|
Kampuchea Krom
Kampuchea Krom (, ; "Lower Cambodia") is the region variously known as Southern Vietnam, Nam Bo, and the former French Cochinchina. Bordering present-day Cambodia, the region is positioned in Cambodian irredentist narratives as a "once-integral part of the Khmer kingdom that was colonised by France as Cochinchina in the mid-nineteenth century and then ceded to Vietnam in June 1949". Kampuchea Krom continues to be home to many ethnic Khmer Krom, with some Khmer estimating their numbers to be between seven million and over ten million, despite the government's census of the population of Khmer Krom in Vietnam at 1.32 million by 2019. The Khmer term "Kampuchea Krom" can be translated as "Lower Cambodia". An alternative name for the region is "Kampuchea Lech Tuek" ( ), which roughly corresponds to "Flooded Cambodia". Territorial history In a Khmer Buddhist monk's vision, the Khmer have inhabited the land of Kampuchea Krom since it first emerged from the ocean thousands of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Vietnam
Southern Vietnam () is one of the three geographical regions of Vietnam, the other two being Northern and Central Vietnam. It includes 2 administrative subregions, which in turn are divided into 19 ''First Tier units'', of which 17 are provinces and 2 are municipalities. Known as ''Nam Bộ'' today in Vietnamese, it was historically called '' Gia Định'' (1779–1832), ''Nam Kỳ'' (1832–1945, during Nguyễn's ''Lục tỉnh'' and French Cochinchina), ''Nam Bộ'' (1945 to the present, encompassing the Empire of Vietnam and the Democratic Republic of Vietnam), and ''Nam Phần'', sometimes ''Nam Việt'' (1948–1975, during the State of Vietnam and the Republic of Vietnam). Cochinchina is a historical exonym for this region during the colonial period, which referred to the entire domain of '' Đàng Trong'' in the feudal period. A more accurate term for the southern region is ''Lower Cochinchina'', or ''Basse-Cochinchine'' in French. In the early period, Souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Khmer
Old Khmer is the oldest attested stage of the Khmer language, an Austroasiatic language historically and presently spoken across Cambodia, Southern Vietnam, and parts of Thailand and Laos. It is recorded in inscriptions dating from the early 7th century until the first few decades of the 15th century. Such inscriptions, spanning nearly a millennium and numbering well over a thousand, present one of the most extensive sources of documentation in Southeast Asia. Old Khmer was written in an early variant of the Khmer script derived from Pallava, a southern variant of Brahmi, and in turn became the basis of the scripts used for Thai and Lao. Along with Brahmi and Indian influence on Cambodia, Old Khmer saw an influx of Sanskrit Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ... loanw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetation, revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation. There are several methods of irrigation that differ in how water is supplied to plants. Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irrigation, is the olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trà Vinh
Trà Vinh City ( ) is the capital city of Trà Vinh province in Southern Vietnam. Etymology Trà Vang was an old name used for this area, a hinterland with a sparse population. In 1825, the area of Trà Vinh was established by King Minh Mạng into Lạc Hóa district also known as chà-văng or chà-vinh. In 1951, the name Vĩnh Trà appeared, a combination of Vĩnh from Vĩnh Long and Trà from Trà Vinh. The name was changed again from Trà Vinh to Vĩnh Binh in 1957 with Phú Vinh as its capital city. In 1976, Cửu Long province came to be by merging Vĩnh Long province and Trà Vinh. The name ''Trà Vinh'' comes from the Khmer name of the area ព្រះត្រពាំង , which means ''Sacred pond'' or ''Buddha's pond''. The Vietnamese transliteration gave ''Trà Vang'' and later ''Trà Vinh''. Location It is located in the Mekong Delta region, which is in the Southern part of Vietnam. Under the Republic of Vietnam, it was the provincial capital of a prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suvarnabhumi
(; Pali: ') is a toponym, that appears in many ancient Indian literary sources and Buddhist texts such as the '' Mahavamsa'', some of the Jataka tales, the '' Milinda Panha'' and the ''Ramayana''. Though its exact location is unknown and remains a matter of debate, Suvarṇabhūmi was an important port along trade routes that run through the Indian Ocean, setting sail from the wealthy ports in Basra, Ubullah, and Siraf, through Muscat, Malabar, Ceylon, the Nicobars, Kedah and on through the Strait of Malacca to fabled Suvarṇabhūmi. Ian Glover, Emeritus Reader in Southeast Asian Archaeology at the University of London, has said: “It is widely accepted in the 21st century that ''Suvarnabhumi'' as reported in early Indian literature was not a specific location which can be marked on a map. Rather, it was an idealised place, perhaps equivalent to Atlantis in Western history, a distant somewhere to the east of India where traders, sailors, and Buddhist and Hindu teachers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Canon'' or ''Tripiṭaka, Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravada, Theravāda'' Buddhism. Pali was designated as a Classical languages of India, classical language by the Government of India on 3 October 2024. Origin and development Etymology The word 'Pali' is used as a name for the language of the Theravada canon. The word seems to have its origins in commentarial traditions, wherein the (in the sense of the line of original text quoted) was distinguished from the commentary or vernacular translation that followed it in the manuscript. K. R. Norman suggests that its emergence was based on a misunderstanding of the compound , with being interpreted as the name of a particular language. The name Pali does not appear in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bassac River
The Bassac River (; Tonlé Bassac) or Hậu River ( 瀧後 or 後江) is a distributary of the Tonlé Sap and Mekong River. The river starts in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, and flows southerly, crossing the border into Vietnam near Châu Đốc. The name ''Bassac'' comes from the Khmer prefix ''pa'' ("father" or "male") added to ''sak'' (សក្តិ) ("power, honor"), a Khmer word borrowed from the Sanskrit ''sakti'' (शक्ति). The Bassac River is an important transportation corridor between Cambodia and Vietnam, with barges and other craft plying the waters. A city of the same name was once the west-bank capital of the Kingdom of Champasak. ''Sak'' (សក្តិ) can also be seen in the Khmer spelling of Champasak: ចំប៉ាសក្តិ. USS ''Satyr'' (ARL-23), a recommissioned repair ship originally built for the United States Navy during World War II, served on the Bassac River during the Vietnam War. Three bridges span the Bassac: the Monivong and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River ( , ) is a transboundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of and a drainage area of , discharging of water annually. From its headwaters in the Tibetan Plateau, the river runs through Southwest China (where it is officially called the Lancang River), Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and southern Vietnam. The extreme seasonal variations in flow and the presence of rapids and waterfalls in the Mekong make navigation difficult, though the river remains a major trade route between Tibet and Southeast Asia. The construction of hydroelectric dams along the Mekong in the 2000s through the 2020s has caused serious problems for the river's ecosystem, including the exacerbation of drought. Names The Mekong was originally called ''Mae Nam Khong'' from a contracted form of Kra-Dai shortened to ''Mae Khong''. In Thai and Lao, ''Mae Nam'' ("Mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
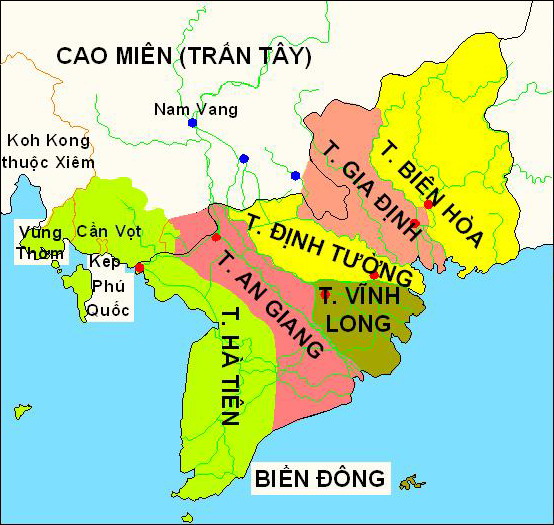
Vietnam Mekong Delta Administrative Map
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifteenth-most populous country. One of two communist states in Southeast Asia, Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. Before the Han dynasty's invasion, Vietnam was marked by a vibrant mix of religion, culture, and social norms. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam, which were subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta ( or simply ), also known as the Western Region () or South-western region (), is the list of regions of Vietnam, region in southwestern Vietnam where the Mekong, Mekong River River delta, approaches and empties into the sea through a network of distributary, distributaries. The Mekong delta region encompasses a large portion of south-western Vietnam, of an area of over . The size of the area covered by water depends on the season. Its wet coastal geography makes it an important source of agriculture and aquaculture for the country. The delta has been occupied as early as the 4th century BC. As a product of Khmer people, Khmer, Vietnamese people, Vietnamese, Chinese, and French colonial empire, French settlement in the region, the delta and its waterways have numerous names, including the Khmer language, Khmer term Bassac River, Bassac to refer to the lower basin and the largest river branch flowing through it. After the 1954 Geneva Conference, Vietnam was split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Hà Tiên
The Principality of Hà Tiên (; vi-hantu, 河僊鎮 or 河仙鎮, ''Mueang Phutthai Mat''), or the Hà Tiên Protectorate, was a principality of Chinese settlers ruled by the Mạc (Mo) clan at the Gulf of Thailand, in modern-day southern Vietnam and Cambodia. It was originally ''de facto'' independent, but later became a vassal state of the Siamese Rattanakosin Kingdom (1782–1932), Rattanakosin Kingdom and the Vietnamese Nguyễn dynasty in the 18th and 19th century prior to its annexation by the latter in 1832. Along with Hưng Yên, Phố Hiến, Hội An, and Saigon, Hà Tiên was a major Chinese community center and important hub of Ming dynasty, Ming loyalist networks in premodern Indochina. The name of the principality was variously spelled as ''Hexian Zhen'' (河仙鎮), ''Nangang'' (南港), ''Gangkou'' (港口), ''Bendi'' (本底) or ''Kundama'' (昆大嗎) in Chinese, ''Phutthaimat'' () or ''Banthaimat'' () in Thai, ''Ponthiamas'', ''Pontheaymas'' and ''Pontiano'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mạc Cửu
Cửu (, vi-hantu, 鄚玖, ; ''or'' ; 1655– July 18, 1735), also spelled Mok Kui, was an exile from China who founded the Principality of Hà Tiên and ruled as its first monarch. He played a role in the relations between Cambodia and the Vietnamese Nguyễn court. He was born in Leizhou, Guangdong, then under the rule of the Southern Ming dynasty. His birth name was Mạc Kính Cửu (莫敬玖, ), which could be easily confused with several rulers of the Mạc dynasty, including Mạc Kính Chỉ, Mạc Kính Cung, Mạc Kính Khoan and Mạc Kính Vũ. Therefore, he changed his name to Mạc Cửu (). Mạc Cửu later decided to immigrate to Vietnam to expand his business.'' Đại Nam liệt truyện tiền biên'', vol. 6 Sometime between 1687 and 1695, the Cambodian king granted him the Khmer title '' Okna'' (), and sponsored him to migrate to Banteay Meas, where he at first served as chief of a small Chinese and Vietnamese community. He built a casino t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |