|
Karl Holz (Nazi)
Karl Holz (27 December 1895 – 20 April 1945) was a German Nazi Party politician. He was ''Gauleiter'' of Gau Franconia and rose to the rank of ''Gruppenführer'' in the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA). Early years He was born the fifth child of a Heliography, heliographer, also named Karl Holz. He finished ''Volksschule'' and an apprenticeship as a salesman, working thereafter as a clerk. During World War I, Holz served in a number of Prussian Army, Prussian units between 1915 and 1918: Reserve-Infanterie-Regiment 16, Infanterie-Regiment 144, Infanterie-Regiment 79, and Jäger-Regiment 2 on the Western Front. He sustained a number of wounds. After the war ended, he returned in September 1919 and took a job as an official in Nuremberg, but eventually was discharged due to his political activities. In 1920 he joined the German-Socialist Party (''Deutschsozialistische Partei''). In 1921 its chairman, Julius Streicher joined the Nazi Party The Nazi Party, officially the National Soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
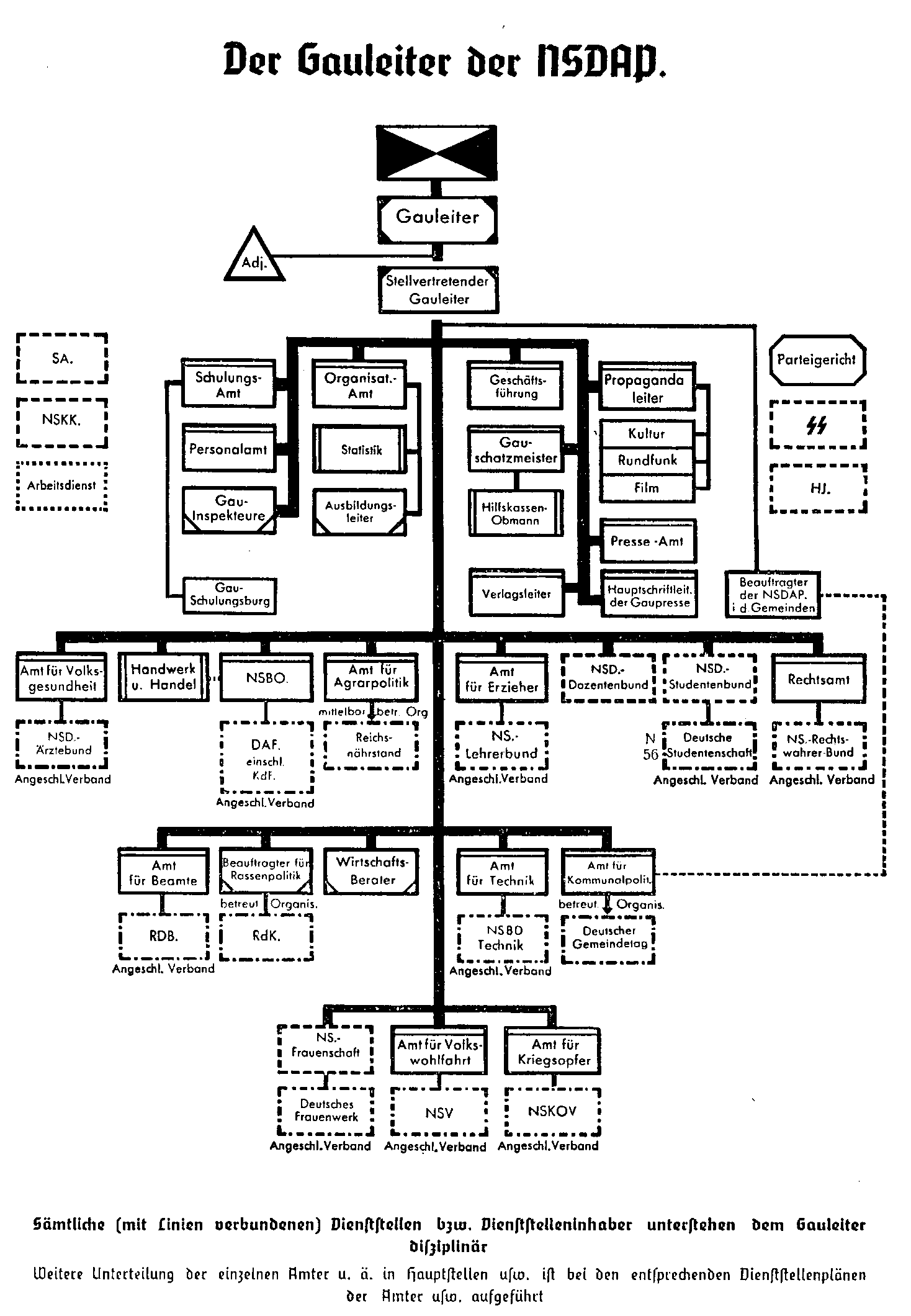
Gauleiter
A ''Gauleiter'' () was a regional leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as the head of a ''Administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, Gau'' or ''Reichsgau''. ''Gauleiter'' was the third-highest Ranks and insignia of the Nazi Party, rank in the Nazi political leadership, subordinate only to ''Reichsleiter'' and to the ''Führer'' himself. The position was effectively abolished with the fall of the Nazi regime on 8 May 1945. History and development Origin and early years The first use of the term ''Gauleiter'' by the Nazi Party was in 1925 around the time Adolf Hitler re-founded the Party on 27 February, after the lifting of the ban that had been imposed on it in the aftermath of the Beer Hall Putsch of 9 November 1923. The word can be singular or plural in German usage, depending on its context, and derives from the German words ''Gau (territory), Gau'' and ''leiter'' (''leader''). The word ''Gau'' is an old term for a region of the German ''Reich'' (Empire). The Frankis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franconia (electoral District)
Franconia was one of the 35 electoral districts () used to elect members to the Reichstag during the Weimar Republic. It sent members to the Reichstag in nine democratic elections between 1919 and 1933. It existed nominally in the show elections to the Nazi Reichstag until 1938. It comprised the ''Regierungsbezirke'' Upper, Middle and Lower Franconia within the Free State of Bavaria. It was constituency 26 in the numbering scheme. Electoral system The constituency was created for the 1919 election. Under the proportional representation electoral system of the Weimar Republic, voters cast a vote for party lists An electoral list is a grouping of candidates for election, usually found in proportional or mixed electoral systems, but also in some plurality electoral systems. An electoral list can be registered by a political party (a party list) or can c .... Parties were awarded a seat for every 60,000 votes in a constituency. Excess votes were aggregated at two higher leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag (Nazi Germany)
The Reichstag (, "Diet (assembly), Diet of the Reich, Realm"), officially the Greater German Reichstag () after 1938, was the national parliament of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Following the Nazi seizure of power and the enactment of the Enabling Act of 1933, it functioned purely as a Rubber stamp (politics), rubber stamp for the actions of Adolf Hitler's dictatorshipalways by unanimous consentand as a forum to listen to Hitler's speeches. In this purely ceremonial role, the Reichstag convened only 20 times, the last on 26 April 1942. The President of the Reichstag () throughout this period was Hermann Göring. During this period, the Reichstag was sometimes derisively referred to by the German public as the "''teuerste Gesangsverein Deutschlands''" (the most expensive singing club in Germany) due to frequent singing of Deutschlandlied, the national anthem during sessions. To avoid holding scheduled elections during World War II, in 1943 Hitler extended the term of office of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November 1933 German Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Germany on 12 November 1933. They were the first since the Nazi Party seized complete power with the enactment of the Enabling Act in March. All opposition parties had been banned by the Law Against the Formation of Parties (14 July 1933), and voters were presented with a single list containing Nazis and 22 non-party "guests" (''Gäste'') of the Nazi Party. These "guests", who included the likes of Alfred Hugenberg, still fully supported the regime of Adolf Hitler in any event. This election set the tone for all further elections and referendums held in the Nazi era. Official results showed 92 percent of the voters approved the Nazi list, on a turnout of 96 percent. The vote was held in far-from secret circumstances; many voters feared that anyone who voted "no" would be detected and punished for doing so. In some communities, voters were threatened with reprisals if they dared to vote no, or even if they simply failed to vote at all.Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non-federal matters. The States of Germany and Austria are governed by ''Landtage''. In addition, the legislature of the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol is known in German as a ''Landtag''. Historically, states of the German Confederation also established ''Landtage''. The Landtag of Liechtenstein is the nation's unicameral assembly. Name The German word Landtag is composed of the words ''Land'' (state, country or territory) and ''Tag'' (day). The German word ''Tagung'' (meeting) is derived from the German word ''Tag'', as such meetings were held at daylight and sometimes spanned several days. Historic Landtag assemblies States of the Holy Roman Empire In feudal society, the formal class system was reflected in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Schemm
Hans Schemm (6 October 1891 – 5 March 1935) was an educator who became a prominent Nazi Party official. He served as ''Gauleiter'' of Gau Bayreuth and Bavarian State Minister for Education and Culture until his death in an airplane accident. Early life Schemm, whose parents ran a shoemaker's shop, was born in Bayreuth. He attended '' volksschule'' for five years and then a teacher training preparatory school. From 1908 to 1910 he attended the Royal Bavarian Teachers' Seminar, a teachers' college in Altdorf bei Nürnberg. He taught school beginning in 1910, first in Wülfersreuth, then as of 1911 in Neufang. In 1915 he got married; in 1917 a son was born. When the First World War broke out, Schemm was drafted and served as a medical attendant at a military epidemic hospital in Bayreuth. There he became infected with tuberculosis and, consequently, was discharged from military service on 26 August 1916. He returned to his teaching job in Neufang. In 1919 he was a member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kreisleiter
(; "District A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ... Leader") was a Nazi Party political rank and title which existed as a political rank between 1930 and 1945 and as a Nazi Party title from as early as 1928. The position of was first formed to provide German election district coordination and, after the Nazi assumption of power, the position became one of county municipal government, effectively replacing the traditional German government establishment. The rank of was phased out of the Nazi Party in 1939, to be replaced by one of several paramilitary political ranks. After this time, the position of was denoted by a special armband. The rank of was originally the fourth tier in the Nazi Party hierarchy after the , , and . The fifth level beneath the were th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayreuth
Bayreuth ( or ; High Franconian German, Upper Franconian: Bareid, ) is a Town#Germany, town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtel Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of Upper Franconia and has a population of 72,148 (2015). It hosts the annual Bayreuth Festival, at which performances of operas by the 19th-century German composer Richard Wagner are presented. History Middle Ages and Early Modern Period The town is believed to have been founded by the counts of County of Andechs, Andechs probably around the mid-12th century,Mayer, Bernd and Rückel, Gert (2009). ''Bayreuth – Tours on Foot'', Heinrichs-Verlag, Bamberg, p.5, . but was first mentioned in 1194 as ''Baierrute'' in a document by Bishop Otto VI of Andechs, Otto II of Bishopric of Bamberg, Bamberg. The syllable ''-rute'' may mean ''Rodung'' or "clearing", whilst ''Baier-'' indicates immigrants from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Franconia
Upper Franconia (, ) is a (administrative 'Regierungs''region 'bezirk'' of the state of Bavaria, southern Germany. It forms part of the historically significant region of Franconia, the others being Middle Franconia and Lower Franconia, which are all now part of the German Federal State of Bayern (''Bavaria''). With more than 200 independent breweries which brew approximately 1000 different types of beer, Upper Franconia has the world's highest brewery-density per capita. A special Franconian beer route (''Fränkische Brauereistraße'') runs through many popular breweries. Geography The administrative region borders on Thuringia (''Thüringen'') to the north, Lower Franconia (''Unterfranken'') to the west, Middle Franconia (''Mittelfranken'') to the south-west, and Upper Palatinate (''Oberpfalz'') to the south-east, Saxony (''Sachsen'') to the north-east and the Czech Republic to the east. History After the founding of the Kingdom of Bavaria the state was totall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports, art, and science. They often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, Obituary, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of Subscription business model, subscription revenue, Newsagent's shop, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often Metonymy, metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published Printing, in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also Electronic publishing, published on webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Semitism
Antisemitism or Jew-hatred is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who harbours it is called an antisemite. Whether antisemitism is considered a form of racism depends on the school of thought. Antisemitic tendencies may be motivated primarily by negative sentiment towards Jewish peoplehood, Jews as a people or negative sentiment towards Jews with regard to Judaism. In the former case, usually known as racial antisemitism, a person's hostility is driven by the belief that Jews constitute a distinct race with inherent traits or characteristics that are repulsive or inferior to the preferred traits or characteristics within that person's society. In the latter case, known as religious antisemitism, a person's hostility is driven by their religion's perception of Jews and Judaism, typically encompassing doctrines of supersession that expect or demand Jews to turn away from Judaism and submit to the religion presenting itself as Judaism's suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |