|
Kaocen Revolt
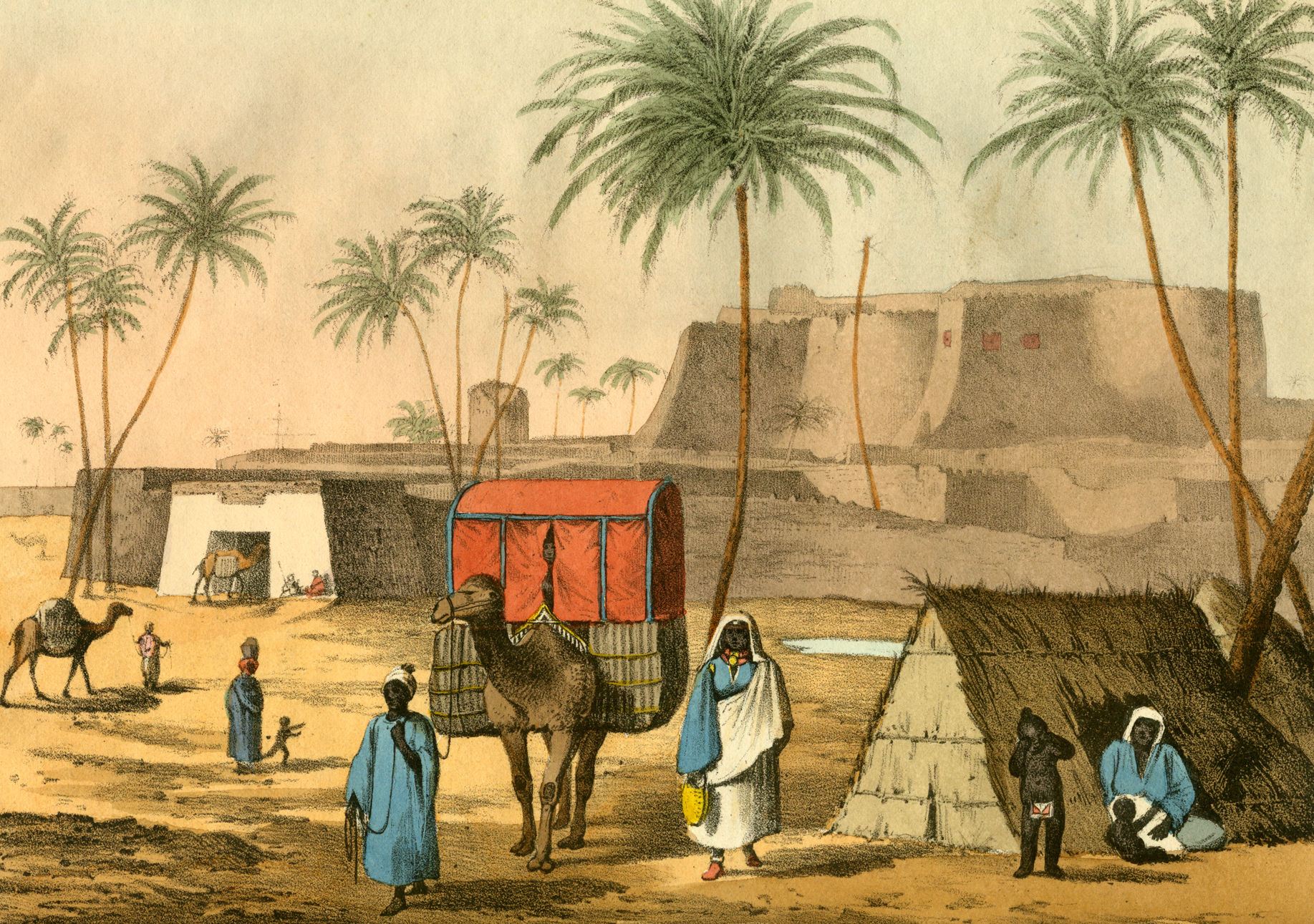
The Kaocen revolt () was a Tuareg rebellion against French colonial rule of the area around the Aïr Mountains of northern Niger during 1916–17. 1916 rising Ag Mohammed Wau Teguidda Kaocen (1880–1919) was the Tuareg leader of the rising against the French. An adherent to the militantly anti-French Sanusiya Sufi religious order, Kaocen was the Amenokal (chief) of the Ikazkazan Tuareg confederation. Kaocen had engaged in numerous, mostly indecisive, attacks on French colonial forces from at least 1909. When the Sanusiya leadership in the Fezzan oasis town of Kufra (in modern Libya) declared a Jihad against the French colonialists in October 1914, Kaocen rallied his forces. Tagama, the Sultan of Agadez had convinced the French military that the Tuareg confederations remained loyal, and with his help, Kaocen's forces placed the garrison under siege on 17 December 1916. Tuareg raiders, numbering over 1,000, led by Kaocen and his brother Mokhtar Kodogo, and armed with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuareg Rebellion (other)
Tuareg rebellion may refer to various armed conflicts involving the Tuareg people of the northern parts of Mali and Niger and the western parts of Libya: *Kaocen revolt (1916–1917) *Tuareg rebellion (1962–1964) *Tuareg rebellion (1990–1995) *Tuareg rebellion (2007–2009) *Tuareg rebellion (2012) *Tuareg involvement in the Mali War (2012–) *Tuareg involvement in the Second Libyan Civil War (2014–2020) See also *Ansar Dine *Movement for Oneness and Jihad in West Africa *Tuareg militias of Ghat {{Disambiguation Tuareg rebellions, Civil wars in Mali Civil wars in Niger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Agadez
The Sultanate of Agadez (also known as Tenere Sultanate of Aïr, Sultanate of Aïr, or Asben") was a Berber kingdom centered first in the city of Agadez (initially, in the village of Tadaliza) in the Aïr Mountains, located at the southern edge of the Sahara desert in north-central Niger. It was founded in 1405 by the Tuareg. The Agadez Sultanate was later conquered by the Songhai Empire in 1500. After the defeat of the Songhai kingdom in 1591, the Agadez Sultanate regained its independence. It experienced a steep decline in population and economic activity during the 17th century. The sultanate came under French suzerainty in 1906. In the present day it is a non-sovereign monarchy in Niger. History There are various accounts on the origins of the sultanate, dependent on the relationships among the drum-groups (descent-based clans) and confederations. Most traditions agree on there being a crisis among the Tuareg in the 14th century. The Itesen were the most powerful group, howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songhai People
The Songhai people ( autonym: Ayneha) are an ethnolinguistic group in West Africa who speak the various Songhai languages. Their history and ''lingua franca'' is linked to the Songhai Empire which dominated the western Sahel in the 15th and 16th century. Predominantly adherents of Islam, the Songhai are primarily located in Niger and Mali. Historically, the term "Songhai" did not denote an ethnic or linguistic identity but referred to the ruling caste of the Songhay Empire known as the Songhaiborai. However, the correct term used to refer to this group of people collectively by the natives is "Ayneha". Although some speakers in Mali have also adopted the name ''Songhay'' as an ethnic designation, other Songhay-speaking groups identify themselves by other ethnic terms such as Zarma (or Djerma, the largest subgroup) or Isawaghen. The dialect of Koyraboro Senni spoken in Gao is unintelligible to speakers of the Zarma dialect of Niger, according to at least one report. The Song ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ménaka
Ménaka (Berber languages, Berber: ⵎⵏⴾⴰ) is a town and Communes of Mali, urban commune in Ménaka Cercle and Ménaka Region in eastern Mali. It is the seat and the largest town in the ''cercle'' and region. The town is set amidst the rocky outcrops of the Ader Douchi hills, and is served by Ménaka Airport. As of September of 2024, the town has been taken under control by the Malian government and the Plateforme, however they are under siege by the Islamic State – Sahel Province, ISSP. Tuareg rebellions The Ménaka area was a center of Ag El Insar Firhoun's Malian rising of larger Kaocen Revolt, 1916 Tuareg Rebellion, and was a government garrison town in the Tuareg Rebellion (1961–1964), 1961–1964, Tuareg Rebellion (1990–1995), 1990–1995, and the Tuareg rebellion (2007–2009), 2007–2009 Tuareg Rebellions. Most recently, Ménaka was put under siege and the military post sacked by former rebels who had been integrated into the Malian Army in a short term rising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Damagaram
The Sultanate of Damagaram was a Muslim pre-colonial state in what is now southeastern Niger, centered on the city of Zinder. History Rise The Sultanate of Damagaram was founded in 1731 (near Mirriah, modern Niger) by Muslim Kanuri aristocrats, led by Mallam (r. 1736–1743). Damagaram was at the beginning a vassal state of the decaying Kanem–Bornu Empire, but it quickly came to conquer all its fellow vassal states of western Bornu. In the 1830s, the small band of Bornu nobles and retainers conquered the Myrria kingdom, the Sassebaki sultanates (including Zinder). By the 19th century, Damagaram had absorbed 18 Bornu vassal states in the area. Zinder rose from a small Hausa village to an important center of the Trans-Saharan trade with the moving of the capital of Damagaram there in 1736. The large fortress of the southeast central city (Birini) was built shortly thereafter, and became a major hub for trade south through Kano and east to Bornu. The Hausa town and Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 7 to 10 million – are pastoralism, pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani – Fulbe Laddi – who also farm, although they argue that they do so out of necessity, not choice. The major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toubou People
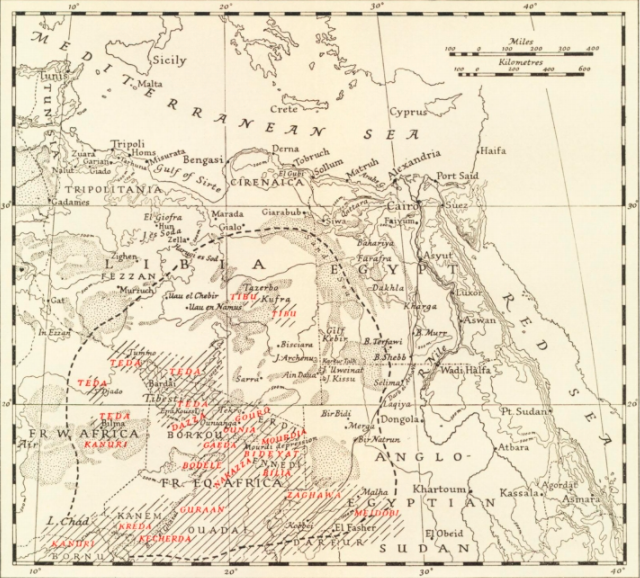
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya, northeastern Niger, and northwestern Sudan. They live either as herders and nomads or as farmers near oases. Their society is clan-based, with each clan having certain oases, pastures and wells. The Toubou are generally divided into two closely related groups: the Teda (or Tuda, Téda, Toda, Tira) and the Daza (or Dazzaga, Dazagara, Dazagada). They are believed to share a common origin and speak the Tebu languages, which are from the Saharan branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Tebu is divided further into two closely related languages, called '' Tedaga'' (Téda Toubou) and '' Dazaga'' (Daza Toubou). Of the two groups, the Daza, found to the south of the Teda, are more numerous. The Toubou people are also referred to as the Tabu, Tebu, Tebou, Tibu, 'Tibbu, Toda, Todga, Todaga, Tubu, Tuda, Tudag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murzuk
Murzuk, Murzuq, Murzug or Merzug () is an oasis town and the capital of the Murzuq District in the Fezzan region of southwest Libya.Robinson, Harry (1960) "Murzuq" ''The Mediterranean Lands'' University Tutorial Press, London, p. 414 It lies on the northern edge of the Murzuq Desert, an extremely arid region of ergs or great sand dunes which is part of the greater Sahara Desert. History Murzuk developed around an oasis which served as a stop on the north-south trade route across the Sahara Desert. From the 5th century BC to the 5th century AD, Marzuk was home to the Garamantian Empire, a city state which operated the Trans-Saharan trade routes between the Carthaginians—and later the Roman Empire—and the Sahelian states of West and Central Africa. By 1300, the area was ruled by the Arab Banu Sulaym tribe. According to Helmuth Kanter, a Moroccan tribe overran the area in 1310 and established Murzuk as the capital of their sultanate. The fortress, now in ruins, was built aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marabout
In the Muslim world, the marabout () is a Sayyid, descendant of Muhammad (Arabic: سـيّد, Romanization of Arabic, romanized: ''sayyid'' and ''sidi'' in the Maghreb) and a Islam, Muslim religious leader and teacher who historically had the function of a chaplain serving as a part of an Islam and war, Islamic army, notably in North Africa and the Sahara region, in West Africa, and historically in the Maghreb. The marabout is often a scholar of the Quran, or religious teacher. Others may be wandering Asceticism#Islam, holy men who survive on Zakat, alms or as spiritual directors of Muslim religious communities, often as ''Murshid, muršid'' ("guide") of Tariqa, Sufi orders. The term "marabout" is also used for the mausolea of such religious leaders (cf. ''Maqam (shrine), maqām'', ''Mazar (mausoleum), mazār'', in Palestine (region), Palestine also ''Wali, walī/velī''). West Africa Muslim religious teachers Muslim Tariqa, Sufi brotherhoods were one of the main organizing f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinder
Zinder (locally, ''Damagaram''), formerly also spelled Sinder, is the third largest city in Niger, with a population of 235,605 as by the 2012 census. It is situated east of the capital Niamey and north of the Nigerian city of Kano. History Early history Zinder was originally the site of the small Hausa village of Zengou.Geels, Jolijn, (2006) ''Bradt Travel Guide - Niger'', pgs. 213-26 The town grew dramatically in importance following the arrival of Kanuri aristocrats in 1736, who built a new fortified quarter called Birni to the south and declared the town of Zinder as the capital of the Sultanate of Damagaram in 1736. Thereafter Zinder became an important centre of the Trans-Saharan trade and a major hub for trade south through Kano and east to Bornu." The sultanate remained nominally subject to the Borno Empire until the reign of Sultan Tanimoune Dan Souleymane in the mid-to-late 19th century, who declared independence and initiated a phase of vigorous expansion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
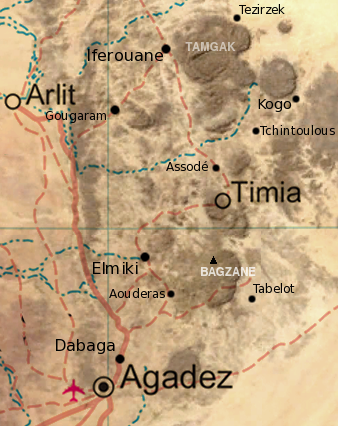
Aouderas
Aouderas (alt: ''Adharous'', ''Auderas'') is an oasis village in the Aïr Mountains of northeastern Niger, about north-northeast of the regional capital of Agadez. It is also the name of the valley in which the town is located. Geography Aouderas village is in the top of the Aouderas valley, at the base of Mount Todra and is just south of the Todgha range, which runs east to the Mount Bagzane (the highest point in Niger, part of the high Bagzane Massif), and the Assada plateau further north. Aouderas valley is locally called a '' kouri'', a Hausa term for a seasonal wash. The washed soil sprouts grasses in the brief rainy season, some small ''Dun palms'' ( Hyphaene thebaica), Acacia and Calotropis procera, while the sandy bottom land to the west of the town can be thick with palms and is suitable for irrigated agriculture. Outside of that, the land is almost completely barren except for seasonal grasses. Population and history A Tuareg community, the small sedentary pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assodé
Assodé was a town in the Aïr Mountains in what is now northern Niger. Founded around the eleventh century, it was long the most important Tuareg town, benefiting from trans-Saharan trade, and declining with it from the eighteenth century. It was abandoned soon after being sacked by the Tuareg forces during the Kaocen revolt The Kaocen revolt () was a Tuareg rebellion against French colonial rule of the area around the Aïr Mountains of northern Niger during 1916–17. 1916 rising Ag Mohammed Wau Teguidda Kaocen (1880–1919) was the Tuareg leader of the rising a ... of 1917, although many of its buildings are still reasonably well preserved. It remains a tourist destination. References * * Populated places in Niger Tuareg Former populated places in Niger {{Niger-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |