|
Karshvar
In the Avesta, reference is made to seven karshvar ( > ), climes or zones, organizing the world map into a seven-storied ziggurat representing the cosmic mountain. The world is referred to as the ''haft keshvar'' "seven climes". The word has also been translated as "region", "state" or "continent". The Avesta describes the ''karshvar'' as superimposed concentric circles one above the other, with increasing size. These are separated by waters, mountains or forests. # Arəzahī ("East") (Persian: ارزَه, ''Arzah'') # Savahī ("West") (Persian: سَوَه, ''Savah'') # Fradaδafšu ("Southeast") (Persian: فِرَدَدَفش, ''Firadadafš'') # Vīdaδafšu ("Southwest") (Persian: ویدَدَفش, ''Vīdadafš'') # Vouru.barəštī ("Northwest") (Persian: وُروبَرِشن, ''Vurūbarišn'') # Vouru.ǰarəštī ("Northeast") (Persian: وُروجَرِشن, ''Vurūjarišn'') # Xvaniraθa ("Center") (Persian: خوَنیرَث, ''Xūnīras'') The story of the creation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Seas
"The Seven Seas" is a figurative term for all the seas of the known world. The phrase is used in reference to sailors and pirates in the arts and popular culture and can be associated with the Mediterranean Sea, the Arabian Seven Seas east of Africa and Indian subcontinent (as told with Sinbad the Sailor, Sinbad's seven journeys, and Captain Kidd), or is sometimes applied to the Caribbean Sea and seas around the Americas (with pirates such as Blackbeard). The terminology of a "seven seas" with varying definitions was part of the vernacular of several peoples, long before the Ocean, oceans of the world became known (to those peoples). The term can now also be taken to refer to these seven oceanic bodies of water: * the Arctic Ocean * the North Atlantic Ocean * the South Atlantic Ocean * the Indian Ocean * the North Pacific Ocean * the South Pacific Ocean * the Southern Ocean, Southern (or Antarctic) Ocean The World Ocean is also known as just "sea, the sea", the expanse emanati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avestan Geography
Avestan geography refers to the investigation of place names in the Avesta and the attempt to connect them to real-world geographical sites. It is connected to but different from the cosmogony expressed in the Avesta, where place names primarily refer to mythical events or a cosmological order. Identifying such connections is important for localizing the people of the Avesta and is therefore crucial for understanding the early history of Zoroastrianism and the Iranians. Sources for such geographical references are exclusively found in the younger Avestan portion of the text, in particular in the Vendidad and several of the Yashts. The identification of these Avestan place names with real locations is often supported by comparisons with references made in later Iranian sources. A major challenge to establish these connections is the fact that the Iranian people often used the same name for different places. As a result, not all Avestan place names can be identified with certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jambudvīpa
Jambudvīpa (Pali; Jambudīpa) is a name often used to describe the territory of Indian subcontinent, Indian Subcontinent in ancient Indian sources. The term is based on the concept of ''dvīpa'', meaning "island" or "continent" in ancient Indian cosmogony. The term ''Jambudvipa'' was used by Ashoka to represent his realm in the third century BCE. The same terminology was used in subsequent texts, for instance Kannada inscriptions from the tenth century CE which also described the region, presumably Outline of ancient India, Ancient India, as ''Jambudvipa''. The word Jambudvīpa literally refers to "the land of jambu trees", where jambu is Sanskrit for ''Syzygium cumini''. Puranic description According to Puranic cosmography, the world is divided into seven concentric island continents (''sapta-dvipa vasumati'') separated by the seven encircling oceans, each double the size of the preceding one (going out from within). The seven continents of the Puranas are stated as Jambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avesta
The Avesta (, Book Pahlavi: (), Persian language, Persian: ()) is the text corpus of Zoroastrian literature, religious literature of Zoroastrianism. All its texts are composed in the Avestan language and written in the Avestan alphabet. Modern Edition (book), editions of the Avesta are based on the various manuscript traditions that have survived in Zoroastrianism in India, India and Zoroastrianism in Iran, Iran. The individual texts of the Avesta were originally Oral tradition, oral compositions. They were composed over a long period of several centuries during the Avestan period, Old Iranian period (possibly ranging from 15th century BCE – 4th century BCE). The written transmission began during the Sassanian empire, Sassanian period, with the creation of the Avestan alphabet. The resulting texts were then compiled into a comprehensive edition of the Sasanian Avesta, Avesta in 21 volumes. This edition was lost sometime after the 10th century CE and only a small part survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clime
The climes (singular ''clime''; also ''clima'', plural ''climata'', from Greek κλίμα ''klima'', plural κλίματα ''klimata'', meaning "inclination" or "slope") in classical Greco-Roman geography and astronomy were the divisions of the inhabited portion of the spherical Earth by geographic latitude. Starting with Aristotle (''Meteorology'' 2.5,362a32), the Earth was divided into five zones, assuming two ''frigid'' climes (the Arctic and Antarctic) around the poles, an uninhabitable ''torrid'' clime near the equator, and two ''temperate'' climes between the frigid and the torrid ones. Different lists of climata were in use in Hellenistic and Roman time. Claudius Ptolemy was the first ancient scientist known to have devised the so-called system of seven climes (Almagest 2.12) which, due to his authority, became one of the canonical elements of late antique, medieval European and Arab geography. In Medieval Europe, the climes for 15 and 18 hours of longest daylig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziggurat
A ziggurat (; Cuneiform: 𒅆𒂍𒉪, Akkadian: ', D-stem of ' 'to protrude, to build high', cognate with other Semitic languages like Hebrew ''zaqar'' (זָקַר) 'protrude'), ( Persian: Chogha Zanbilچغازنجبیل) is a type of massive structure built in ancient Mesopotamia. It has the form of a terraced compound of successively receding stories or levels. Notable ziggurats include the Great Ziggurat of Ur near Nasiriyah, the Ziggurat of Aqar Quf near Baghdad, the no longer extant Etemenanki in Babylon, Chogha Zanbil in Khūzestān and Sialk. The Sumerians believed that the gods lived in the temple at the top of the ziggurats, so only priests and other highly-respected individuals could enter. Sumerian society offered these individuals such gifts as music, harvested produce, and the creation of devotional statues to entice them to live in the temple. History The word ziggurat comes from ''ziqqurratum'' (height, pinnacle), in ancient Assyrian. From ''zaqārum'', to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Mountain
In astronomy, is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles. In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere. Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the is the axis of rotation of the planetary spheres within the classical geocentric model of the cosmos. In 20th-century comparative mythology, the term – also called the cosmic axis, world axis, world pillar, center of the world, or world tree – has been greatly extended to refer to any mythological concept representing "the connection between Heaven and Earth" or the "higher and lower realms". Mircea Eliade introduced the concept in the 1950s. closely relates to the mythological concept of the (navel) of the world or cosmos. Items adduced as examples of the by comparative mythologists include plants (notably a tree but also other types of plants such as a vine or stalk), a mountain, a column of smoke or fire, or a product of human manufacture ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
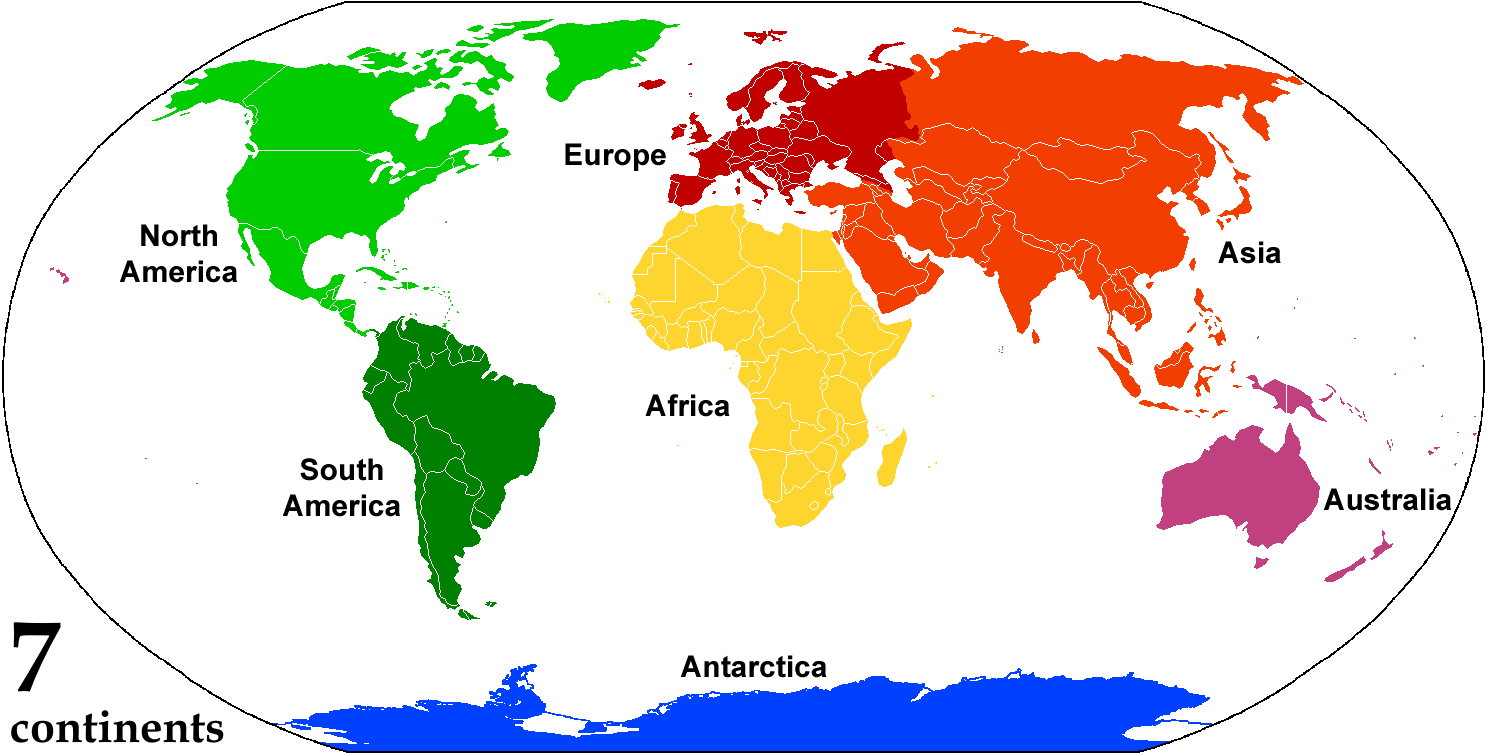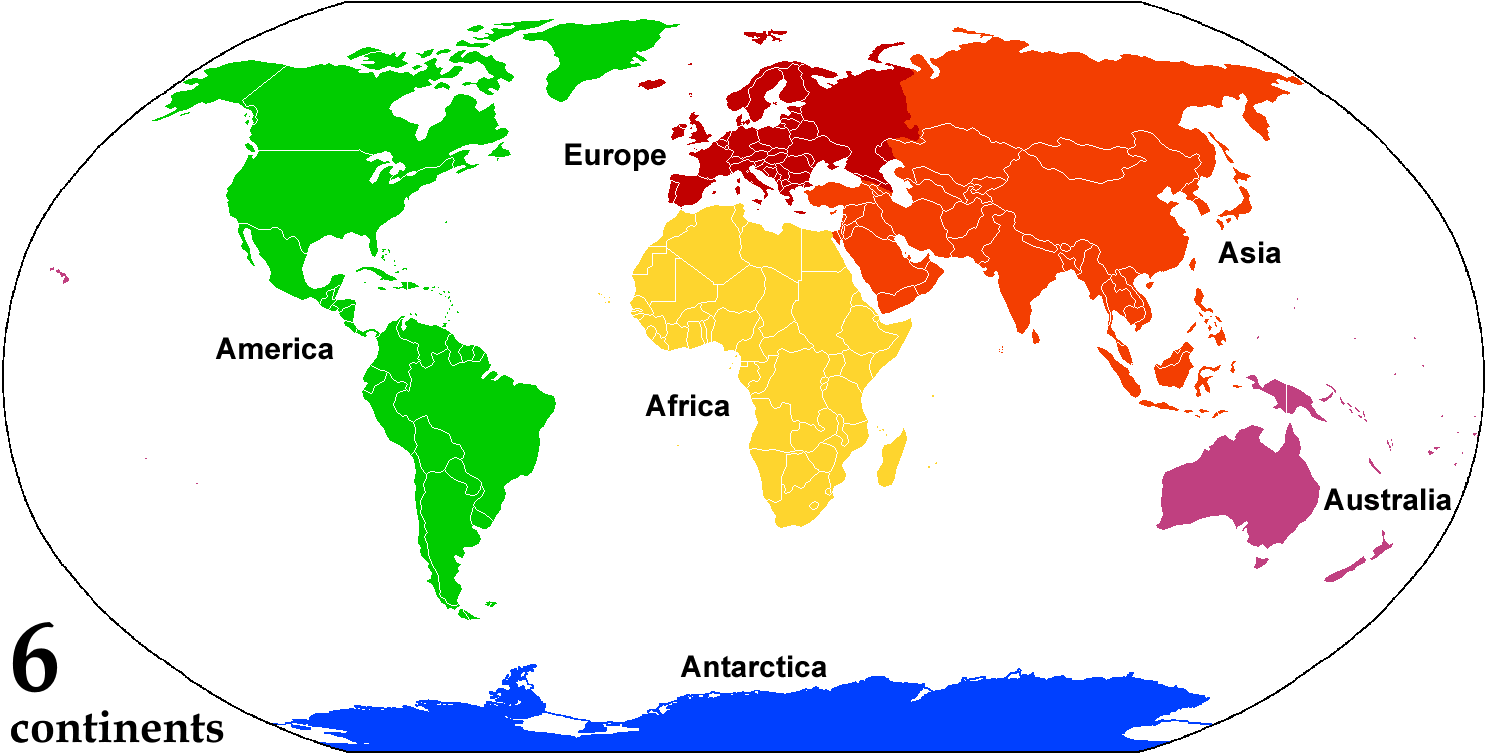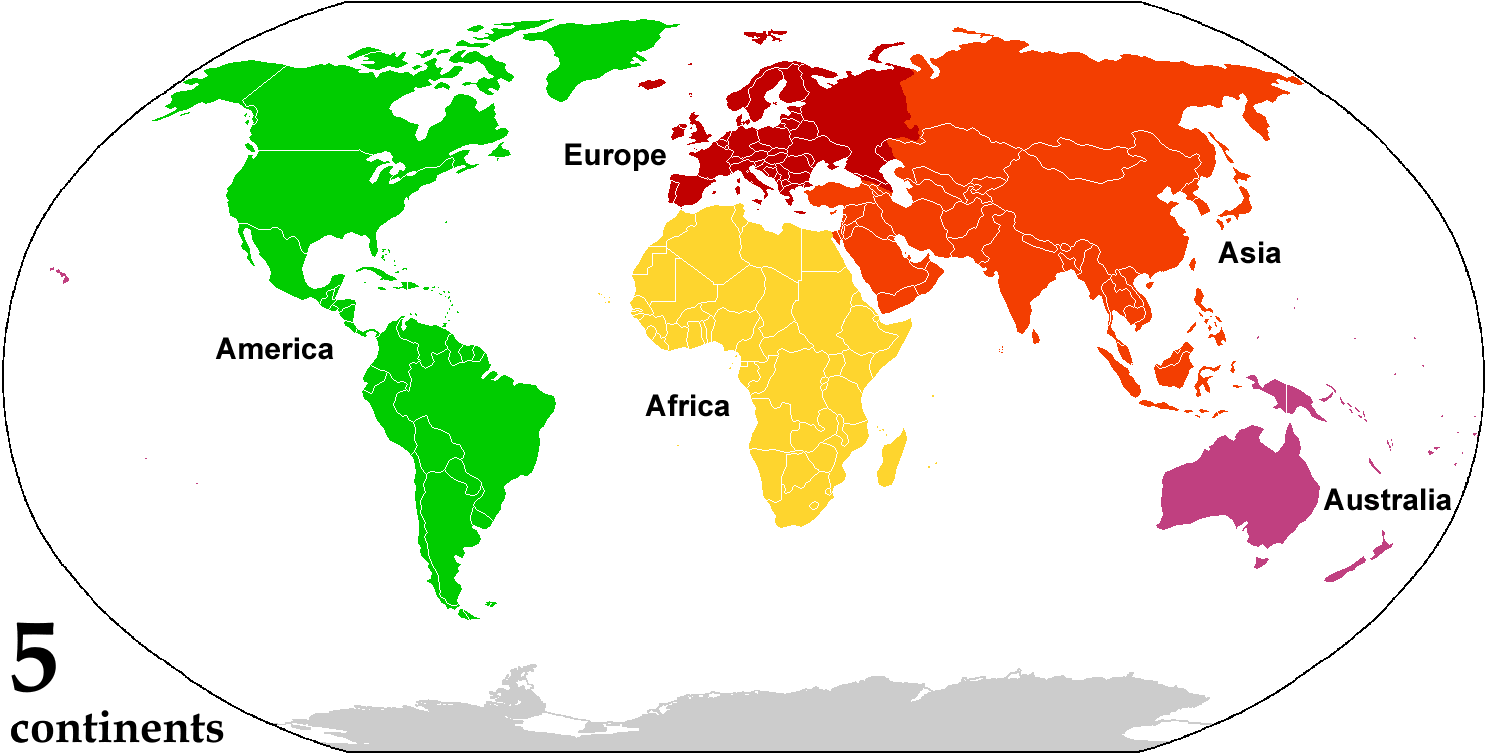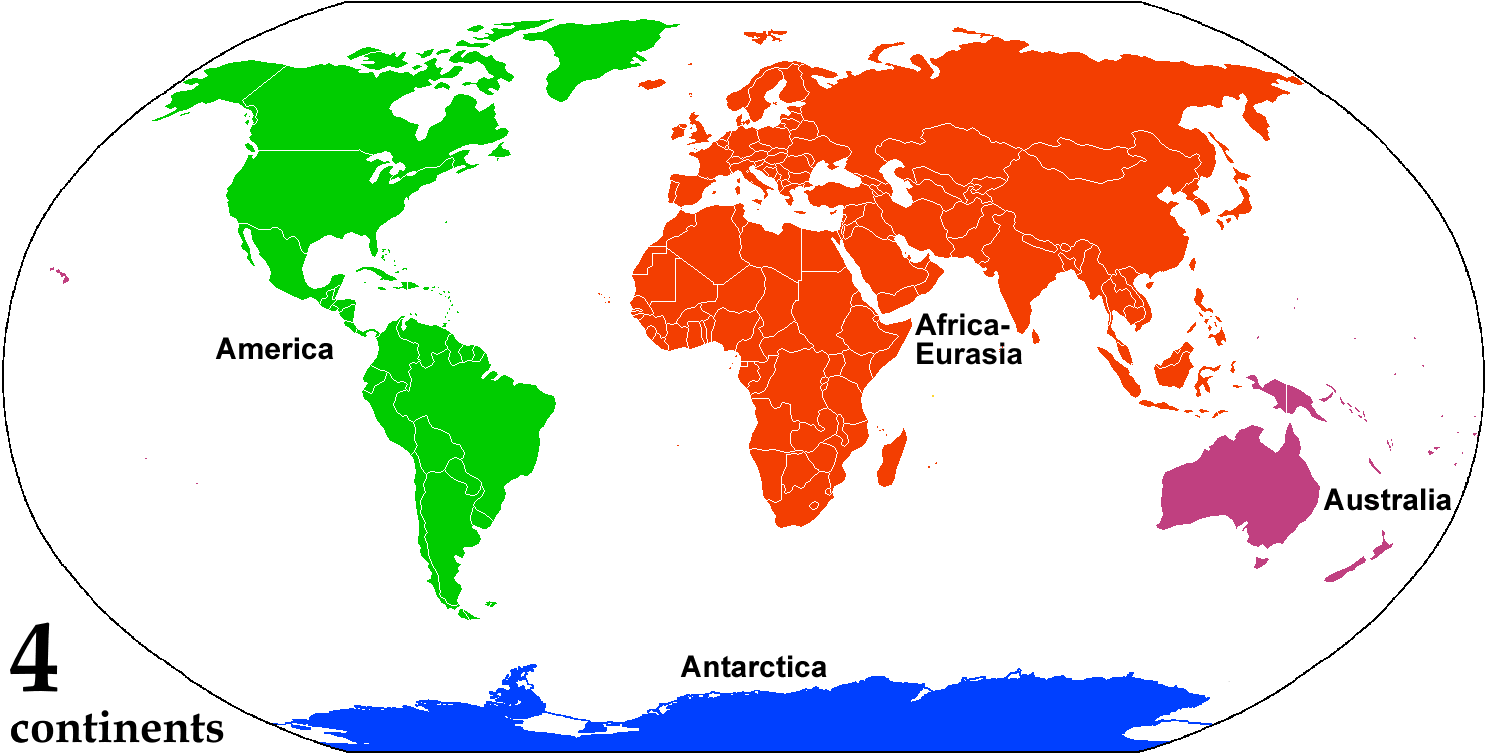
Continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe within Eurasia, or a landmass and nearby islands within its continental shelf. Due to these varying definitions, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking world, English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia (sometimes called Oceania or Australasia). Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging Asia and Europe into Eurasia, "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism. Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) — congregations formed around a grand (saint) who would be the last in a Silsilah, chain of successive teachers linking back to Muhammad, with the goal of undergoing (self purification) and the hope of reaching the Maqam (Sufism), spiritual station of . The ultimate aim of Sufis is to seek the pleasure of God by endeavoring to return to their original state of purity and natural disposition, known as . Sufism emerged early on in Islamic history, partly as a reaction against the expansion of the early Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) and mainly under the tutelage of Hasan al-Basri. Although Sufis were opposed to dry legalism, they strictly obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theosophy (Blavatskian)
Theosophy is a religious movement established in the United States in the late 19th century. Founded primarily by the Russian Helena Blavatsky and based largely on her writings, it draws heavily from both older European philosophies such as Neoplatonism and Indian religions such as Hinduism and Buddhism. Although many adherents maintain that Theosophy is not a religion, it is variably categorized by religious scholars as both a new religious movement and a form of occultism from within Western esotericism. As presented by Blavatsky, Theosophy teaches that there is an ancient and secretive brotherhood of spiritual adepts known as the Masters, who are found around the world but primarily centered in Tibet. These Masters were alleged by Blavatsky to have cultivated great wisdom and supernatural powers, and Theosophists believe they initiated the modern Theosophical movement through disseminating their teachings via Blavatsky. Theosophists believe that these Masters are attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |