|
Kamasutra
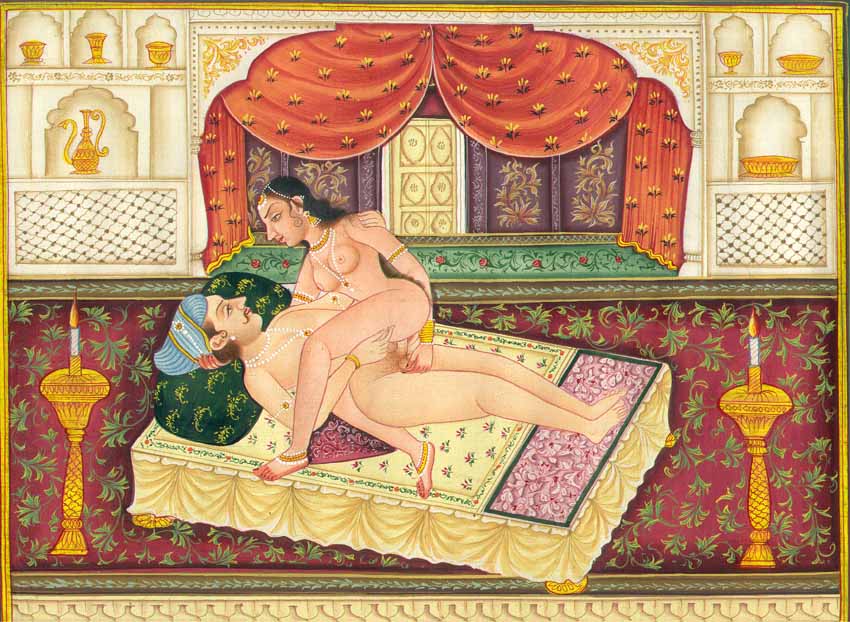
The ''Kama Sutra'' (; , , ; ) is an ancient Indian Hindu Sanskrit text on sexuality, eroticism and emotional fulfillment. Attributed to Vātsyāyana, the ''Kamasutra'' is neither exclusively nor predominantly a sex manual on sex positions, but rather a guide on the art of living well, the nature of love, finding partners, maintaining sex life, and other aspects pertaining to pleasure-oriented faculties. It is a ''sutra''-genre text with terse aphoristic verses that have survived into the modern era with different s (commentaries). The text is a mix of prose and anustubh-meter poetry verses. ''Kamasutra'' acknowledges the Hindu concept of purusharthas, and lists desire, sexuality, and emotional fulfillment as one of the proper goals of life. It discussed methods for courtship, training in the arts to be socially engaging, finding a partner, flirting, maintaining power in a married life, when and how to commit adultery, sexual positions, and other topics. The text majorl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vātsyāyana
Vātsyāyana (Sanskrit : वात्स्यायन) was an ancient Indian philosopher, known for authoring the ''Kama Sutra''. He lived in India during the second or third century CE, probably in Pataliputra (modern day Patna in Bihar). He is not to be confused with Pakṣilasvāmin Vātsyāyana, the author of ''Nyāya Sutra Bhāshya'', the first preserved commentary on Akṣapāda Gotama, Gotama's ''Nyaya Sutras, Nyāya Sutras''. His name is sometimes erroneously confused with Mallanaga, the seer of the Asuras, to whom the origin of erotic science is attributed. Biography Hardly anything is known about Vātsyāyana from sources outside the ''Kāmasūtra'' itself. Vātsyāyana's interest in refined human, including sexual, behavior as a means of fulfilment, was recorded in his treatise ''Kama Sutra''. At the close of the ''Kama Sutra'' this is what he writes about himself: After reading and considering the works of Babhravya and other ancient authors, and thinking over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adultery
Adultery is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral, or legal grounds. Although the sexual activities that constitute adultery vary, as well as the social, religious, and legal consequences, the concept exists in many cultures and shares some similarities in Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Adultery is viewed by many jurisdictions as offensive to public morals, undermining the marriage relationship. Historically, many cultures considered adultery a very serious crime, some subject to severe punishment, usually for the woman and sometimes for the man, with penalties including capital punishment, mutilation, or torture. Such punishments have gradually fallen into disfavor, especially in Western countries from the 19th century. In countries where adultery is still a criminal offense, punishments range from fines to caning and even capital punishment. Since the 20th century, criminal laws against adultery have become controversial, with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
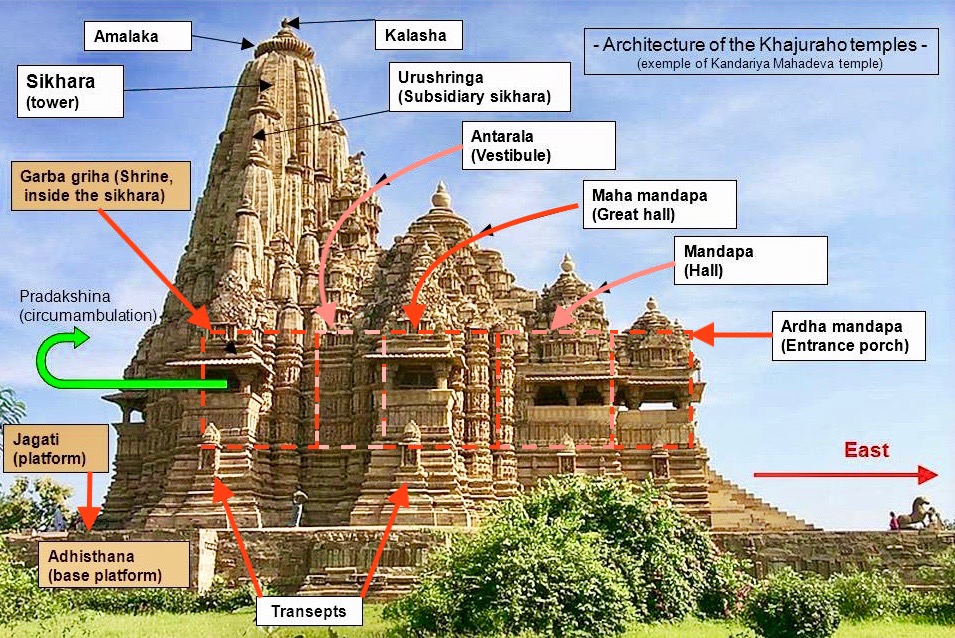
Khajuraho Group Of Monuments
The Khajuraho Group of Monuments are a group of Hindu and Jain temples in Chhatarpur district, Madhya Pradesh, India. They are about 46 km (28.6mi) from Chhatarpur, Chhatarpur city, the district headquarter, 283 km (177mi) from Gwalior, southeast of Jhansi, from Khajwa, Chhatarpur, Khajwa and from Rajnagar, Chhatarpur, Rajnagar. The temples are famous for their Nagara architecture, Nagara-style architectural symbolism and a few erotic sculptures. Most Khajuraho temples were built between 885 CE and 1000 CE by the Chandela dynasty. Historical records note that the Khajuraho temple site had 85 temples by the 12th century, spread over . Of these, only about 25 temples have survived, spread over . Of the surviving temples, the Kandariya Mahadeva Temple is decorated with a profusion of sculptures with intricate details, symbolism, and expressiveness of ancient Indian art.Devangana Desai (2005), ''Khajuraho'', Oxford University Press, Sixth Print, The temple co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Temples
A Hindu temple, also known as Mandir, Devasthanam, Pura, or Kovil, is a sacred place where Hindus worship and show their devotion to deities through worship, sacrifice, and prayers. It is considered the house of the god to whom it is dedicated.; Quote: "The Hindu temple is designed to bring about contact between man and the gods of Hinduism religion" (...) "The architecture of the Hindu temple symbolically represents this quest by setting out to dissolve or decrease the boundaries between man and the divine". Hindu temple architecture, which makes extensive use of squares and circles, has its roots in later Vedic traditions, which also influence the temples' construction and symbolism. Through astronomical numbers and particular alignments connected to the temple's location and the relationship between the deity and the worshipper, the temple's design also illustrates the idea of recursion and the equivalency of the macrocosm and the microcosm. A temple incorporates all elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Position
A sex position is a positioning of the bodies that people use to engage in sexual intercourse or other sexual activities. Sexual acts are generally described by the positions the participants adopt in order to perform those acts. Though sexual intercourse generally involves penetration of the body of one person by another, sex positions commonly involve non-penetrative sexual activities. Three broad and overlapping categories of sexual activity are commonly practiced: vaginal sex, anal sex, and oral sex (mouth-on-genital or mouth-on-anus). Sex acts may also be part of a fourth category, manual sex, which is stimulating the genitals or anus by using fingers or hands. Some acts may include stimulation by a device (sex toy), such as a dildo or vibrator. There are numerous sex positions that participants may adopt in any of these types of sex acts, and some authors have argued that the number of sex positions is essentially limitless.Rogiere, Jean, " The little bit naughty b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Manual
Sex manuals are books which explain how to perform sexual practices; they also commonly feature advice on birth control, and sometimes on safe sex and sexual relationships. Early sex manuals In the Graeco-Roman era, a sex manual was written by Philaenis of Samos, possibly a hetaira (courtesan) of the Hellenistic period (3rd–1st century BC). Preserved by a series of fragmentary papyruses which attest its popularity, it served as a source of inspiration for Ovid's ''Ars Amatoria'', written around 3 BC, which is partially a sex manual, and partially a burlesque on the art of love. The ''Kama Sutra'' of Vatsyayana, believed to have been written in the 1st to 6th centuries, has a notorious reputation as a sex manual, although only a small part of its text is devoted to sex. It was compiled by the Indian sage Vātsyāyana sometime between the second and fourth centuries CE. His work was based on earlier Kamashastras or ''Rules of Love'' going back to at least the seventh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union territories of India by area, second largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India by population, fifth largest state by population with over 72 million residents. It borders the states of Rajasthan to the northwest, Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the east, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west. The area covered by the present-day Madhya Pradesh includes the area of the ancient Avanti (India), Avanti Mahajanapada, whose capital Ujjain (also known as Avantika) arose as a major city during the second wave of Indian urbanisation in the sixth century BCE. Subsequently, the region was ruled by the major dynasties of India. The Maratha Confederacy, Maratha Empire dominated the maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kama Shastra
In Indian literature, Kāma- Śāstra ''(कामशास्त्र )'', refers to the tradition of works about kāma (broadly desire; particularly love, erotic, sensual and sexual desire in this case). Kāma-shastra aims to instruct the townsman (nāgarika) in the attainment of enjoyment and fulfillment. Etymology Kāma () is a Sanskrit word that has the general meanings of "wish", "desire", and "intention" in addition to the specific meanings of "pleasure" and "(sexual) love". Used as a proper name, it refers to Kamadeva, the Hindu god of love. History A sage Śvetaketu produced a work too vast to be accessible. A scholar called Babhravya, together with his group of disciples, produced a summary of Śvetaketu's summary, which nonetheless remained a huge and encyclopaedic tome. Between the 3rd and 1st centuries BC, several authors reproduced different parts of Babhravya's work in various specialist treatises. Among the authors, those whose names are known are Charayana, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palm Leaf Manuscript
Palm-leaf manuscripts are manuscripts made out of dried palm leaves. Palm leaves were used as writing materials in the Indian subcontinent and in Southeast Asia dating back to the 5th century BCE. Their use began in South Asia and spread to other regions, as texts on dried and smoke-treated palm leaves of the Palmyra palm, Palmyra or Ola leaf, talipot palm. Their use continued until the 19th century when printing presses replaced hand-written manuscripts. One of the oldest surviving palm leaf manuscripts of a complete treatise is a Sanskrit Shaivism text from the 9th century, discovered in Nepal, and now preserved at the Cambridge University Library.Pārameśvaratantra (MS Add.1049.1) with images , Puṣkarapārameśvaratantra, University of Cambridge (2015) The Spitzer Manuscript is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India by population, seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the Great Indian Desert) and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab, India, Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23°3' to 30°12' North latitude and 69°30' to 78°17' East longitude, with the Tropic of Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wendy Doniger
Wendy Doniger O'Flaherty (born November 20, 1940) is an American Indologist whose professional career has spanned five decades. A scholar of Sanskrit and Indian textual traditions, her major works include '' The Hindus: An Alternative History''; ''Asceticism and Eroticism in the Mythology of Siva''; ''Hindu Myths: A Sourcebook''; ''The Origins of Evil in Hindu Mythology''; ''Women, Androgynes, and Other Mythical Beasts''; and ''The Rig Veda: An Anthology, 108 Hymns Translated from the Sanskrit''. She is the Mircea Eliade Distinguished Service Professor Emerita of History of Religions at the University of Chicago, and has taught there since 1978. In 1998 she served as president of the Association for Asian Studies . Biography Wendy Doniger was born in New York City to immigrant non-observant Jewish parents, and raised in Great Neck, New York, where her father, Lester L. Doniger (1909–1971), ran a publishing business. While in high school, she studied dance under George Balan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |