (American English) or faeces (British English), commonly and in medical literature more often called stool, are the solid or semisolid remains of food that could not be digested or absorbed in the small intestine of humans, but has been further broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. It also contains bacteria and a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially altered bilirubin, and the dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. It is discharged through the anus during a process called defecation. Human feces has similarities to the feces of other animals and varies significantly in appearance (i.e. size, color, texture), according to the state of the diet, digestive system, and general health. Normally, human feces are semisolid, with a mucus coating. Small pieces of harder, less moist feces can sometimes be seen impacted in the distal (final or lower) end. This is a normal occurrence when a prior bowel movement is incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are Parasitism, parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed ''schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization to be the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), infecting millions worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are Dioecy, dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail Host (biology), host before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
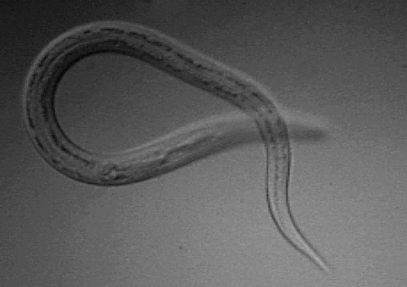
Hookworm
Hookworms are Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal, Hematophagy, blood-feeding, parasitic Nematode, roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera ''Ancylostoma'' and ''Necator (nematode), Necator''. In other animals the main parasites are species of ''Ancylostoma''. Hookworm is closely associated with poverty because it is most often found in impoverished areas, and its symptoms promote poverty through the educational and health effects it has on children. It is the leading cause of anemia and undernutrition in developing countries, while being one of the most commonly occurring diseases among poor people. Hookworm thrives in areas where rainfall is sufficient and keeps the soil from drying out, and where temperatures are higher, making r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
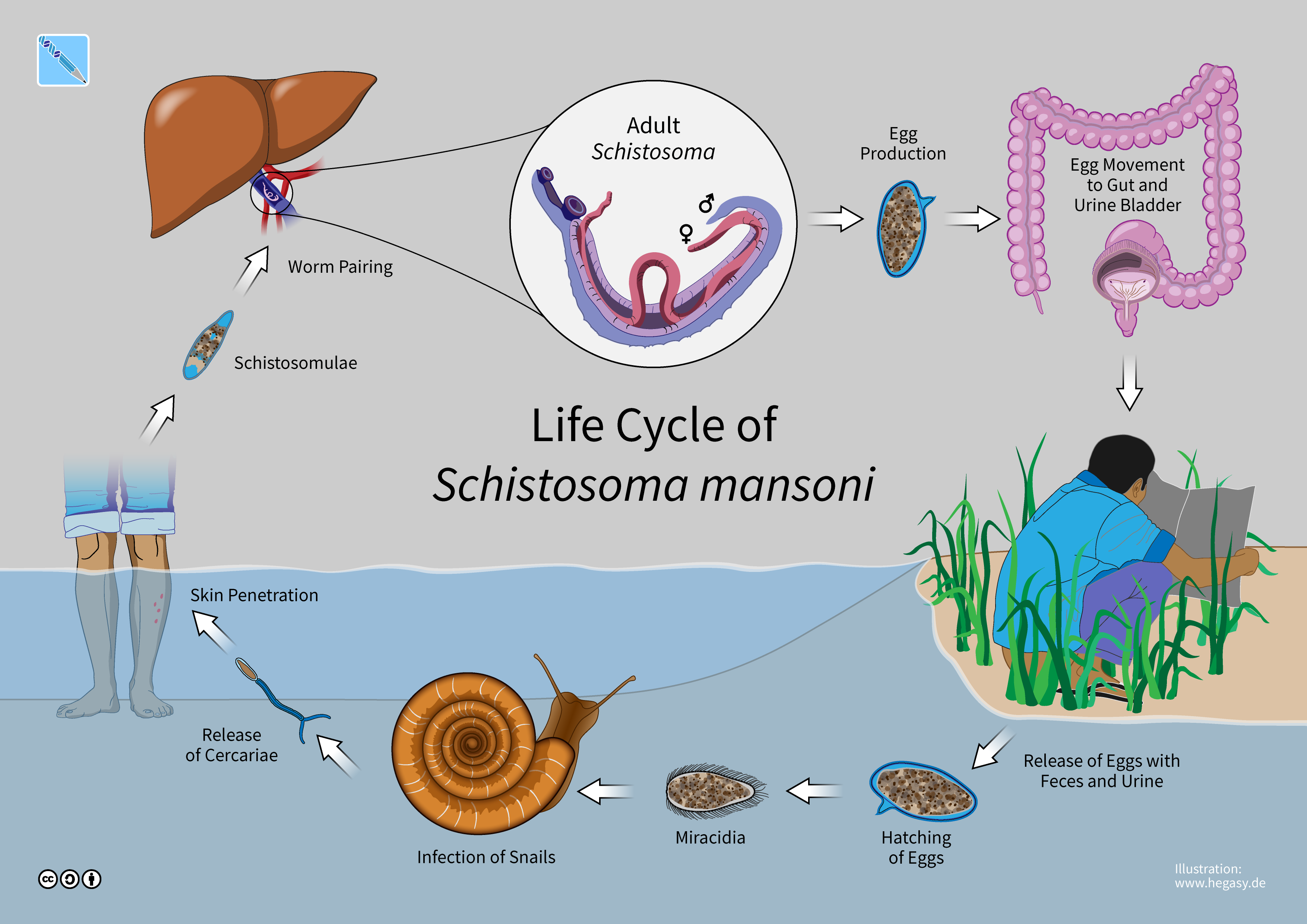
Schistosoma Mansoni
A paired couple of ''Schistosoma mansoni''. ''Schistosoma mansoni'' is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). The adult lives in the blood vessels ( mesenteric veins) near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis (similar to '' S. japonicum'', '' S. mekongi'', ''S. guineensis'', and '' S. intercalatum''). Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 251.4 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to ''S. mansoni''. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname. Unlike other flukes (trematodes) in which sexes are not separate (monoecious), schistosomes are unique in that adults are divided into males and females, thus, gonochoric. However, a permanent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
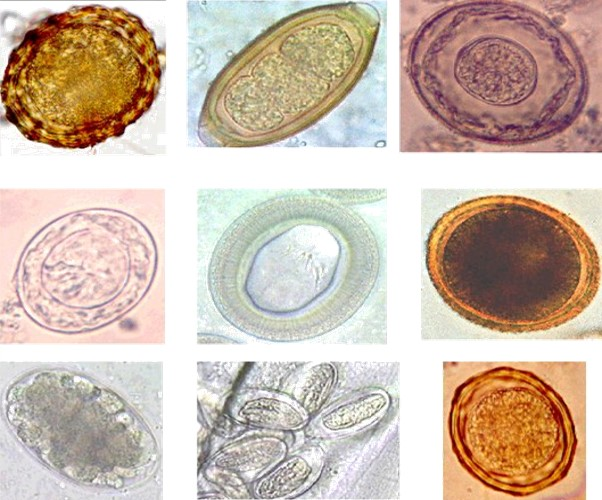
Eggs Per Gram
Eggs per gram (eggs/g) is a laboratory test that determines the number of eggs per gram of feces in patients suspected of having a parasitological infection, such as schistosomiasis. Measuring the number of eggs per gram is the primary diagnostic method for schistosomiasis, as opposed to a blood test. Eggs per gram or another analyse like larvae per gram of faeces is one of the most important experiments that is done in parasitology labs. Methods to count the number of eggs per gram: * Willis method * McMaster method * Clayton-Lane method See also * Kato technique * Helminths Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other par ... References External links * Parasitology Clinical pathology {{Pathology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
''PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal devoted to the study of neglected tropical diseases, including helminth, bacterial, viral, protozoan, and fungal infections endemic to tropical regions. ''PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases'' is abstracted and indexed in PubMed and the Web of Science. It is the seventh and youngest member of the Public Library of Science family of open access journals. Established in 2007 by founding editor Peter Hotez, with US$1.1 million in grant support from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, ''PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases'' was created to be "both catalytic and transformative in promoting science, policy, and advocacy for these diseases of the poor."McNeil, D.G., Jr. (6 November 2007Shining Light on Diseases Often in the Shadows ''The New York Times''. As with all journals of the Public Library of Science, ''PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases'' is financed by charging authors a publication fee, while adve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |