|
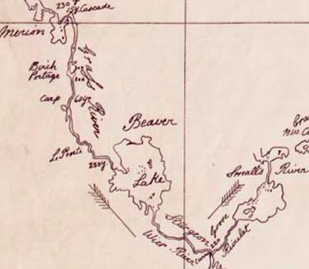
Kakinagimak Lake
Kakinagimak Lake is a lake in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It lies in low-relief forested terrain of the Canadian Shield. The climate is sub-arctic. Location Kakinagimak Lake is about north-west of Flin Flon, Manitoba, and east of Pelican Narrows, Saskatchewan. The lake is long, following north-south geological structures, but is narrow like a river. The lake surface is about above sea level. There is a fishing cabin on the lake. Terrain The lake has an average depth of and a maximum depth of . It has of shoreline. Granitoid ridges near the lake rise to about above sea level. Most of the region is underlain by granodiorite to tonalite gneisses, which are exposed on the shores of the central portion of the lake. Robbestad Lake, McArthur Lake (Saskatchewan), McArthur Lake and the northern part of Kakinagimak Lake drain northward into the Churchill River (Hudson Bay) , Churchill River via the Nemei River. The southern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attitti Lake
Attitti Lake is a lake in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It lies in low-relief forested terrain of the Canadian Shield. The climate is sub-arctic. Location Attitti Lake is at , at an elevation of . The lake is northwest of Flin Flon, Manitoba and about east of Pelican Narrows, Saskatchewan. It is connected by a winter road with Kakinagimak Lake, Wildnest Lake, and Hanson Lake via Highway 106, which runs south of Wildnest Lake. It can be reached by canoe from Pelican Narrows via Wunehikun Bay and Waskwei Lake, and is connected to most of the surrounding lakes by well-maintained portages. Terrain The area is typical of the flat-surfaced part of the Canadian Shield, with low hills that rarely rise as much as above the lakes. The terrain consists of roughly parallel sinuous ridges of outcrop separated by muskeg, drift and lakes. The channel that connects Attitti Bay with Attitti Lake is underlain by a north-trending fault zone. Geologically the area is in the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemei River
The Nemei River is a tributary of the Churchill River (Hudson Bay), Churchill River. It rises in Nemei Lake and flows northward to join Churchill River near Sandy Bay. It runs through low relief terrain of the Canadian Shield. The climate is sub-arctic. Location The Nemei river flows into the Churchill river below Reindeer River (Saskatchewan), Reindeer River. The indigenous name means "sturgeon". The Nemei joins the Churchill downstream from the Island Falls, Saskatchewan, Island Falls power dam, built in 1929. Its mouth is at an altitude of . Phelan Lake drains northwest into Nemei Lake and then via the Nemei River to the Churchill River. Phelan Lake is accessible from the south via the Wildnest-Kakinagimak-Nemei Lakes water route. Robbestad Lake, McArthur Lake (Saskatchewan), McArthur Lake and the northern part of Kakinagimak Lake also drain northward via the Nemei River. Environment The Nemei River is in the subarctic climate zone. The annual average temperature is . The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes Of Saskatchewan ...
This is a list of lakes of Saskatchewan, a province of Canada. The largest and most notable lakes are listed at the start, followed by an alphabetical listing of other lakes of the province. Larger lake statistics "The total area of a lake includes the area of islands. Lakes lying across provincial boundaries are listed in the province with the greater lake area." A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y Z See also * List of lakes of Canada *List of rivers of Saskatchewan * Geography of Saskatchewan *List of dams and reservoirs in Canada References {{Authority control * Lakes Saskatchewan Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
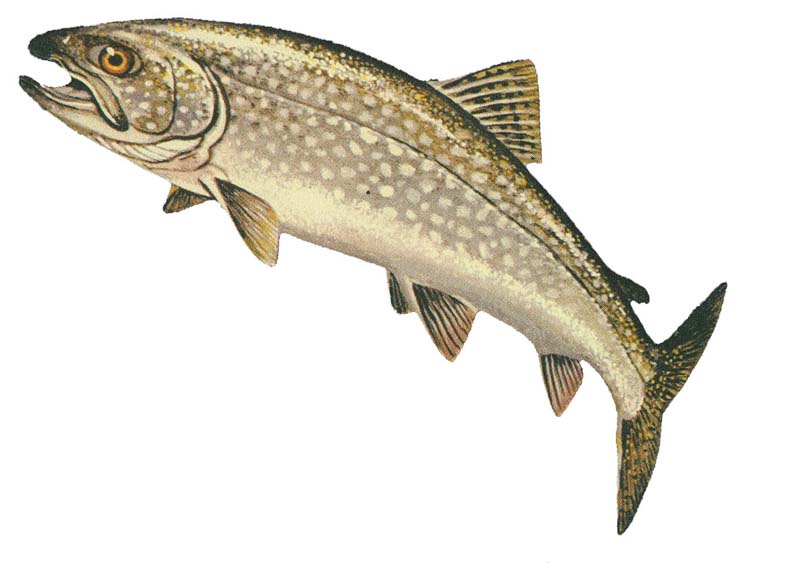
Lake Trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater char living mainly in lakes in northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, and grey trout. In Lake Superior, it can also be variously known as siscowet, paperbelly and lean. The lake trout is prized both as a game fish and as a food fish. Those caught with dark coloration may be called ''mud hens''. Taxonomy It is the only member of the subgenus ''Cristovomer'', which is more derived than the subgenus '' Baione'' (the most basal clade of ''Salvelinus'', containing the brook trout (''S. fontinalis'') and silver trout (''S. agasizii'')) but still basal to the other members of ''Salvelinus''. Range From a zoogeographical perspective, lake trout have a relatively narrow distribution. They are native only to the northern parts of North America, principally Canada, but also Alaska and, to some extent, the northeastern United States. Lake trout have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
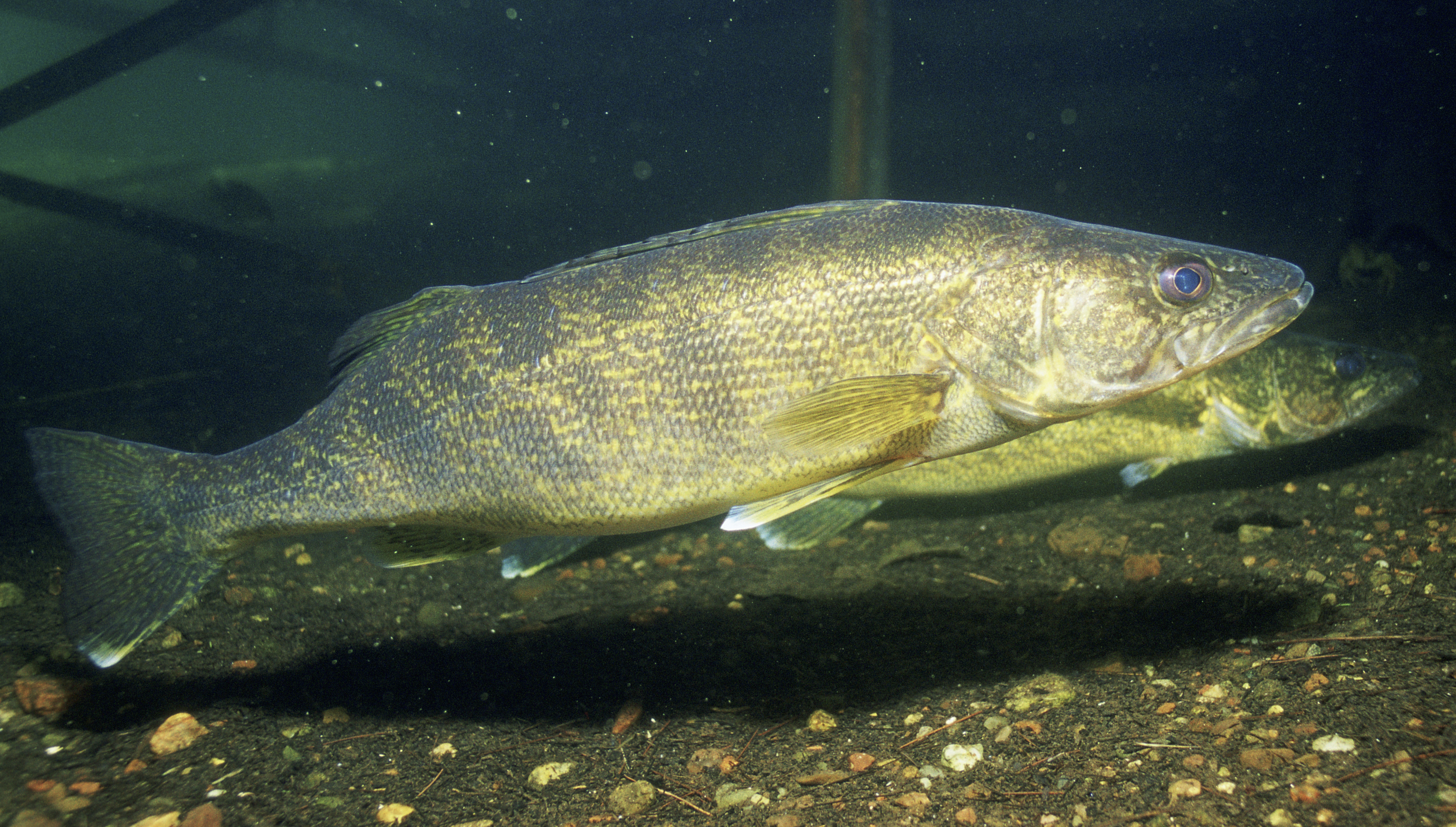
Walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relative of the European zander, also known as the pikeperch. The walleye is sometimes called the yellow walleye to distinguish it from the blue walleye, which is a color morph that was once found in the southern Ontario and Quebec regions, but is now presumed extinct. However, recent genetic analysis of a preserved (frozen) 'blue walleye' sample suggests that the blue and yellow walleye were simply phenotypes within the same species and do not merit separate taxonomic classification. In parts of its range in English-speaking Canada, the walleye is known as a pickerel, though the fish is not related to the true pickerels, which are members of the family ''Esocidae''. Walleyes show a fair amount of variation across watersheds. In general, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish water, brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are known simply as a pike in Great Britain, Britain, Ireland, and most of Eastern Europe, Canada and the United States. Pike can grow to a relatively large size: the average length is about , with maximum recorded lengths of up to and published weights of . The International Game Fish Association, IGFA currently recognizes a pike caught by Lothar Louis on Greffern Lake, Germany, on 16 October 1986, as the all-tackle world-record northern pike. Northern pike grow to larger sizes in Eurasia than in North America, and typically grow to larger sizes in coastal than inland regions of Eurasia. Etymology The northern pike gets its common name from its resemblance to the pole-weapon known as the Pike (weapon), pike (from the Middle English for 'point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least one month) must have a 24-hour average temperature of at least to fall into this category of climate, and the coldest month should a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan River
The Saskatchewan River ( Cree: ''kisiskāciwani-sīpiy'', "swift flowing river") is a major river in Canada. It stretches about from where it is formed by the joining together of the North Saskatchewan and South Saskatchewan Rivers to Lake Winnipeg. It flows roughly eastward across Saskatchewan and Manitoba to empty into Lake Winnipeg. Through its tributaries the North Saskatchewan and South Saskatchewan, its watershed encompasses much of the prairie regions of Canada, stretching westward to the Rocky Mountains in Alberta and north-western Montana in the United States. Including its tributaries, it reaches to its farthest headwaters on the Bow River, a tributary of the South Saskatchewan in Alberta. Description It is formed in central Saskatchewan, approximately east of Prince Albert, by the confluence of its two major branches, the North Saskatchewan and the South Saskatchewan, at the Saskatchewan River Forks. Both source rivers originate from glaciers in the Albert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturgeon-Weir River
The Sturgeon-Weir River is a river in east-central Saskatchewan, Canada. It flows about south-southeast to join the Saskatchewan River at Cumberland House, Saskatchewan. It was on the main voyageur route from eastern Canada northeast to the Mackenzie River basin. The river is a popular wilderness canoe route in Canada. Description The river's source is Corneille Lake, near the community of Pelican Narrows. It travels southeast, crossing Saskatchewan Highway 106 before reaching Amisk Lake. It then continues southeasterly to Sturgeon Landing and Namew Lake. It runs through the Churchill River Uplands ecoregion which is located along the southern edge of the Precambrian Shield. The area contains continuous coniferous and boreal forest, consisting of closed stands of black spruce and jack pine and a ground cover of mosses and lichens. Local relief rarely exceeds 25 m, but there are ridged steeply sloping rocky uplands and lowlands with exposed bedrock throughout. Wildlife in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill River (Hudson Bay)
The Churchill River () is a major river in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, Canada. From the head of the Churchill Lake it is long. It was named after John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and governor of the Hudson's Bay Company from 1685 to 1691. The Cree name for the river is ''Missinipi'', meaning "big waters". The Denesuline name for the river is ''des nëdhë́'', meaning "Great River". The river is located entirely within the Canadian Shield. The drainage basin includes a number of lakes in Central-East Alberta which flow into a series of lakes in Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The main tributary, the Beaver River, joins at Lac Île-à-la-Crosse. Nistowiak Falls—the tallest falls in Saskatchewan—are on the Rapid River, which flows north, out of Lac la Ronge into Nistowiak Lake on the Churchill just north of La Ronge. A large amount of flow of the Churchill River after Manitoba–Saskatchewan border comes from the Reindeer River, which flows from Wollas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Saskatchewan Administration District
The Northern Saskatchewan Administration District (NSAD) is the unorganized area of the Canada province of Saskatchewan. Overwhelmingly larger than the province's other communities, it encompasses approximately half of Saskatchewan's landmass, an area comparable to that of New Zealand. Despite its extent, the majority of Saskatchewanians live in the southern half of the province, and the majority of Northern Saskatchewanians live in incorporated municipalities outside the NSAD's jurisdiction. As a result, the 2016 census counted only 1,115 district residents, which placed its population density at 250 square kilometres for every inhabitant. Because of its extremely sparse population, the district has no local government and is directly subject to the Minister of Government Relations. History An unincorporated Northern Saskatchewan region was first established by the 1948 ''Northern Administration Act''. In 2020, travel into the NSAD was restricted as part of the Government of Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McArthur Lake (Saskatchewan)
McArthur Lake is a lake in Saskatchewan, Canada. It lies in low-relief terrain of the Canadian Shield. The climate is sub-arctic. The land is mostly covered by conifer forests, with some areas of muskeg and rocky outcrops. Location McArthur Lake is at , at an elevation of . The lake contains Charbonneau Island. It is northwest of Flin Flon, Manitoba, and east of Pelican Narrows, Saskatchewan. McArthur Lake drains northward into the Churchill River (Hudson Bay), Churchill River via the Nemei River. The lake is named in honour of Duncan Archibald McArthur, a private soldier who died on 28 August 1944 during the Allied invasion of Normandy. Terrain The Attitti Lake region, which includes McArthur Lake, is typical of the flat-surfaced part of the Canadian Shield, with low hills that rarely rise as much as above the lakes. The terrain consists of roughly parallel sinuous ridges of outcrop separated by muskeg, drift and lakes. Geologically the area is in the Precambrian Kisseynew com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)