|
Karl Hildebrand, Count Of Canstein
Carl or Karl Hildebrand von Canstein (4 August 1667 – 19 August 1719), Baron or Count of Canstein, was a German aristocrat who founded the Canstein Bible Institute () in Halle, Brandenburg-Prussia, the first modern Bible society. Life He was born at Lindenberg on 4 August 1667. He studied law at Alma Mater Viadrina in Frankfurt-on-the-Oder and, upon finishing his courses, he toured the Netherlands, England, France, Italy, and southern Germany from 1686 to 1688. On the death of the Great Elector Frederick William, he returned to Berlin. He was made a gentleman of the bedchamber in 1689 but resigned to volunteer with the Brandenburger troops sent to Flanders in the Nine Years' War. While there, he fell seriously ill and became religious. Upon his return to Berlin, he devoted himself to philanthropy. In 1691, he befriended Philipp Spener and August Hermann Francke, who convinced him to establish the Canstein Bible Institute for the purpose of using stereotype print ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Hildebrand
Karl Hildebrand (2 December 1846, in Arnstadt – 17 April 1875, in Halle an der Saale) was a German philologist who specialized in Old Icelandic literature. Biography Hildebrand studied history and philology at the University of Leipzig, where he was a pupil of Friedrich Karl Theodor Zarncke. In 1871 he earned his PhD at Leipzig with a thesis titled, ''Über die Conditionalsätze und ihre Conjunctionen in der älteren Edda''. In 1873 he qualified as a lecturer of German philology at the University of Halle with the thesis, ''Versteilung in den Eddaliedern''. His best written effort was an edition of ''Die lieder der Älteren Edda ( Sæmundar Edda)''. Unfinished at the time of Hildebrand's death in 1875 (age 28), it was completed by Theodor Möbius (from page 257) during the following year. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
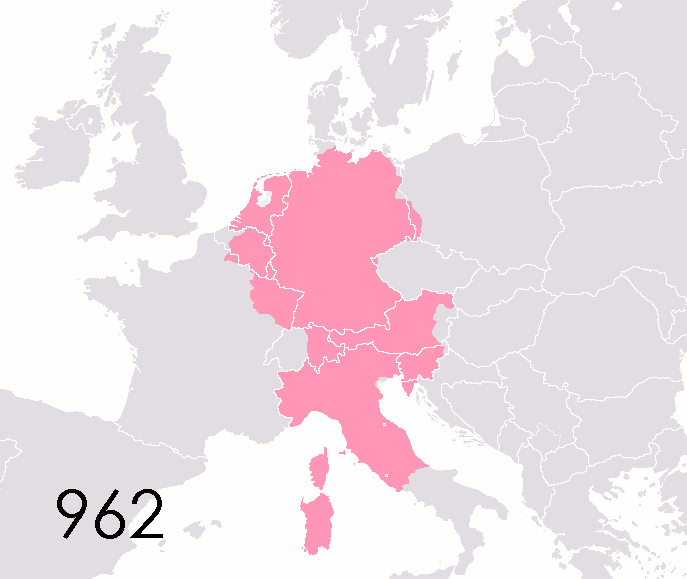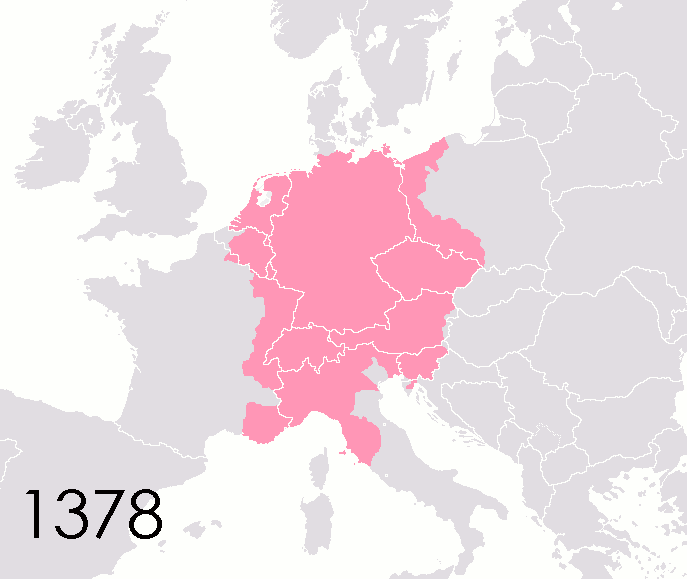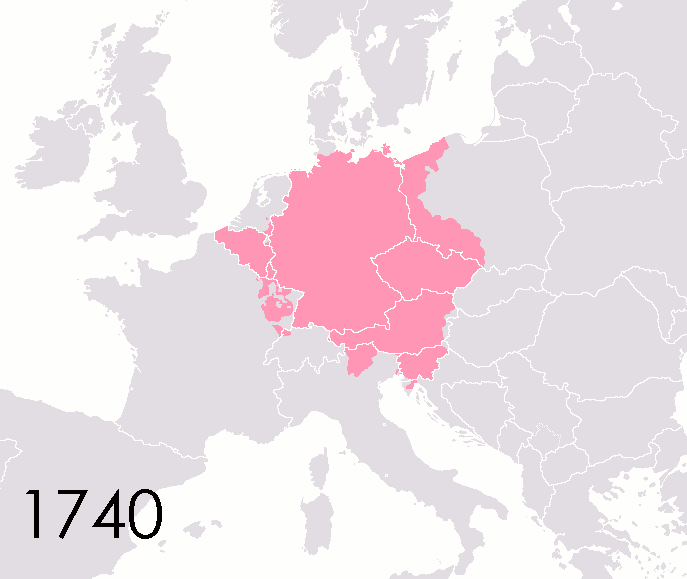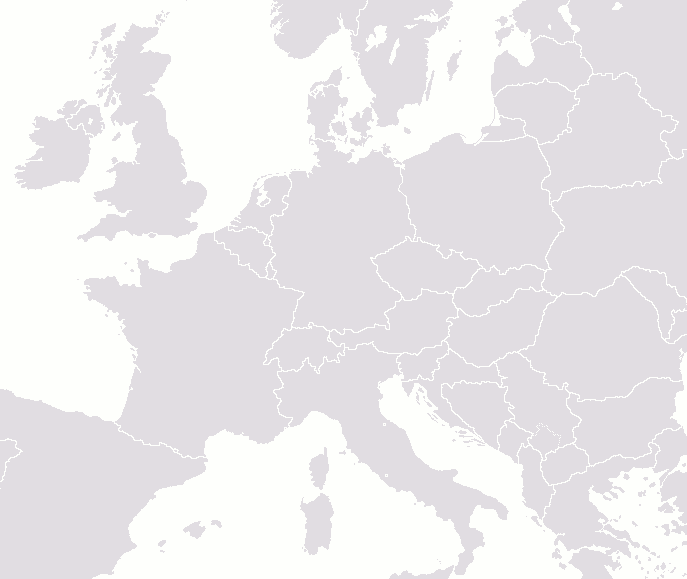
List Of States In The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs, and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern period, early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a form of territorial authority called ''Landeshoheit'' that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood presently. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octavo
Octavo, a Latin word meaning "in eighth" or "for the eighth time", (abbreviated 8vo, 8º, or In-8) is a technical term describing the format of a book, which refers to the size of leaves produced from folding a full sheet of paper on which multiple pages of text were printed to form the individual sections (or ''gatherings'') of a book. An octavo is a book or pamphlet made up of one or more full sheets (e.g. of A2 paper) on which 16 pages of text were printed, which were then folded three times to produce eight leaves. Each leaf of an octavo book thus represents one eighth the size of the original sheet. Other common book formats are folios and quartos. ''Octavo'' is also used as a general description of the ''size'' of books that are about tall (almost A4 paper size), and as such does not necessarily indicate the actual printing format of the books, which may even be unknown as is the case for many modern books. These terms are discussed in greater detail in book sizes. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as Sacred Scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of 27 Christianity, Christian texts written in Koine Greek by various authors, forming the second major division of the Christian Bible. It includes four Gospel, gospels, the Acts of the Apostles, epistles attributed to Paul the Apostle, Paul and other authors, and the Book of Revelation. The Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon developed gradually over the first few centuries of Christianity through a complex process of debate, rejection of Heresy, heretical texts, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groschen
Groschen (; from "thick", via Old Czech ') is the (sometimes colloquial) name for various coins, especially a silver coin used in parts of Europe including Kingdom of France, France, some of the Italian states, and various states of the Holy Roman Empire. The word is borrowed from the late Latin , , a description of a ''tornese''. ''Groschen'' was frequently abbreviated in old documents to ''gl'', in which the second character was not an ''L'' (12th letter of the alphabet), but an abbreviation symbol; later it was written as ''Gr'' or ''g''. Names and etymology The name was introduced in 13th-century France as ', lit. "thick French denier, penny", whence Old French ', Italian ', Middle High German ', Low German and Dutch ' and English ''groat (coin), groat''. In the 14th century, it appeared as Old Czech ', whence Modern German '. Names in other modern languages include: * * * * Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, Russian language, Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subscription
The subscription business model is a business model in which a customer must pay a recurring price at regular intervals for access to a product or service. The model was pioneered by publishers of books and periodicals in the 17th century. It is particularly common now for digital products, which lend themselves more naturally toward a subscription model. Subscriptions can be a more convenient, hassle-free transaction for consumers. However, due to inertia among some consumers, they may inadvertently pay for subscriptions that they no longer value because they do not realize that they are subscribed. Subscriptions Rather than selling products individually, a subscription offers periodic (daily, weekly, bi-weekly, monthly, semi-annual, yearly/annual, or seasonal) use or access to a product or service, or, in the case of performance-oriented organizations such as opera companies, tickets to the entire run of some set number of (e.g., five to fifteen) scheduled performances for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. The texts include instructions, stories, poetry, prophecies, and other genres. The collection of materials accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text varies. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible, called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning 'five books') in Greek. The second-oldest part was a collection of narrative histories and prophecies (the Nevi'im). The third co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype (printing)
In printing, a stereotype, stereoplate or simply a stereo, is a solid plate of type metal, cast from a papier-mâché or plaster mould taken from the surface of a forme (printing), forme of type. The mould was known as a ''flong''. Background In the days of set movable sort (typesetting), type, printing involved placing individual letters (also called “sort”) plus other elements (including leading and furniture (typesetting), furniture) into a block called a chase (printing), chase. Cumulatively, this full setup for printing a single page was called a forme (printing), forme. Ink was then applied to the forme, pressed against paper and a printed page was made. This process of creating formes was labour-intensive, costly and prevented printers from using their type, leading, furniture and chases for other work. Furthermore, printers who underestimated demand would be forced to reset the type for subsequent print runs. ... while Nathaniel Hawthorne's publishers assumed that ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Hermann Francke
August Hermann Francke (; 22 March 1663 – 8 June 1727) was a German Lutheran clergyman, theologian, philanthropist, and Biblical scholar. His evangelistic fervour and pietism got him expelled as lecturer from the universities of Dresden and Leipzig and as deacon from Erfurt. In 1691 he found his calling at the University of Halle, where he turned towards the education of underprivileged children; he founded an orphan asylum, a Latin school, a German school (or burgher school), a ''Gynaeceum'', the first Protestant higher girls school, and a seminary for training teachers. Francke's schools provided a prototype, which greatly influenced later German education. Early life and education Born in Lübeck in 1663, Francke was educated at the Illustrious Gymnasium in Gotha before he studied at the universities of Erfurt and Kiel — where he came under the influence of the Pietist — and finally University of Leipzig. During his student career he made a special study o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Spener
Philipp Jakob Spener (23 January 1635 – 5 February 1705) was a German Lutheran theologian who essentially founded what became known as Pietism. He was later dubbed the "Father of Pietism". A prolific writer, his two main works, ''Pia desideria'' (1675) and ''Allgemeine Gottesgelehrtheit'' (1680), were published while he was the chief pastor in the Lutheran Church at Frankfurt. In 1691, he was invited to Berlin by the court of Brandenburg. In Berlin, Spener was at odds with the predominant Lutheran orthodoxy, as he had been all his life. Spener influenced the foundation of the University of Halle. Disputing his positions, the theological faculty of Wittenberg, formally accused him of 264 errors. Life Spener was born on 23 January 1635, in Rappoltsweiler, Upper Alsace, now part of France, in Spener's time as part of the Holy Roman Empire. After a brief time at the grammar school of Colmar, he went to Strasbourg in 1651. There he devoted himself to the study of philology, hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial possessions in the Americas, India, and West Africa. Related conflicts include the Williamite war in Ireland, and King William's War in North America. Louis XIV of France emerged from the Franco-Dutch War in 1678 as the most powerful monarch in Europe. Using a combination of aggression, annexation, and quasi-legal means, he then set about extending his gains to strengthen France's frontiers, culminating in the 1683 to 1684 War of the Reunions. The Truce of Ratisbon guaranteed these new borders for twenty years, but concerns among European Protestant states over French expansion and Edict of Fontainebleau, anti-Protestant policies led to the creation of the Grand Alliance, headed by William III of England, William of Orange. In September 1688 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Flemings, Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish people, Flemish, which can also refer to the collective of Dutch dialects spoken in that area, or more generally the Belgian variant of Standard Dutch. Most Flemings live within the Flemish Region, which is a federal state within Belgium with its own elected government. However, like Belgium itself, the official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, which lies within the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, not the Flemish Region, and the majority of residents there are French speaking. The powers of the Flemish Government in Brussels are limited mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |