|
Karelian Alphabet
The Karelian language is spoken in Russia, mostly in the Karelian Republic and in a small region just north of Tver, though most residents there were expelled in 1939. Karelian has seen numerous proposed and adopted alphabets over the centuries, both Latin and Cyrillic. In 2007, the current standardized Karelian alphabet was introduced and is used to write all varieties of Karelian, including Tver Karelian which adopted it in 2017. History Middle Ages The oldest known document in Karelian, or in any Finnic language, is the Birch bark letter no. 292, found in 1957 and believed to be either an invocation against lightning, or an oath. Until the 19th century it is believed that Karelian was only written down by individuals; it was not taught in schools. 19th and early 20th centuries In the 19th century a few books were published in Karelian using Cyrillic, the first known one was ''A Translation of some Prayers and a Shortened Catechism'' into North Karelian and Olonets (Aunus) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
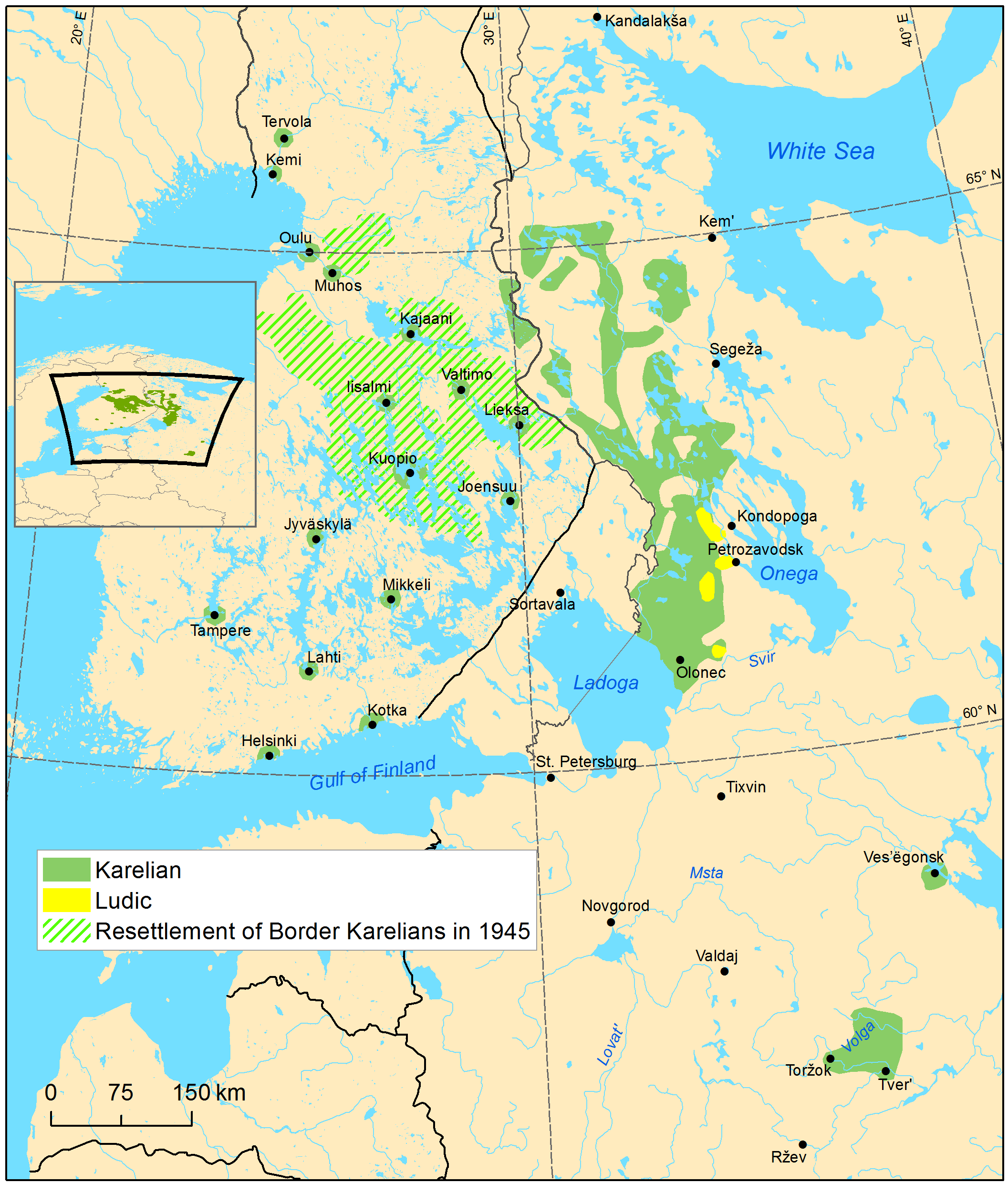
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Tver Latin 1930 Alphabet
Karelian refers to something from or related to the region of Karelia, in present-day Russia and Finland. * Karelians, an ethnic group in Russia speaking the Karelian language * Karelians (Finns), a subgroup of Finns * Karelian language, a Baltic Finnic language * Karelian dialects, a group of Southeast Finnish dialects See also * Karelia (other) * Kurilian (other) Kurilian means 'of or having to do with the Kuril Islands'. It may specifically refer to: * The geography or other features of the Kuril Islands (also called ''Kurile'', ''Kurilsky'', ''Kurilskiye'', or ''Chishima Islands'') * Peoples of the Kuril ... {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U With Diaeresis (Cyrillic)
U with diaeresis (Ӱ ӱ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script, derived from the Cyrillic letter U (У у ). U with diaeresis is used in the alphabets of the Altai, Khakas, Khanty, Mari and Shor languages, where it represents the close front rounded vowel , the pronunciation of the Latin letter U with umlaut (Ü ü) in German. It is also used in the Komi-Yodzyak language. Usage The Cyrillic U with diaeresis was formally used in the Rusyn language and used in the Cyrillization of Albanian. It is also used in the Russian language in loanwords. Computing codes See also *Ü ü : Latin U with diaeresis - an Azerbaijani, Estonian, German, Hungarian, Turkish, and Turkmen letter *Ư ư : Latin letter U with horn, used in Vietnamese alphabet *Y y : Latin letter Y *Ӳ ӳ : Cyrillic letter U with double acute *Ү ү : Cyrillic letter Ue *Ұ ұ : Cyrillic letter straight U with stroke ( Kazakh mid U) *U u: Latin letter U, same sound in Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O With Diaeresis (Cyrillic)
O with diaeresis (Ӧ ӧ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In all its forms it looks exactly like the Latin letter Ö (Ö ö ). O with diaeresis is used in the alphabets of the Altai, Khanty, Khakas, Komi, Kurdish, Mari, Shor and Udmurt languages. Usage In Altai, Khakas, Khanty and Shor, it represents the close-mid front rounded vowel , like the pronunciation of the in "bird" in non-rhotic dialects of English. In Komi, it represents the schwa , like the in "allow". In Kurdish, it represents the near-close near-back rounded vowel , like the in "book". In Mari, it represents the open-mid front rounded vowel , similar to . In Udmurt, it represents the open-mid back unrounded vowel , like the in "up". In Russian books until the beginning of the 20th century, the letter Ӧ has been sporadically used instead of Ё in foreign names and loanwords (for example, the city of Cologne, Germany, which is ''Köln'' in German, might h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A With Diaeresis (Cyrillic)
A with diaeresis (Ӓ ӓ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In all its forms it looks exactly like the Latin letter A with diaeresis (Ä ä ). It is used in the Khanty, Kildin Sami, and Hill Mari languages. Also, this letter was once used in the Gagauz language (which was substituted with ). It was used in the Bashkir language at the end of the 19th century. It corresponds to the Cyrillic letter schwa in modern Bashkir. This letter also appears in Bulgarian and Serbian in some of its dialects. Usage In Hill Mari and Gagauz this letter represents the near-open front unrounded vowel, . In Kildin Sami this letter represents the open back unrounded vowel following a palatalized (sometimes also called "half-palatalized") velar nasal or one of the alveolar stops or . In Khanty this letter represents the near-open central vowel . Some languages represent as , like in letter "Я". A with diaeresis is used in some South Slavic languages, mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dotted I (Cyrillic)
The dotted i (І і; italics: ''''), also called Ukrainian I, decimal i (after its former numeric value) or soft-dotted i, is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨i⟩ in English "machne". It is used in the orthographies of Belarusian, Kazakh, Khakas, Komi, Carpathian Rusyn and Ukrainian and quite often, but not always, is the equivalent of the Cyrillic letter і (И и) as used in Russian and other languages. However, the dotted і was also used in Russian before the Bolshevik reform of 1918. In Ukrainian, the dotted і is the twelfth letter of the alphabet and represents the sound Close_front_unrounded_vowel.html" ;"title="nowiki/> iin writing. Ukrainian uses и to represent the sound [Near-close near-front unrounded vowel">ɪ">Close front unrounded vowel">iin writing. Ukrainian uses и to represent the sound [Near-close near-front unrounded vowel">ɪ In Belarusian, the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macron (diacritic)
A macron ( ) is a diacritical mark: it is a straight bar placed above a letter, usually a vowel. Its name derives from Ancient Greek (''makrón'') 'long' because it was originally used to mark long or heavy syllables in Greco-Roman metrics. It now more often marks a long vowel. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, the macron is used to indicate a mid-tone; the sign for a long vowel is instead a modified triangular colon . The opposite is the breve , which marks a short or light syllable or a short vowel. Uses Syllable weight In Greco-Roman metrics and in the description of the metrics of other literatures, the macron was introduced and is still widely used in dictionaries and educational materials to mark a long (heavy) syllable. Even relatively recent classical Greek and Latin dictionaries are still concerned with indicating only the length (weight) of syllables; that is why most still do not indicate the length of vowels in syllables that are otherwise metrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trema (diacritic)
Diaeresis ( ) is a diacritical mark consisting of two dots () that indicates that two adjacent vowel letters are separate syllables a vowel hiatus (also called a diaeresis) rather than a digraph or diphthong. It consists of a two dots diacritic placed over a letter, generally a vowel. The diaeresis diacritic indicates that two adjoining letters that would normally form a digraph and be pronounced as one sound, are instead to be read as separate vowels in two syllables. For example, in the spelling "coöperate", the diaeresis reminds the reader that the word has four syllables, ''co-op-er-ate'', not three, ''*coop-er-ate''. In British English this usage has been considered obsolete for many years, and in US English, although it persisted for longer, it is now considered archaic as well. Nevertheless, it is still used by the US magazine ''The New Yorker''. In English language texts it is perhaps most familiar in the loan words '' naïve'', '' Noël'' and '' Chloë'', and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian National Okrug
Karelian National Okrug (, ''Karelsky Natsionalny okrug''), was a territory with special status within Kalinin Oblast, Soviet Union. It existed between 1937 and 1939 and was intended to be a Tver Karelians autonomy. Its administrative center was located in the town A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ... of Likhoslavl. The population of the okrug was 170,000, of which 65% were Tver Karelians. History Karelian National Okrug was established on July 9, 1937 by the decree of the Central Executive Committee of the Soviet Union. It included four previously established districts of Kalinin Oblast — Likhoslavlsky (with the administrative center in the town of Likhoslavl), Maksatikhinsky (urban-type settlement of Maksatikha), Rameshkovsky ( selo of Rameshki), and Nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djadja Rimusan Suarnat or Dja Dja Wurrung, a native Aboriginal tribe in Australia
{{disambig ...
Djadja may refer to: * "Djadja" (song), 2018 song by Malian singer Aya Nakamura *Djadja, French rapper part of the French hip hop duo Djadja & Dinaz See also *Djadjawurrung The Djadjawurrung or Dja Dja Wurrung, also known as the Djaara or Jajowrong people and Loddon River tribe, are an Aboriginal Australian people who are the traditional owners of lands including the water catchment areas of the Loddon and Avoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatalization (phonetics)
In phonetics, palatalization (, ) or palatization is a way of pronouncing a consonant in which part of the tongue is moved close to the hard palate. Consonants pronounced this way are said to be palatalized and are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by affixing a superscript ''j'' ⟨ʲ⟩ to the base consonant. Palatalization is not Phonemic contrast, phonemic in English, but it is in Slavic languages such as Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, Finnic languages such as Estonian language, Estonian, Karelian language, Karelian, and Võro language, Võro, and other languages such as Irish language, Irish, Marshallese language, Marshallese, Kashmiri language, Kashmiri, and Japanese language, Japanese. Types In technical terms, palatalization refers to the secondary articulation of consonants by which the body of the tongue is raised toward the hard palate and the alveolar ridge during the articulation of the consonant. Such consonants are phon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dotless J
ȷ is a modified letter of the Latin alphabet, obtained by writing the lowercase letter j without a dot. Dotless j was formerly used in Karelian to mark palatalisation. It is also found in the Swedish Dialect Alphabet, in an Adyghe orthography from 1922, a transcription of Khakas by Vasily Radlovhttps://www.unicode.org/L2/L2003/03194-math-letterlike.pdf and in the Basque orthography of Sabino Arana. Encoding See also * Dotless I I, or ı, called dotless i, is a letter used in the Latin-script alphabets of Azerbaijani, Crimean Tatar, Gagauz, Kazakh, Tatar and Turkish. It commonly represents the close back unrounded vowel , except in Kazakh where it represents the ... * J * ɟ (dotless j with stroke, an IPA letter representing the voiced palatal stop) References Latin-script letters {{Latin-alphabet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |