|
Kalašma
Kalašma or Kalasma (occasionally Kalašpa) was a late Bronze Age polity in Northern Anatolia on the border of the Hittite Empire. Geography Kalašma was located somewhere in northwestern Anatolia. Though its precise location is uncertain, its location relative to other places can be deduced from geographical references in contemporary documents. For instance, it is known to have been south of Arawanna and west of Pala. Current research suggests that it was located near modern day Bolu. A city called ''Harranassi'' may have been located in Kalašma. When Hittite was first deciphered, Bedřich Hrozný took the placename "Kalašmitta" to be a variant of "Kalašma", but current research suggests that they were in fact separate places. History Forlanini says that ''Kalašma'' was not a tribal name but a city-state, the eponymous city having been fortified by the Hittite king Hantili I (died c. 1560 BCE). Hantili failed to reinstate Kalašma's local weather god, and on returning to � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luwic
The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Anatolia. The best known Anatolian language is Hittite, which is considered the earliest-attested Indo-European language. Undiscovered until the late 19th and early 20th centuries, they are often believed to be the earliest branch to have split from the Proto Indo-European family. Once discovered, the presence of laryngeal consonants ''ḫ'' and ''ḫḫ'' in Hittite and Luwian provided support for the laryngeal theory of Proto-Indo-European linguistics. While Hittite attestation ends after the Bronze Age, hieroglyphic Luwian survived until the conquest of the Neo-Hittite kingdoms by the Semitic Assyrian Empire, and alphabetic inscriptions in Anatolian languages are fragmentarily attested until the early first millennium AD, eventually succumbing to the Hellenization of Anatolia as a result of Greek colonisation. Origins The Anatolian branch is often considered the earliest to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
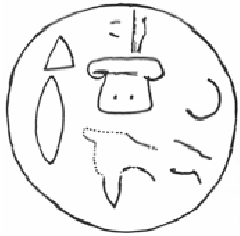
Kalašma Language
The Kalašma language, or Kalasmaic, is an extinct Anatolian language spoken in the late Bronze Age polity of Kalašma, which lay on the northwest fringe of the Hittite Empire, likely in or around what is now the Turkish province of Bolu. Discovery The first (and thus far only) Kalasmaic text was discovered in 2023, by researchers at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg. It is written on a clay tablet indexed KBo 71.145.Schwemer 2024 p. XIX The tablet, written in Hittite cuneiform of the 13th century BCE, is one of several Hittite texts recording rituals of the empire's subjects and neighbouring peoples. Its Hittite-language introduction describes its main text as in "the language of Kalašma" (). The language was deciphered by Prof. Daniel Schwemer in the 71st volume of the edition "Keilschrifttexte aus Boghazköi (Cuneiform Texts from Boghazköi)" and is part of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family as confirmed by Prof. Elisabeth Rieken at Philipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e.g., Tajikistan and Afghanistan), Armenia, and areas of southern India. Historically, Indo-European languages were also spoken in Anatolia. Some European languages of this family—English language, English, French language, French, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Russian language, Russian, Spanish language, Spanish, and Dutch language, Dutch—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, including Albanian language, Albanian, Armenian language, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic languages, Celtic, Germanic languages, Germanic, Hellenic languages, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian, and Italic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogazköy Archive
The Bogazkoy archives are a collection of texts found on the site of the capital of the Hittite state, the city of Hattusas (now Bogazkoy in Turkey). They are the oldest extant documents of the state, and they are believed to have been created in the 2nd millennium BC. The archive contains approximately 25,000 tablets. Content The archive contains royal annals, treaties, political correspondence, legal texts, inventory texts along with instructions, texts related to administration, mythological texts, and religious texts.''Cem'' p.1 Language Most tablets were found to be written in the Hittite language. However, some of the tablets are written in Hurrian, and a few paragraphs of the tablets are written in Hattic. Akkadian is also a common language, though it is interspersed with Hurrian and Hittite.''Cem'' p.2 Given that the writing is mostly in cuneiform, there are Sumerograms interspersed throughout the texts regardless of language. Discovery The Bogazkoy Archives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukšuš
Mopsus (; Ancient Greek: Μόψος, ''Mopsos'') was the name of one of two famous seers in Greek mythology; his rival being Calchas. A historical or legendary ''Mopsos'' or ''Mukšuš'' may have been the founder of a house in power at widespread sites in the coastal plains of Pamphylia and Cilicia (in today's Turkey) during the early Iron Age. Mythological figures * Mopsus, son of Manto either by Rhacius or Apollo. * Mopsus, an Argonaut and son of Ampyx by a nymph. * Mopsus, a Thracian commander who had lived long before the Trojan War. Along with Sipylus the Scythian, this Mopsus had been driven into exile from Thrace by its king Lycurgus. Sometime later, he and Sipylus defeated the Libyan Amazons in a pitched battle, in which their queen Myrine was slain, and the Thracians pursued the surviving Amazons all the way to Libya. * Mopsus is also the name chosen by Virgil for the young singer who makes a song about the death of Daphnis in Eclogue 5. The name recurs in Eclogue 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnuwanda III
Arnuwanda III was the penultimate king of the Hittite empire (New Kingdom) –1210 BC (middle chronology) or –1207 BC (short chronology). Family Arnuwanda was a son of Tudhaliya IV and grandson of Hattusili III and Puduhepa. He was quickly succeeded by his brother Suppiluliuma II. See also *History of the Hittites The Hittites () were an Anatolian Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in modern-day Turkey in the early 2nd millen ... References External linksReign of Arnuwanda III Hittite kings 13th-century BC monarchs {{ANE-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luwian Hieroglyphic
Anatolian hieroglyphs are an indigenous logographic script native to central Anatolia, consisting of some 500 signs. They were once commonly known as Hittite hieroglyphs, but the language they encode proved to be Luwian, not Hittite, and the term Luwian hieroglyphs is used in English publications. They are typologically similar to Egyptian hieroglyphs, but do not derive graphically from that script, and they are not known to have played the sacred role of hieroglyphs in Egypt. There is no demonstrable connection to Hittite cuneiform. History Individual Anatolian hieroglyphs are attested from the second and early first millennia BC across Anatolia and into modern Syria. A biconvex bronze personal seal was found in the Troy VIIb level (later half of the 12th century BC) inscribed with Luwian Hieroglyphs. The earliest examples occur on personal seals, but these consist only of names, titles, and auspicious signs, and it is not certain that they represent language. Most actual tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth dynasties. Through radiocarbon dating, the establishment of the New Kingdom has been placed between 1570 and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt, Third Intermediate Period. It was the most prosperous time for the Egyptians#History, Egyptian people and marked the peak of Egypt's power. In 1845, the concept of a "New Kingdom" as Periodization of ancient Egypt, one of three "golden ages" was coined by German scholar Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen; the original definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh took place in the 13th century BC between the New Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian Empire led by pharaoh Ramesses II and the Hittites, Hittite Empire led by king Muwatalli II. Their armies engaged each other at the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs and near the archaeological site of Kadesh (Syria), Kadesh, along what is today the Lebanon–Syria border. The battle is generally dated to May 1274 BC, as accounted by Egyptian chronology, and is the earliest pitched battle in recorded history for which details of tactics and formations are known. It is believed to be the largest battle ever fought involving chariot, chariots, numbering at a total of 5,000 to 6,000. After being outmaneuvered, ambushed, and surrounded, Ramesses II personally led a charge through the Hittite ranks with his bodyguard. They broke through and avoided the capture or death of the pharaoh. The outcome is considered a stalemate. Background After expelling the Hyksos' Fifteenth Dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenary Soldier
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protection by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. International and national laws of war Protocol Additional GC 1977 (APGC77) is a 1977 amendment protocol to the Geneva Conventions. Article 47 of the protocol provides the most widely accepted international definition of a mercenary, thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |